What is IP income
Not only the main activity brings money to enterprises and entrepreneurs. Income is generated from all receipts reduced by material costs, from which wages are excluded.
Income and expenses in the declaration
Costs related to cost include:
- depreciation;
- raw materials and materials, fuel and electricity. Finding them in the expense column is easy;
- social contributions for extra-budgetary funds;
- salary.
Income includes profit and labor costs. If a business has no material costs, then it is equal to revenue from sales of products. An individual entrepreneur can figure out how to find out turnover without any problems.
What taxes can be verified by an entrepreneur?
The subject of a tax audit may be the receipt of profit by an individual entrepreneur, which is subject to the following taxes:
1. At a rate of 13% under the general tax system of the OSN.
In this case we are talking about income tax in a broad sense. Strictly speaking, the use of the term “income tax” in the context of the activities of individual entrepreneurs is not entirely correct. This tax is paid by organizations - at a higher rate, however, also working under the general taxation system (therefore, with a certain degree of convention, some legal analogy is appropriate here).
Conducting business under the OSN by an entrepreneur also requires him to pay VAT on the proceeds received. In general, the VAT rate is 18%, but in cases provided for by law it may be reduced.
2. At a rate of 6% (when only revenue is taken into account) or at a rate of 15% (when profit is taken into account) - within the framework of the simplified system or simplified tax system.
If an individual entrepreneur operates under the simplified tax system, then he does not need to pay VAT. However, if the entrepreneur’s business indicators exceed the limits established by law - for example, in terms of revenue or headcount, then he will be required to begin work under the OSN.
3. Accrued according to UTII - with fixed tax payments.
The amount of these payments does not depend on revenue or profit. Therefore, the activities of individual entrepreneurs on UTII to the least extent fall under the definition of taxable income tax (except with the most expanded interpretation of this concept).
4. Accrued under other taxation systems:
- PSN (similar to UTII - in that an individual entrepreneur pays a fixed tax on the corresponding system, but this payment is calculated according to different principles);
- Unified Agricultural Tax (similar to the simplified tax system - in that it involves paying a tax at a rate of 6%, but based on the difference between income and expenses).
Thus, the income tax of individual entrepreneurs (if we agree to understand this as profit in a broad sense) can be calculated according to different principles, while the Tax Service (FTS) can give priority to different methods when checking the corresponding accruals.
Thus, when checking taxes, the amount of which does not depend on revenue - UTII, PSN, the emphasis can be placed on checking the accuracy of the information reflected in the declaration, as well as, of course, on checking the individual entrepreneur’s compliance with the deadlines for submitting these reporting documents.
In turn, when checking taxes that directly depend on revenue - under the OSN, simplified tax system, unified agricultural tax systems, tax authorities can pay increased attention, first of all, to the calculation by entrepreneurs of correct payments to the budget.
The Federal Tax Service carries out tasks related to the verification of taxes on the profits of individual entrepreneurs (for one reason or another) within the framework of tax audits. What is their specificity?
We can consider it, first of all, in the context of the classification of these checks - provided for by Russian legislation.
Business income is revenue or profit
How to calculate income over 300,000 individual entrepreneurs on UTII and simplified tax system - what tax is paid
Example. The store received 60 thousand rubles in a month. through the sale of products. A common mistake is when the entire number is considered the profit of the individual entrepreneur. To determine profit, you need to subtract the main expense items from income.
About income based on a patent
Here are just a few of the acceptable items that are deducted:
- interest on a loan for commercial equipment;
- transport services and communications, stationery, cash register services;
- employees' salaries;
- taxes;
- rental of retail premises;
- purchase price of goods. They are important for those who are interested in how to calculate the income of an individual entrepreneur.
Note! Income is the funds received by the entrepreneur, which he can spend in the future at his own discretion. Profit is the balance of money minus expenses. You can analyze the activities of an enterprise to determine both income and profit and predict them for the future.
Features of on-site inspection
An on-site inspection is an event that is carried out at the address where an entrepreneur conducts commercial activities (but if it is not possible to receive Federal Tax Service inspectors, the entrepreneur himself pays a visit to the department and then interacts with the inspectors in the prescribed manner).
This procedure is initiated in accordance with the order of the head of the territorial division of the Federal Tax Service. Unlike a desk check, which the individual entrepreneur may not even be aware of, with regard to an off-site event, the entrepreneur can be informed if it is planned.
An on-site inspection is a fairly lengthy procedure. It can last, if there are grounds provided for by law, up to 6 months (but, as a rule, it does not exceed 2-4). Its duration depends, first of all, on the scope of the objects being inspected: their list can be either quite narrow (for example, when an on-site inspection of cash register equipment is carried out) or very wide (when all the financial documentation of an entrepreneur is checked).
After conducting an on-site inspection, inspectors draw up a report in 2 copies, which records the results of their work. They can reflect both the absence of any violations and their detection by tax authorities. With regard to these violations, the individual entrepreneur can submit reasonable objections within the period prescribed by law.
How to calculate it correctly
How to find out what taxation system an individual entrepreneur is on - is it possible to check?
The declaration for the tax period is the main document that displays factual information regarding the actual income received. This is an official statement to the state about the results of business activities of a particular entity. The declaration is signed by the entrepreneur to confirm the completeness of the information provided.
For contributions
With UTII
In this case, real income may differ from the estimated or imputed one. To confirm it under such circumstances, two main documents are used:
- patent;
- a book of accounting for expenses and income from business activities is a prerequisite.
In the case of a book, the following requirements are imposed on the document:
- lacing;
- numbering;
- certification with a seal;
- in some cases, a tax stamp is required, otherwise the information will not be considered correct regarding revenue or profit.
For your information! The tax office puts its stamp only if you give it at least one copy of the accounting book. If the UTII system is used, there is no alternative to the above solutions, even if there is a significant difference between real and imputed income.
On OSNO
Here, the income received by the individual entrepreneur is taken into account minus the VAT charged to customers. The picture is even simpler if the participant in the transaction is exempt from VAT. In this case, income and revenue are the same numbers, which are not difficult to calculate.
The amount of annual income is usually taken from the fourth section of the accounting book for any business transactions. In the 3NDFL declaration, line number 030 is used to record the relevant information. The information is also displayed as part of the annual reporting; they are used when it is necessary to determine alimony.
Note! The calculation of the additional insurance premium for the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation deserves special consideration. Then professional deductions or accepted expenses contribute to a decrease in overall income.
simplified tax system
If an entrepreneur works on the simplified tax system, then he receives income:
- non-operating;
- sales for the year.
Determining the final figures involves using the so-called cash method. Everything will be easy to calculate.
simplified tax system
Annual income is the figure from column 4 KUDiR. 113 or 213 are declaration lines where such information is required to be displayed. They need to be calculated in advance.
PSN
The patent system is considered a simplified option for paying taxes and interacting with regulatory authorities. The main subjects for this taxation option are representatives of small and ultra-small businesses. But there are some features that you need to know about in advance:
- the patent is calculated based on the approved amounts for potential income;
- there are restrictions on the amount of actual revenue and the amount of hired labor;
- contributions are paid separately. Supervisory authorities give recommendations on how to solve the problem.
Important! Potentially possible income in this case is called the estimated amount approved by the regional authorities for tax purposes. This is a hypothetical profit, in relation to which taxes established by the state apply.
There are two options by which this indicator is calculated in the case of patents.
- when an individual entrepreneur does not have hired workers, there is only one object of taxation. Then just look at the information in your Personal Account on the Federal Tax Service website;
- It’s another matter when there is hired labor or several objects for taxation. Then everything is more difficult to check.
For your information! Depending on the number of employees, local authorities may increase the amount of calculated income. In this case, the standard rate of 6% is multiplied by the estimated number of units covered by the scheme. It is better to find out the features of the formula in advance.
Regional laws or deflator coefficients are the most important indicators when it comes to changes in income; they must be checked. The main thing is to check the necessary information in time and carry out an inspection. Then everything is simple to calculate.
What are tax audits?
Depending on the method of conducting inspections, they are divided into desk and field inspections. Let's look at them in more detail.
Desk inspection
Every time an entrepreneur submits some form of reporting, a desk audit begins in relation to it. It is carried out within the walls of the tax office without visiting the entrepreneur. The audit begins after the deadline for receiving the report and lasts a maximum of 3 months .
During a desk inspection, inspectors determine:
- whether the entrepreneur submitted the form and whether he violated the deadline for submitting it;
- whether he filled out the report correctly;
- whether the calculations were made correctly;
- whether the information provided in the documents is correct.
Such checks are carried out on a routine basis, that is, taxpayers are not informed about their conduct. And if everything is in order with the form being checked, the individual entrepreneur in most cases does not even know that a check has been carried out.
If any questions arise during the audit, inspectors may request clarification or documents from the taxpayer. Most often this happens if Federal Tax Service specialists believe that the individual entrepreneur has not paid additional taxes. But the reasons for demanding clarification may vary.
Requests from tax authorities must be responded to immediately, since the entrepreneur will have a five-day period . If there is no response or the taxpayer’s explanation does not satisfy the inspector, he will be held administratively liable. As a result, he will not only be charged arrears, but also fines and penalties.
On-site inspection
From the name it is clear that such an audit is carried out on-site to the taxpayer . However, in cases where the taxpayer cannot provide premises for inspectors, the inspection may be carried out by the Federal Tax Service. The basis for its initiation is the decision of the head of the tax inspectorate or his deputy. The decision to conduct an inspection is made based on the results of the pre-inspection analysis.
Please note that until the end of 2020 there is a moratorium on scheduled inspections of small businesses. The exception is socially significant areas - healthcare, education, social sphere, electric power industry and others.
However, an on-site inspection may be carried out outside of the plan . For example, an entrepreneur may be knocked on the door if, during a desk audit, the inspectorate identifies grounds for a more detailed analysis of his activities.
About scheduled and unscheduled inspections:
The on-site inspection covers a period of no more than the last 3 years . It is carried out in relation to one or more taxes. If a tax has already been audited, the Federal Tax Service does not have the right to reschedule it during the year.
The maximum period for conducting an on-site inspection is 2 months . Sometimes it can be increased, for example, if force majeure circumstances arose, other violations were discovered along the way, or the individual entrepreneur did not provide the requested documents on time.
During the inspection, inspectors try to study all the circumstances and find out whether the individual entrepreneur calculated the tax correctly . For this purpose, they can inspect the taxpayer’s premises, request and seize documents and items, involve experts, and interview witnesses.
As a result, the individual entrepreneur will receive an inspection report, which will list all the violations identified by the inspectors, as well as recommendations for eliminating them. If an entrepreneur does not agree with the inspectors’ conclusions, he will be able to appeal .
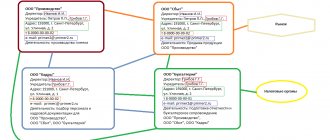
Is it possible to see the income of an individual entrepreneur somewhere?
How to calculate UTII for individual entrepreneurs - tax calculation formula
There are several official documents that confirm the main income of entrepreneurs:
- tax return;
- income certificate.
Note! In most cases, confirmation of information is the right and responsibility of the tax service. After all, it is to the territorial offices of this body that all documents confirming such information are submitted.
The following sources of information are available to outsiders:
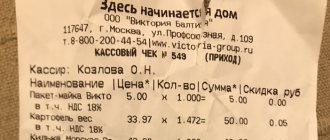
- sales receipts;
- invoices;
- contracts;
- bank statements and invoices.
Calculations
But this is only proof that the taxpayer performed a particular transaction and received revenue.
Note! Usually requests are made with the participation of representatives of the bailiff service.
They, in turn, may require additional verification of the entrepreneur’s income. He presents all official documents containing relevant information.
Tax audits of simplified people and new art. 54.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation: what to pay attention to
Art. 54.1 appeared in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation quite recently (introduced by law dated July 18, 2017 No. 163-FZ) and is devoted to issues of unjustified tax benefits.
You will become familiar with the concept of “unjustified tax benefit” in the material “Presumption of good faith of the taxpayer - a new article in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation” .
When conducting desk and field audits, controllers will collect evidence of the reality of transactions, and will also look with particular scrupulousness for evidence of deliberate tax evasion.
For example, a “simplifier” may be suspected of deliberate tax evasion if he fragmented his business solely for one purpose - to reduce the tax burden through the use of special tax regimes. The controllers themselves directly indicate this in their letter No. ED-4-2/13650 dated July 13, 2017 (clause 13.2 of the Methodological Recommendations for establishing, during tax and procedural audits, circumstances indicating intent in the actions of taxpayer officials aimed at non-payment of taxes ).
Get free trial access to ConsultantPlus and find out 17 criteria for assessing business fragmentation, which tax authorities focus on when conducting an audit.
Thus, a “simplifier” needs to be ready to prove a reasonable business purpose for his actions (for example, the purpose of splitting up a business), as well as take care of documentary support for the reality of his transactions, confirm due diligence when choosing counterparties, etc.
Features of separate accounting
The legislation does not clearly establish the procedure for separate accounting. This also applies to situations where an individual entrepreneur combines several systems at once. It is worth fixing the order of certain actions yourself, and then recording it in internal documents. The main thing is to rely on general standards related to accounting.
All articles are divided into several groups. There are two main income groups according to the systems used. Expenses are divided into three groups - separately for each system, and those that fall under both at the same time. Additional subaccounts will become indispensable assistants for separate accounting.
Analysis by parameters
Income accounting for expenses distribution
If different regimes are combined, the following obligations arise:
- maintaining separate records for each of the special regimes. If there are items that cannot be clearly attributed to one of them, the money is distributed proportionally;
- accounting;
- book of income and expenses. This requirement is especially important for those who use simplified language.
It is necessary to rely on the Tax Code, in particular, its Art. 249, 250 and 251. The calculation of the proportion also includes income, which is called non-operating income. Only expenses that do not increase the tax base for the corresponding types of charges are not taken into account.
As payment is made, income from activities on UTII is determined. When making calculations, the accountant must exclude any transactions that remain unpaid.
It is allowed to reduce the amount of UTII accrued for the quarter:
- the amount of insurance premiums that have actually been paid;
- under personal voluntary insurance contracts for employees. They are concluded in case of temporary disability; exact payments must be determined individually;
- paid hospital benefits at the expense of the organization. The identification number is indicated separately.
Important! The total amount of deduction cannot exceed 50% of the amount of tax that has already been paid.
Income and expenses are distributed proportionally to make it easier to calculate the contributions and taxes themselves that require transfer to the budget.
Individual entrepreneur on the simplified tax system, what do tax authorities ask for during an audit?
1 clause 1 art. 31 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax authorities have the right to demand from taxpayers documents confirming the correctness of tax calculations. Taxpayers applying the Simplified Taxation System with the taxable object Income calculate tax on the amount of income received. Expenses, in general, do not affect the amount of tax.
Therefore, in general, the tax office does not have the right to require documents confirming the taxpayer’s expenses.
The same conclusion was made in the Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North Caucasus District dated October 19, 2009 N A32-4454/2009-3/50. The court indicated that since the taxpayer applies the simplified tax system with the object of taxation in the form of income, he does not have the obligation to keep records of expense transactions and submit primary documents confirming them.
The same conclusion is in Letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 16, 2010 N 03-11-11/169, dated October 20, 2009 N 03-11-09/353, dated August 15, 2008 N 03-11-04/2/118.
But there are cases when expenses affect the amount of the 6% simplified tax system or other taxes.
I) The Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation approved the Book of accounting of income and expenses of organizations and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified taxation system by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 22, 2012 N 135n. Clause 2.5 of the Procedure for filling out the book establishes the procedure for reflecting taxpayer expenses in the book. Expenses are reflected by taxpayers applying the simplified tax system with the object of taxation in the form of income reduced by the amount of expenses. Taxpayers applying the simplified tax system with the object of taxation in the form of income are required to reflect only the following expenses:
- actually incurred expenses provided for by the conditions for receiving payments to promote self-employment of unemployed citizens and stimulate the creation by unemployed citizens who have opened their own businesses of additional jobs for the employment of unemployed citizens at the expense of the budgets of the budgetary system of the Russian Federation in accordance with programs approved by the relevant government bodies;
— actual expenses incurred using financial support in the form of subsidies received in accordance with Federal Law No. 209-FZ of July 24, 2007 “On the development of small and medium-sized businesses in the Russian Federation.”
II) If the taxpayer carries out expenses provided for in paragraph 3.1 of Art. 346.21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and reduces the amount of the single tax by them, such expenses must be documented and the tax authorities have the right to claim them when exercising tax control.
This conclusion is made by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in its letter dated 01.09.2006 N 03-11-04/2/181.
Clause 3.1 art. 346.21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows you to reduce the amount of expenses of the simplified tax system by the amounts:
1) insurance contributions for compulsory pension insurance, compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity, compulsory medical insurance, compulsory social insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases, paid (within the calculated amounts) in this tax (reporting ) period in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation;
2) expenses for payment in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation of temporary disability benefits (except for industrial accidents and occupational diseases) for days of temporary disability of the employee, which are paid at the expense of the employer and the number of which is established by Federal Law of December 29, 2006 N 255-FZ “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity”, in the part not covered by insurance payments made to employees by insurance organizations that have licenses issued in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation to carry out the relevant type of activity, according to agreements with employers in favor of employees in the event of their temporary disability (except for industrial accidents and occupational diseases) for days of temporary disability, which are paid at the expense of the employer and the number of which is established by Federal Law of December 29, 2006 N 255-FZ “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity”;
3) payments (contributions) under voluntary personal insurance contracts concluded with insurance organizations that have licenses issued in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation to carry out the relevant type of activity, in favor of employees in the event of their temporary disability (except for industrial accidents and occupational diseases) for days of temporary disability, which are paid at the expense of the employer and the number of which is established by Federal Law of December 29, 2006 N 255-FZ “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity.” The specified payments (contributions) reduce the amount of tax (advance tax payments) if the amount of insurance payment under such contracts does not exceed the amount of temporary disability benefits determined in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation (except for industrial accidents and occupational diseases) for days of temporary employee disability, which is paid at the expense of the employer and the number of which is established by Federal Law of December 29, 2006 N 255-FZ “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity.”
III) Cash transactions
Directive of the Bank of Russia dated March 11, 2014 N 3210-U approved the Procedure for conducting cash transactions by legal entities and the simplified procedure for conducting cash transactions by individual entrepreneurs and small businesses. The requirements of this document apply to all organizations carrying out cash transactions.
If a taxpayer, for example, gave funds to his employee, then the employee must report on the expenses incurred, and the tax authority has the right to check this report. In the absence of such a report, the tax authority may include in the income of such an employee the amount of accountable funds received.
Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation for Moscow dated January 20, 2009 N 19-11/003082 indicates that the taxpayer using the simplified tax system (6%) must confirm expenses for cash transactions.
IV) Expenses for which the taxpayer acts as a tax agent
In some cases, the taxpayer may act as a tax agent for expenses incurred. The tax authority has the right to check such expenses for the purpose of fulfilling the duty of a tax agent.
If, for example, a taxpayer pays remuneration to individuals (not individual entrepreneurs) under civil contracts, then he acts as a tax agent for personal income tax for such payments and the tax authority has the right to check such expenses.
Another example is when a taxpayer purchases goods (work, services) from a foreign organization that is not registered with the Russian tax authorities. In this case, the taxpayer must withhold and transfer VAT to the budget, despite the fact that he himself is not recognized as a VAT payer (Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Property taxes
Taxes under UTII are paid on real estate, for which the base is the cadastral value. Calculations and transfers are carried out for the organization as a whole. But separate accounting may be necessary to correctly record all the information.
The main thing is to correctly determine the total amount of property tax. It is necessary to take into account the mode in which the property itself is used. Internet programs such as an online calculator are a great help with this.
Under different taxation systems, an entrepreneur’s income is considered differently, and this must be taken into account. The main thing is to correctly draw up documents that record expenses and the level of current profit. It often happens that a declaration is the only suitable option for resolving the issue. Neither the tax office nor other market participants can obtain information in any other way.
Additionally
Simplified taxation system (STS)
Individual entrepreneurs
Step 1 - checking for the right to use the simplified tax system
The very first thing the tax inspector will try to do is prove that you are unlawfully using the “simplified taxation”. And if they prove it, then you will be charged additional taxes that you had to pay when applying the general taxation system. And if you violated tax laws, you will be fined and late fees charged. Inspectors always strive to find such a violation, since it is the most profitable in terms of additional taxes. If you need inexpensive accounting services, go to baliot.ru.
So, tax authorities will apply sanctions to you if, using the simplified tax system, you:
before the end of the tax period, they switched to a different taxation regime.
In accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 346.13 of the Tax Code, you do not have the right to voluntarily change the regime. As a general rule, you can switch from “simplified taxation” to a different tax regime first in the new calendar year (clause 3 of Article 346.13 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). You must notify the tax office about the transition no later than January 15 of the year in which you intend to apply a different tax regime (clause 6 of Article 346.13 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
switched to another object of taxation without notifying the tax service (clause 1 of article 346.13 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If you decide to change the selected object of taxation, you are required to notify the tax office about this before December 20 of the year preceding the year in which you will apply the simplified tax system for the first time. Initially, the taxpayer has the right to independently choose the object of taxation;
if at the end of the reporting (tax) period your income under the object of taxation “income” exceeded 20 million rubles, multiplied by the deflator coefficient (in 2009 it was 1.538 - order of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated November 12, 2008 No. 395; clause 4 of Art. 346.13 Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same stage, income is checked. Have you underestimated them? Using cash and bank documents, inspectors will analyze the completeness of accounting for income received in cash and non-cash form, and will also check your counterparties;
switched to the simplified tax system earlier than one year after they lost the right to use it (clause 7 of article 346.13 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The list of situations when a taxpayer does not have the right to apply the simplified tax system is given in paragraph 3 of Article 346.12 of the Tax Code. So, you do not have the right to remain in the “simplified” position if you changed your type of activity and became a bank, insurer, private notary, non-state pension fund, investment fund, professional participant in the securities market, etc. If you began to produce excisable goods, engage in gambling business or switched to the unified agricultural tax, you also do not have the right to apply the simplified tax system.
And yet, it is more likely that, having changed, for example, the type of activity, the taxpayer will check whether he has the right to apply the simplified tax system before remaining in this mode. Most often, the taxpayer does not monitor the legality of applying this special regime when:
the average number of its employees for the tax period exceeds 100 people;
the residual value of fixed assets and intangible assets of the organization exceeds 100 million rubles;
the share of participation in the organization of other organizations is more than 25 percent (does not apply to organizations whose authorized capital consists entirely of contributions from public organizations of disabled people, subject to certain conditions);
is obliged to pay UTII for a certain type of activity. At the same time, for another type of activity, the taxpayer has the right to remain on the simplified tax system, combining modes.
Please note: the reason for ordering an on-site inspection may be indicators that are as close as possible to the limit value, for example, the number of employees, income for the reporting period. For example, if the number of the company is 97 people out of 100 allowed when applying the simplified tax system.
It is important
If you have previously had an inspection, the inspector will analyze its materials. This is done in order to monitor whether you are complying with tax laws that you have previously violated.
Step 2 – run the “scanner” to check your accounting!
After the tax authorities have checked your right to use the simplified tax system, they will check your accounting, namely its completeness and correctness of maintenance. Moreover, inspectors must take into account the following: “simplified” workers are exempt from the obligation to keep accounting records. At the same time, they must take into account fixed assets and intangible assets in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation on accounting (Federal Law of November 21, 1996 No. 129-FZ “On Accounting”).