The use of cash registers for non-cash payments with individuals
Federal Law No. 192-FZ dated July 3, 2018, signed by the President of the Russian Federation, excluded from the Federal Law No. 54-FZ dated May 22, 2003 “On the use of cash register equipment...”, including from its name, most references to “electronic means of payment.” " This term has been replaced by “non-cash payments”.
Thus, confusion and confusion in the interpretation of the law was eliminated. For example, previously it was not entirely clear whether it was necessary to use cash registers if goods were paid for remotely by crediting money to the seller’s bank account. In particular, in cases of settlement by payment orders.
Now the law says that organizations and individual entrepreneurs, when making non-cash payments with individuals, are required to use cash registers and issue cash receipts to customers (Clause 5, Article 1.2 of Federal Law No. 54-FZ dated 22.05.03).
At the same time, the law still separates non-cash payments proper from electronic means of payment (EPP). ESP are bank cards, Internet banking systems, electronic wallets, payment software applications, etc. Non-cash payments are not limited to the above mentioned ESPs. For example, payment by bank receipt and payment order are also non-cash payments.
Regarding the last two payment methods, the amendments establish a transition period of 1 year so that sellers can adapt to the new rules for working with payment cards (Clause 4, Article 4 of the Federal Law of July 3, 2018 No. 192-FZ).
Thus, if an organization/individual entrepreneur works, for example, by bank transfer, using payment cards and its own current account, then the obligation to use cash registers and produce checks for it will appear from July 1, 2019.
If an organization/individual entrepreneur accepts bank cards and electronic money for payment, then it is obliged to observe cash discipline now. Moreover, the amendments significantly softened the procedure for working with cash registers during distance selling.
Federal Law-54 on the use of cash register equipment: basic provisions
Law 54-FZ regulates the procedure for using cash registers on the territory of Russia when conducting non-cash and cash payments. Based on its provisions, by-laws are adopted, which should not contradict 54-FZ on cash register equipment.
In particular, this law defines:
- conditions, rules, procedure, features of using online cash registers (Articles 1.2, 2, 4.3);
- requirements for the fiscal drive and cash register (Articles 4, 4.1);
- what the issued check should be, as well as strict reporting forms replacing it (Article 4.7), etc.
Federal Law 54-FZ requires that only online cash registers be registered with the tax department. If previously cash registers duplicated each punched check on the control tape, now data on the completed sale is transmitted directly to the tax authority. To do this, cash registers are connected to the Internet and the OFD (fiscal data operator).
The regulation on the transition of individual entrepreneurs and enterprises according to Law No. 54-FZ to online cash registers has been in effect since February 1, 2017 (clauses 4, 6 of Article 7 of Law No. 290-FZ of July 3, 2016, clauses 4, 6). From the same date, clause 4 of Art. 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, which establishes liability for the use of a cash register that does not comply with the requirements of the law. For organizations, the maximum fine reaches 10,000 rubles, for individual entrepreneurs and officials – 3,000 rubles.
Making checks for remote payment
Remote payment for goods does not exempt the seller from using a cash register and issuing cash receipts to the buyer. Moreover, previously it was not clear how sellers could ensure the production/transfer of a receipt at the time of payment for the goods (Clause 2 of Article 5 of Law No. 54-FZ).
Now legislators have taken into account the specifics of distance trading and have written down in paragraphs. 5.3-5.4 art. 1.2 of Law No. 54-FZ special rules for the use of online cash registers and issuance of checks for such cases. Now, when trading remotely, a cash receipt/BSO must be prepared no later than the business day following the day of settlement. In this case, the check cannot be issued later than the moment of transfer of the goods. That is, today they paid, tomorrow delivery - tomorrow a receipt, today they paid and delivered today - the receipt is also today.
The check can be sent to the buyer in one of the following ways:
- in electronic form to a subscriber number or e-mail (the check is sent no later than the business day following the day of settlement);
- on paper along with the goods without sending an electronic receipt;
- on paper during the first direct interaction between the buyer and the seller without sending an electronic receipt.
The use of cash registers in settlements between organizations and individual entrepreneurs
The law directly establishes that cash register equipment is not used for non-cash payments between organizations and individual entrepreneurs (clause 9 of article 2 of Law No. 54-FZ). At the same time, it is clarified that if an electronic means of payment is presented between organizations/individual entrepreneurs, then the use of cash registers becomes mandatory.
Thus, if during settlements between organizations money is transferred from account to account, then there is no need to use a cash register. If organizations pay each other with cash or a bank card, they are required to use online cash registers in the general manner.
Please note that, contrary to numerous conversations on this topic, accountable persons of organizations acting on the buyer’s side will not print receipts when purchasing goods/services from organizations. Only the selling organization will be required to issue checks. This was confirmed in an interview with BUKH.1S by the head of the Operational Control Department of the Federal Tax Service of Russia Andrey Budarin.
He clarified that when making payments between an accountable person and a third-party legal entity, it is enough to punch one cash receipt: “The identification of the buyer as a legal entity occurs on the basis of the power of attorney he presents to make payments on behalf of the legal entity. Another important factor in the interaction of legal entities is the contract. If these conditions are met, then it turns out that two legal entities have actually met, making one payment, which is issued by one check generated at one cash desk.”
If the accountable person makes purchases without presenting a power of attorney from the company, then the seller should use the cash register in the same way as with an ordinary buyer.
At the same time, now the cash receipt generated during settlements between the organization and the individual entrepreneur must contain additional details. These details will allow you to identify the buyer and the purchased products (clause 6.1, article 1.2 of Law No. 54-FZ). The list of additional check details includes:
- name of the buyer (name of organization, full name of individual entrepreneur);
- INN of the buyer (client);
- information about the country of origin of the goods (when making payments for the goods);
- excise tax amount (if applicable);
- Customs declaration registration number (if applicable).
Other amendments to 54-FZ
Legislators also made other amendments to Law 54:
- It is mandatory to issue a cash receipt when repaying a loan issued for the purchase of goods.
- When paying out winnings, gambling organizers are required to issue a receipt marked “expense”.
- It is allowed to generate one check per day, week or month for all cases of refund to clients of overpayments for services or carrying out mutual offsets.
- The deregistration of a cash register is carried out automatically upon liquidation of a business entity based on an extract from the state register.
- To correct errors in a check, you must use a correction check. Previously, it was recommended to issue a refund of the receipt and issue a new check.
- The period for issuing a cash register registration card has been increased to 10 days.
- All cash receipts must display a QR code from 07/03/2018.
Read why you need a QR code here.
Using cash registers for prepayment
The amendments complement Art. 1.2 of Law No. 54-FZ with a new clause 2.1, which establishes the rules for processing payments in cases where individuals make prepayments/advance payments for certain services. For example, when an individual presents a theater subscription, a public transport ticket, or uses a certain tariff package for communication and Internet services.
In accordance with the new rules, when making payments in the form of offset or return of prepayments and advances, organizations and individual entrepreneurs can generate one cash receipt (CSR). This check will contain information about all such payments for a day or another billing period. This period should not exceed a calendar month. The consolidated check will be sent to the Federal Tax Service for control purposes.
As for the cash receipt, the buyer, for example, of a gift certificate, naturally needs to be issued a receipt. Presentation of such a certificate for payment is a special case of payment in the form of an advance offset. And the bearer of the certificate (and this may be another person) does not need to issue any check.
FINES for working without an online cash register
If, during an inspection, the Federal Tax Service discovers that an enterprise is operating without a cash register, it faces a fine.
For individual entrepreneurs, the fine ranges from 25% to 50% of revenue received without a cash register, but not less than 10 thousand rubles.
For an organization - from 75% to 100% of unaccounted revenue, but not less than 30 thousand rubles.
If the violator continues to work without a cash register and his revenue has already amounted to at least 1 million rubles, the manager will be prohibited from holding this position for a period of one to two years, and the activities of the organization or individual entrepreneur will be suspended for up to 90 days.
There is an opinion among entrepreneurs that the Federal Tax Service does not pay attention to businesses with a turnover of less than 10 million rubles per month, and some individual entrepreneurs may decide not to buy a cash register until the first fine. But the Federal Tax Service does not have to carry out comprehensive audits; any buyer who has not been given a check can complain to the tax office ; the Federal Tax Service has a special mobile application for this , available to anyone.
What to do if your fiscal drive breaks down
The amendments complement Art. 4 of Law No. 54-FZ with a new clause 8.1, which approves the procedure for action in the event of a breakdown of the fiscal drive. A drive failure here means the impossibility of reading all fiscal data from memory and generating a closure report.
Now the user will be required to hand over the broken drive to the manufacturer for examination. If the breakdown occurred due to a manufacturing defect, the examination is carried out free of charge.
Within five working days from the date of breakdown, the user of the cash register will have to submit an application for registration (re-registration) of the cash register with a new drive or to deregister it.
The manufacturer, within 30 days from the date of receipt of the broken fiscal drive, must conduct an examination and send its result to the cash register user and the tax authorities.
If data can be read from a broken fiscal drive, the user will be required to transfer this data to the tax authority within 60 days.
Deregistration of a cash register upon termination of activity
The amendments complement Art. 4.2 of Law No. 54-FZ with a new clause 18, which establishes the rules for deregistering cash registers upon termination of business activity.
According to the innovations, when the organization/individual entrepreneur ceases its activities, it will not be necessary to deregister the cash register. The cash register will be deregistered by tax authorities unilaterally.
That is, there is no need to send an application to the Federal Tax Service to deregister the cash register. The basis for deregistration of a cash register is an entry in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities or Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs about the termination of the activities of the organization/individual entrepreneur.
Who has been permanently exempted from using CCT?
The federal law supplements and clarifies the list of cases in which organizations and individual entrepreneurs have the right to carry out trade without the use of cash registers at all.
In particular, it is clarified that credit organizations are exempt from the use of cash registers (Clause 1, Article 2 of Law No. 54-FZ).
Instead of using cash registers, they are required to maintain a list of automatic payment devices that make it possible to carry out operations for issuing and receiving money (ATMs).
Along with credit institutions, the following are exempt from the use of cash registers:
- trade in newspapers and magazines on paper, as well as sale of related products at newsstands (paragraph 2, clause 2, article 2 of Law No. 54-FZ);
- trade in soft drinks, milk and bottled drinking water (paragraph 8, paragraph 2, article 2 of Law No. 54-FZ);
- peddling trade in food and non-food products by hand, from hand carts, baskets and other special devices for display, ease of carrying and selling goods (paragraph 7, clause 2, article 2 of Law No. 54-FZ), as well as trade in passenger train cars and on board aircraft (with the exception of cases of peddling trade in technically complex goods - when selling them, the use of cash desks will be required);
- sale of insurance policies by insurance agents (the responsibility to send an electronic check to the client rests with the insurer, who is obliged to send an electronic document when receiving money from the agent (Clause 11, Article 2 of Law No. 54-FZ));
- activities of organizations that exercise the powers of constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local governments to provide paid parking (clause 10, article 2 of Law No. 54-FZ);
- sale of goods through mechanical machines, where payments are made exclusively with Bank of Russia coins, except for machines that are powered by electricity, including through a battery (clause 1.1 of Article 2 of Law No. 54-FZ);
- paid services of state and municipal libraries related to librarianship (clause 12 of article 2 of Law No. 54-FZ).
The amendments also allow organizations and individual entrepreneurs not to use cash registers in the administrative centers of municipal districts classified as hard-to-reach areas and at the same time being the only populated area of the district (paragraph 1, paragraph 3, article 2 of the Federal Law of May 22, 2003 No. 54-FZ).
In addition, individual entrepreneurs using PSN are exempt from the use of cash register systems, subject to the issuance to the buyer of a document confirming the fact of payment (clause 2.1 of Article 2 of Law No. 54-FZ).
Exceptions are the types of activities carried out by individual entrepreneurs on the PSN, which are specified in paragraphs. 3, 6, 9 - 11, 18, 28, 32, 33, 37, 38, 40, 45 - 48, 53, 56, 63 p. 2 art. 346.43 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For these types of activities, the use of CCP will become mandatory from July 1, 2019.
When you can not issue checks and use the cash register autonomously
According to the changes (clause 5.1 of Article 1.2 of Law No. 54-FZ), organizations and individual entrepreneurs that sell goods through machines (vending) may not issue paper checks to customers.
They also have the right not to send them electronic checks if buyers do not provide their contact information (email address or mobile phone number) before payment. The exception is cases of trade in excisable products, technically complex goods, as well as goods subject to mandatory labeling.
At the same time, vending machines must be equipped with an online cash register and ensure the transfer of payment data to the Federal Tax Service. From February 1, 2020, a new requirement is introduced for vending machines - mandatory display of a QR code on the display (Clause 3, Article 4 of Law No. 192-FZ). Such a code should allow the buyer to read it and identify the cash receipt (strict reporting form).
Another case when it is allowed not to issue checks is payments for the provision of services for the transportation of passengers, luggage, cargo and cargo luggage, if clients pay for travel/carriage using a card (clause 5.1 of Article 1.2 of Law No. 54-FZ).
The amendments also complement the list of cases when organizations and individual entrepreneurs can use cash registers offline (without access to the Internet and instant transmission of information about settlements to the Federal Tax Service server).
According to the innovations, this list includes trade in the territories of military installations, facilities of the federal security service, state security agencies and foreign intelligence agencies (paragraph 1, paragraph 7, article 2 of Law No. 54-FZ).
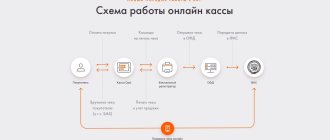
How the payment process has changed with the introduction of online cash registers
Operators of fiscal data OFD appeared . These are intermediaries between the entrepreneur and the tax office.
Conventional cash registers are being replaced by modern online cash registers . Such cash registers can not only print paper receipts, but also generate electronic ones and send sales data for the OFD.
| Before the law | After the law |
| The buyer pays for the product/service | The buyer pays for the product/service |
| Money goes to the store | Money goes to the store |
| A salesperson at a regular cash register prints a receipt. | Online cash register generates an electronic receipt |
| The online cash register sends an electronic check to the OFD | |
OFD receives an electronic check and sends it to:
| |
| The tax office receives information about the sale from you | The tax office receives sales data from the OFD |
| The tax office can check the cash register only during inspections | The tax office can check the cash register in real time |
Postponement for the use of online cash registers until July 1, 2019
Simultaneously with the establishment of a list of entities exempt from the use of cash registers, amendments to the law on online cash registers essentially expanded the list of organizations and individual entrepreneurs required to use them. At the same time, all new users of online cash registers were given a 1-year deferment so that they could reorganize their activities to comply with cash discipline.
In accordance with paragraph 4 of Art. 4 of Law No. 192-FZ, organizations and individual entrepreneurs received a deferment for the mandatory use of online cash registers until July 1, 2020 when implementing:
- non-cash payments with individuals through receipts and payment cards (the deferment does not apply to bank cards, Internet banking, electronic wallets and other electronic payment systems);
- calculations when accepting payments for residential premises and utilities, including contributions for major repairs;
- offset and return of prepayment and (or) advances;
- when providing loans to pay for goods, works, services (repayment of loans to pay for goods, works and services requires organizations and individual entrepreneurs to use cash register systems as of July 3, 2020, paragraph 21 of Article 1.1 of Law No. 54-FZ).
When should you switch to online cash registers?
The transition to online cash registers is gradual; the list of enterprises that should use online cash registers is increasing every year. Almost everyone is switching to online cash registers, even those who previously issued BSOs, receipts and sales receipts.
Entrepreneurs who have previously worked with CCP
That is, if you have previously accepted cash, cards, or used payment terminals, you should switch to online cash registers.
Sellers of excise goods
Sellers of alcohol, tobacco products, gasoline, cars, fur products, etc. should switch to online cash registers.
Beer sellers
Beer is not excise alcohol, so standard transition periods are used for them. If you work for OSNO - in 2017, if for UTII with hired employees - in 2020.
Online stores
Online cash registers should be used to sell goods and services via the Internet. If delivery occurs through a courier, he must use a portable terminal. If a remote service is provided, an electronic receipt is sent.
Services sector
Online cash registers should be used by individual entrepreneurs and legal entities providing services: hairdressing salons, laundries, training centers, delivery services. To understand whether your activity belongs to the “service sector”, use OKVED2, OKPD2 and transition keys with OKUN.
Vending machines and payment terminals
Online cash registers are becoming mandatory for coffee machines and payment terminals. An exception will be mechanical vending machines for goods under 100 rubles.
Entrepreneurs under “simplified tax regimes”
Online cash registers should be implemented even for entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system, PSN and UTII.
When combining the simplified tax system and a patent
When combining the simplified tax system and the patent system, you are required to keep separate records. Since 2020, you have been processing checks according to the simplified tax system at the online cash register, but for UTII you do not use the online cash register until 2018–2019.