In this article we will look at what insurance premiums and taxes an individual entrepreneur pays on a patent. We will analyze the mandatory payments for ourselves and for our employees, and also find out whether an entrepreneur on the PSN must pay 1% on income over 300 thousand rubles.
Important! If you have not yet registered an individual entrepreneur, we recommend that you do so in our free service or with the help of a specialist online, free of charge, without visiting the tax office or paying state fees!
Go to service Go to service
What fees and taxes does an individual entrepreneur pay on a patent?
An individual entrepreneur with a patent pays the cost of the patent and insurance premiums. If he combines a patent with a simplified patent, UTII or Unified Agricultural Tax, then he also pays taxes provided for by these special regimes.
An individual entrepreneur pays other taxes only if he acts as a tax agent or the object of taxation does not fall under special regimes.
Personal income tax
As a tax agent, an individual entrepreneur pays personal income tax on wages of employees. Individual entrepreneur income is subject to personal income tax if it is:
- payment for sold property that the individual entrepreneur did not use in business activities;
- dividends from participation in Russian and foreign organizations;
- insurance payments;
- interest on deposits in banks or on circulating bonds of Russian organizations;
- royalties from the use of copyright or related rights;
- winnings from the lottery or gambling.
Payment received for goods sold, work performed or services provided is subject to personal income tax, unless special regimes are applied to these types of activities or the money came from a foreign buyer.
Property tax for individuals
Under the patent taxation system, an individual entrepreneur pays personal income tax if the property is not used in business or is included in the regional list of objects, the amount of tax on which is calculated based on the cadastral value.
Value added tax
The use of a patent does not exempt individual entrepreneurs from paying VAT, for example, when renting state property, purchasing waste paper, scrap metal, raw animal skins, or purchasing goods, works and services from a foreign seller.
An individual entrepreneur pays VAT for himself if this type of activity falls under the OSNO or income is received from operations under simple or investment partnership agreements, trust management and concession agreements.
You can get an exemption from paying VAT for yourself. To do this, it is necessary that for 3 consecutive months the revenue from transactions subject to VAT does not exceed 2 million rubles. If you submit a notification and extracts from accounting documents in a timely manner, you will not need to pay VAT for the next 12 months. The right to exemption from VAT is terminated if the individual entrepreneur sells excisable goods or his revenue exceeds 2 million rubles for any 3 consecutive months.
Other taxes
Transport, water and other taxes that ordinary citizens pay are paid by an individual entrepreneur on a patent in the general manner.
We recommend reading: Taxes and contributions of individual entrepreneurs: types, terms and amounts of payments to the tax office.
Types of benefits
All benefits for individual entrepreneurs with disabilities are divided into several types:
| Municipal | Federal |
| Providing funds (subsidies) for business development | Partial or complete exemption from paying state fees when applying to courts or notaries |
| Reduced tax rates when applying the simplified tax system to 5% instead of 6% (not always) | Benefits for land and property taxation |
Providing a subsidy
Currently in the Russian Federation there is a program for subsidizing small businesses, thanks to which individual entrepreneurs can receive money from the state for business development. To do this, it is important to meet the following criteria:
- Conducting popular activities that are useful for society: opening kindergartens, private schools, etc.
- No debts to the Federal Tax Service.
- The period of existence of the individual entrepreneur is no more than two years.
- The staff number is no more than 100 people, and in some cases it is reduced to 15 employees.
An activity that is in demand and useful for society should be understood as an activity towards the development of which state policy is aimed. For example, in 2020, farming is being actively promoted, and it will be the easiest way to get money for it. This also includes the production of consumer goods, the provision of housing and communal services, the agricultural industry, scientific activity, and agricultural development.
How it all works in practice:
- A citizen registers with the Employment Center as an unemployed person. To do this, you will need a passport, marriage or divorce certificate (if you have one), educational documents, and a work record book. Based on the documentation submitted, he is assigned a monthly allowance.
- The subsidy applicant draws up a business plan. It is necessary to clearly reflect costs and estimated profits (profitability), and conduct an analysis of purchasing power. Also, when designing, it is important to take into account the location of the store if it opens: for example, in residential areas, small shops will be in demand, but in places with nearby large supermarkets they are in most cases unprofitable.
- Registration as an individual entrepreneur. To do this, the future entrepreneur must contact the Federal Tax Service.
- Providing a certificate of registration of an individual as an individual entrepreneur and a business plan to the Employment Center or the economic development department of the municipality. A special commission reviews the documentation within 60 days, and based on the results, a decision is made to issue a subsidy. Its size is determined individually, based on the profitability of the business. In some cases, the commission decides to reimburse only the costs of the state duty when registering an individual entrepreneur.
Subsequently, after spending, receipts for them are provided to the administration. The money is allocated for a specific purpose and cannot be spent on personal needs.
“Entrepreneurs developing small businesses in certain areas may need bank lending. In such cases, creditors require guarantors or collateral, because The individual entrepreneur has no profit yet. The SME Support Fund can act as a guarantor if the citizen presents us with a competent business plan and the commission determines that it is truly profitable.”
O. Kolesnikov, General Director of the Belgorod Fund for the Promotion of SMEs.
Tax systems
The choice of a convenient taxation system is up to the entrepreneur. Disabled persons may be provided with the following benefits:
- simplified tax system – reduction of the tax rate from 6 to 5%.
- PSN – providing a 30% discount on the purchase of a patent.
A lot depends on the choice of taxation system. For example, if a citizen is engaged in agricultural activities, it is more profitable for him to choose the Unified Agricultural Tax.
| View | pros | Minuses |
| BASIC | There are no restrictions on profit or the number of employees on staff; Possibility of documenting losses for tax exemption; No rental restrictions; Reduced tax rate for entrepreneurs who suffered losses during the reporting period | Complex accounting; Increased requirements for storage and documentation; Possibility of establishing additional contributions to the regional budget; Taxation of profits, property, VAT, personal income tax, mandatory payment of insurance contributions |
| UTII | Exemption from VAT and personal income tax: instead of them, an imputed tax is paid, calculated on the expected profit in the future; Possibility of reducing insurance premiums for employees; It is not necessary to register a cash register; Easy reporting | Paying tax even in the absence of profit; Unprofitable for trading over large areas; You cannot deduct expenses from the amount of income received, unlike the simplified tax system; Impossibility of cooperation with legal entities. We will have to combine two systems |
| PSN | Possibility of choosing the validity of a patent – from 1 to 12 months. Its cost depends on this; Paying only one tax - for a patent. There is no need to pay personal income tax, the amount of earnings does not affect taxation; Providing installments to pay for a patent; Simplified accounting procedures; There is no need to provide declarations; Application of reduced insurance rates when paying contributions for employees; Use of strict reporting forms instead of cash registers; Validity of the patent throughout the Russian Federation | Advance calculation method: the patent is paid before profit is received; The cost of insurance premiums cannot be deducted from the cost of the patent; Income restrictions – up to RUB 60,000,000. per calendar year; Personnel restrictions – up to 15 people |
| simplified tax system | Possibility of deducting expenses from income to reduce tax (relevant for the simplified tax system “income minus expenses”; Exemption from property tax and VAT; Minimum number of reports | It is mandatory to use a cash register for cash payments; Inability to account for losses over the past period; |
| Unified agricultural tax | Reducing the tax burden to 6%, as under the simplified tax system; Making advance payments once every six months, final payments - once a year; Minimum reporting package | Compliance with income criteria; Limitation of expense items of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
Payment of insurance premiums
As a rule, disabled people receive an insurance or social pension. This exempts them from paying insurance premiums, unlike employers with employees for whom they must make payments.
Important! The presence of a disability in an individual entrepreneur does not exempt him from paying insurance premiums. 22% should be transferred to the insurance part, and the transfer of MHIF payments is also required.
Tax benefits
The authorities have the right to establish additional tax benefits for individual entrepreneurs with disabilities. For example, you can get a discount of 500 rubles. for each month of business when paying tax. The following nuances are present here:
- Privileges are provided for monthly income of no more than 100,000 rubles;
- If the limits are exceeded even by 10 rubles, the tax is paid in accordance with the general procedure.
Example No. 1: tax calculation for an entrepreneur using the simplified tax system
A citizen with a disability of group 2 works as an individual entrepreneur on the simplified tax system “6%”, i.e. Tax is paid only on the income actually received. Also, his obligations include the transfer of pension and medical contributions annually until December 31 for the previous calendar year.
During the reporting period, the individual entrepreneur received income in the amount of 570,000 rubles. How tax is calculated:
570,000 x 6% = 34,200 rub.
Benefits when going to court
The issue of granting privileges to individual entrepreneurs with disabilities when going to court is regulated by Art. 333.36 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It establishes that disabled people are exempt from state duty in the following situations:
- when filing a claim of a non-property nature in order to protect rights and legitimate interests;
- in cases regulated by the Code of Civil Procedure or the CAS of the Russian Federation - disabled people of groups 1 and 2.
Public organizations of people with disabilities are also exempt.
Benefits when contacting a notary
Receive a 50% discount when paying the state fee or notary fee in accordance with Art. 333.38 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation can be used by disabled people of groups 1 and 2. This rule does not apply to the provision of technical services by a specialist: drawing up contracts, powers of attorney, requesting information from government agencies, etc. All this is paid separately depending on the price list of the notary office.
Individual entrepreneur on a patent without employees
An individual entrepreneur on a patent who does not hire employees pays insurance premiums only for himself. The calculation of insurance premiums includes a fixed amount and 1% of income over 300 thousand rubles per year.
Fixed contribution rates for 2020 are:
- for contributions to the Pension Fund - 32,448 rubles;
- for contributions to the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund - 8,426 rubles.
The total amount of fixed payments is RUB 40,874.
An individual entrepreneur who does not actually carry out activities, but has not been deregistered, is not exempt from paying fixed insurance premiums for himself.
If an entrepreneur was registered as an individual entrepreneur for an incomplete calendar year, then the amounts of payments are recalculated in proportion to the time when he had this status. At the first step, the calculation is made in proportion to the number of months worked, in the second - in proportion to the number of days worked in an incomplete month.
Other mandatory payments, except personal income tax for employees, for individual entrepreneurs without employees are no different from individual entrepreneurs with employees. The following rates apply for basic taxes:
- Personal income tax - 9, 13, 15, 30 or 35% (depending on the type and source of income);
- VAT - 20% (for some basic food products and essential goods - 10%);
- property tax - up to 2% of the market or cadastral value (the rate depends on the category of property).
What is individual entrepreneurship?
An individual entrepreneur should be understood as an individual registered as an individual entrepreneur with the Federal Tax Service. A citizen can work either independently or with the assistance of employees under employment contracts. The maximum number of personnel depends on the taxation system:
- patent – 15 people;
- UTII or simplified tax system – 100 people.
When using OSNO, no restrictions are set. If an individual entrepreneur works on the simplified tax system and exceeds the established number, he loses the right to use this system and is transferred to OSNO.
The responsibilities of an individual entrepreneur to the tax office include the following:
- Timely provision of reports. If there are no employees, it is enough to report annually before April 30 by submitting a declaration.
- Payment of insurance premiums and payments to the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.
- Pay fees and taxes.
- Apply cash register and use strict reporting forms.
- Maintain accounting and tax documentation.
Important! The list of responsibilities depends on the chosen system. For example, an individual entrepreneur using the simplified tax system without employees should not make advance payments. It is enough for him to timely report to the Federal Tax Service once a year until April 30.
Personal income tax and insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs and employees
The individual entrepreneur with a patent additionally pays taxes and insurance contributions for employees:
| Mandatory payments for employees | Bid | Peculiarities |
| Personal income tax | 13% | For all labor income of tax residents and persons equivalent to them, for the income of non-residents - 30% |
| Contributions to the Pension Fund | 22% | Until the maximum income is reached (in 2020 - 1,292 thousand rubles), if it is exceeded - 10% |
| Contributions to the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund | 5,1% | Not paid for foreigners required to register in the voluntary health insurance system |
| Contributions to the Social Insurance Fund for temporary disability and maternity | 2,9% | Until the maximum income is reached (in 2020 - 912 thousand rubles), if it is exceeded - 0%. For those temporarily staying in Russia, rates of 1.8 and 0% are applied, respectively. |
| Contributions to the Social Insurance Fund for injuries | 0,2-8,5% | The rate is set taking into account the type of activity. Accrued on all income. |
We recommend reading: What kind of reporting does an individual entrepreneur submit to the tax authorities and funds: types, rules, dates and deadlines.
How can a disabled person register an individual entrepreneur: step-by-step instructions
To register as an individual entrepreneur, you must do the following:
- Collect a package of documents, fill out an application for registration in form No. P21001.
- Submit documentation in any of the convenient ways: in person to the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate, at the MFC, through the State Services portal, personal account on the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate website, through a notary. If a citizen cannot do this on his own, he has the right to entrust the matter to a representative using a notarized power of attorney. A power of attorney without certification by government agencies will not be accepted.
- After submitting the documents, the applicant is given a notification with the date the certificate is ready. As a rule, the review period does not exceed 10 days; during holidays or weekends it increases.
- Receive a certificate of registration of a citizen as an individual entrepreneur and an extract from the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs. Activities will be carried out on the basis of these documents.
Initially, all entrepreneurs are assigned an OSNO. To switch to another tax system, you may need to submit an application to the Federal Tax Service.
Important! When applying to the MFC or a notary to register an individual entrepreneur, the state fee is not paid. This rule also applies when submitting electronic documents from 01/01/2020.
Documentation
When registering an individual entrepreneur, you will need a passport, SNILS and INN, and a receipt for payment of the duty.
State duty and payment methods
In 2020, the amount of state duty based on Art. 333.33 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is 800 rubles. It is paid according to the details of the Federal Tax Service, which can be found on the official website of the service.
To pay, you can choose any of the convenient methods:
| Way | Description | Enrollment period |
| Sberbank branch | Payment is made during a personal visit to the bank by the entrepreneur himself or his representative. You will need written details from the Federal Tax Service. | Instantly |
| Sberbank Online | Payment is made remotely. The payment receipt is saved and printed for submission to the Federal Tax Service | |
| Website of the Federal Tax Service | A receipt is generated, the money is transferred from the payer’s bank card after entering his details. Tax data is entered automatically |
Should an individual entrepreneur with a patent pay 1% on income exceeding 300 thousand rubles?
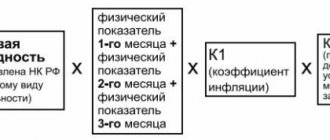
The use of a patent does not exempt an individual entrepreneur from paying 1% of the amount of income exceeding 300,000 rubles to the Pension Fund.
To calculate the amount that must be paid, the potential annual income for the selected activity, established in the region, is taken. If there are several patents, the values for each of them are added up. If a patent is used for less than 12 months, it is taken into account only for the period of use of the patent.
If an individual entrepreneur combines a patent with other taxation regimes, then the amount of income is over 300 thousand rubles. is calculated taking into account income under all tax regimes. When combined with OSNO, simplified tax system or unified agricultural tax, actual income is added to the potential income from the patent; when combined with UTII, imputed income is added.
The maximum amount of additional insurance contribution to the Pension Fund for 2020 is RUB 259,584.
FAQ
Question No. 1. What other benefits can a disabled person take advantage of, besides tax ones?
Citizens with disabilities are provided with social, housing and medical benefits. Their volume depends on the group. The widest list is given to persons with the first group, the minimum is given for the third.
Question No. 2. When can the Federal Tax Service refuse to register an individual entrepreneur?
The grounds for refusal are the provision of an incomplete package of documents, an expired passport, or incorrect completion of the application. If the appeal is submitted through State Services, the citizen is notified of the results of the consideration by notification in his personal account. When submitting an application in person, a reasoned refusal is issued with a description of detailed reasons.
How to hire a disabled person
Employers hire people with disabilities on a voluntary basis. But the state had to somehow guarantee such citizens the opportunity to find employment, and therefore some legal entities are obliged to hire disabled people to the company within the limits of the number of employees approved by law.
Such enterprises are those that have a staff of more than one hundred people. For them, a quota has been established at the legislative level to attract unemployed disabled people to work in the amount of from 2 employees to 4% of the average number of employees. For example, the quota for hiring disabled people in Moscow and the Moscow Region is 2% of the average number of employees.
It is not enough to hire a person with disabilities; it is also necessary to create conditions for him to perform his job duties. The conditions may be different - it all depends on the nature of the person’s illness and the rehabilitation program. Administrative liability is provided for all legal entities that neglect this requirement.
The amount of the fine for refusing to hire a disabled person or create the necessary working conditions is 5-10 thousand rubles.
Benefits for individual entrepreneurs with disabilities of groups 1, 2, 3 on insurance premiums
According to Art. 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation defines a list of amounts not subject to insurance premiums. This list does not contain preferences for individual entrepreneurs with disabilities of groups 1, 2, 3.
According to Art. 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation defines reduced rates of insurance premiums for payers, but even in this case, no advantages have been established for individual entrepreneurs with disabilities.
Thus, the possibility of applying reduced insurance premium rates is influenced not by the status of a disabled person, but by the type of economic activity.
Important! It is worth considering that the use of reduced tariffs is only possible if individual entrepreneurs with disabilities make payments and other remuneration to individuals.
The essence of PSN
The patent tax system, or PSN, is the youngest tax regime in Russia. It was introduced in 2013 and replaced the previously existing simplified tax system based on a patent. PSN can only be used by entrepreneurs with no more than 15 employees. This special regime does not apply to legal entities.
The essence of the PSN is that when purchasing a patent, an entrepreneur is exempt from other taxes. For example, when purchasing a patent for retail trade, an individual entrepreneur may not pay tax on the revenue he receives (as in the simplified tax system) or profit (as in the OSNO).
Only those entrepreneurs who work in the field of activity that falls under the patent can switch to PSN. These are businessmen who provide household services (repair of apartments, shoes, furniture, etc.), are engaged in retail or retail trade, work in the catering industry, rental and rental services for real estate, etc.
The acquisition of a patent does not relieve an individual entrepreneur of the obligation to pay pension contributions. Contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation do not reduce the value of the patent, as is practiced in other special regimes: simplified tax system and UTII, which is an important disadvantage of the PSN.
Meanwhile, PSN allows many entrepreneurs to optimize their expenses for paying taxes and fees and reduce the time spent on preparing reports.
How to hire a disabled employee
Companies employ people with disabilities on a voluntary basis, but for some organizations the hiring of such persons on their staff is mandatory within the limits of the quota established for them. For organizations with more than 100 employees, the legislation of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation establishes a quota for hiring disabled people as a percentage of the average number of employees (but not less than 2 and not more than 4%). Thus, the state guarantees the right to employment for people with disabilities. For example, in Moscow and the Moscow region, the quota for hiring disabled people is 2 - 4% of the average number of employees. The differentiation as a percentage depends on the average number of employees.
For refusing to hire a disabled person within the established quota, the employer may be held liable under Part 1 of Art. 5.42 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation in the amount of 5,000 to 10,000 rubles.
Working conditions for disabled people are as follows:
- For disabled people of groups I and II, a reduced working time of no more than 35 hours per week is established while maintaining full wages (Article 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Limitations on the duration of daily work (shift) for disabled people are established in a medical report, for example, in an individual rehabilitation program (Article 94 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- A disabled employee can be involved in overtime work, work on weekends and holidays and at night only with his consent and provided that such work is not prohibited for him due to health reasons. At the same time, these employees must be informed in writing of their right to refuse to work at odd hours. The employee's consent must also be obtained in writing. There are no special provisions for payment for overtime work, work on weekends, holidays and night time.
- Disabled persons are provided with extended annual paid leave; it is at least 30 calendar days. Persons who became disabled as a result of the Chernobyl disaster have the right to additional paid leave of 14 calendar days in accordance with clause 5, part 1, art. 14 of the Law on social protection of citizens exposed to radiation as a result of the disaster at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant.
- For disabled employees due to family circumstances or other valid reasons, based on a written application, the employer is obliged to provide unpaid leave for up to 60 calendar days a year (Article 128 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Violation of the rights of disabled workers entails liability in the form of an administrative fine on officials in the amount of 1,000 to 5,000 rubles; for legal entities - from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles. or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days (Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Most common mistakes
Mistake #1. Subsidies for business development are given to absolutely everyone.
No. You can find out the list of directions beneficial for the region on the official website of the administration. Subsidization is provided only for them. For example, the likelihood of receiving funds for the development of trade is negligible, because it is not always profitable for the state.
Mistake #2. Anyone can use the installment plan when paying state fees.
No, this will require an application and documents confirming your difficult financial situation. The appeal is reviewed by the body receiving the appeal. Individual entrepreneurs will most likely be denied installment plans, because registering a business is not a vital necessity.
Social Insurance Fund: percentage of contributions for contributions in case of occupational illnesses and injuries
Contributions from injuries and illnesses at work are the only ones left in the administration of Social Insurance. In 2020, as before, their size depends on the level of risk characteristic of the main activity of the enterprise.
The rates are specified in 419-FZ dated December 19, 2016. The regulation divides risks into 32 levels. Each of them has its own rate. Values range from 0.2 to 8.5%.
The policyholder will learn the 2020 FSS interest from the Fund’s official notice, sent after the company has submitted documents confirming its main type of activity.
At its discretion, the FSS has the right to reduce or increase the rate, but not by more than 40%. The relevant decision of the supervisory authority is based on the following facts:
- features of working conditions at the enterprise;
- results of medical examinations of company employees;
- the amount of insurance costs.
If the enterprise has had at least one fatal case, a discount on the tariff is not provided.
The following can apply for a maximum “discount” of 40%:
- organizations that employ disabled people of all groups, in terms of payroll allocated to pay these employees;
- public organizations of disabled people;
- companies created for scientific, educational, cultural activities, etc.
Since 2020, organizations and individual entrepreneurs are required to annually confirm their main type of activity by April 15. If they ignore this need, a tariff will be applied to them based on the most “expensive” from the point of view of injury insurance OKVED, specified in the registration documents. Previously, the FSS did the same, but firms had the opportunity to prove their case in court. Now there is a legislative justification for inflating rates.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
.
In the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund, Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation? Is information about disabled people subject to reflection in Form-4 of the Social Insurance Fund?
Having considered the issue, we came to the following conclusion:
From January 1, 2020, reduced insurance premium rates for insurance premium payers making payments and other benefits to individuals who are disabled people of groups I, II or III have been abolished. The general insurance premium rates of 30% apply to payments and rewards accrued in favor of disabled people.
For organizations and individual entrepreneurs paying for the work of employees who are disabled people of groups I, II and III, insurance premiums from NS and PP are paid in the amount of 60% of the insurance rates established by Art. 1 of Federal Law N 179-FZ.
Let us note that the legislative acts of the Russian Federation do not oblige an employee to inform the employer about the fact of his disability and provide documents confirming this fact. If the employee did not report his disability, then when calculating contributions to NS and PP, the general tariff without the 60% “discount” is applied.
Information about disabled employees must be reflected in Form-4 of the Social Insurance Fund.
Rationale for the conclusion:
Insurance contributions to the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund, Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation
The procedure for calculating and paying (transferring) insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation for compulsory pension insurance, the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation for compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity, the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund for compulsory medical insurance is regulated by Federal Law dated July 24, 2009 N 212-FZ (hereinafter referred to as Law N 212-FZ).
According to Part 1 of Art. 7 of Law N 212-FZ, the object of taxation with insurance premiums is recognized, in particular, as payments and other remunerations accrued by payers of insurance premiums in favor of individuals within the framework of labor relations and civil contracts, the subject of which is the performance of work, the provision of services (with the exception of remunerations , paid to the persons specified in clause 2 of part 1 of article 5 of Law No. 212-FZ).
Thus, remuneration paid to an individual, including a disabled person who is not an individual entrepreneur, under an employment contract is subject to insurance contributions.
Insurance premium rates are established in Part 2 of Art. 12 of Law No. 212-FZ. However, in the period 2012-2017, when choosing tariffs, one must be guided by Art. 58.2 of Law N 212-FZ, from which it follows that, unless otherwise provided by Law N 212-FZ (reduced tariffs - Article 58 and Article 58.1 of Law N 212-FZ), insurance premiums in 2015-2017 are paid according to tariffs , established by Part 1.1 of Art. 58.2 of Law N 212-FZ, namely:
1) Pension Fund of the Russian Federation:
22.0% within the established limit of the base for calculating insurance contributions for compulsory pension insurance;
10.0% above the established maximum base for calculating insurance contributions for compulsory pension insurance;
2) Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation - 2.9% within the established limit of the base for calculating insurance contributions for compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity;
3) Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund - 5.1%.
Article 58 of Law N 212-FZ for the transition period 2011-2027 established reduced insurance premium rates for certain categories of insurance premium payers.
Here we draw your attention to the fact that this article lists all categories of insurance premium payers who are currently entitled to benefits or who previously had them (for example, only in 2011). That is, the presence of a particular policyholder in the list of payers of insurance premiums established by this article does not mean the right of the specified policyholder to apply benefits during the entire period 2011-2027. Mention of the policyholder in Art. 58 of Law N 212-FZ only says that this policyholder had or has the right to apply a reduced tariff either during the entire specified period (from 2011 to 2027), or for some time falling within this period (for example, during 2012-2013).
In particular, in paragraph 3 of part 1 of Art. 58 of Law N 212-FZ provides benefits for payers of insurance premiums who make payments and other remunerations to individuals who are disabled people of groups I, II or III - in relation to these payments and remunerations.
For these categories of policyholders, reduced insurance premium rates are established in Part 2 of Art. 58 of Law No. 212-FZ. The tariffs defined by this norm were in effect only during 2012-2014 (as follows from a direct reading of the norm in question).
The right to apply reduced rates of insurance premiums to categories of policyholders named in clause 3, part 1, art. 58 of Law N 212-FZ, in 2020 and subsequent years, currently not provided for by current legislation.
Thus, in 2020, in relation to payments and rewards accrued in favor of disabled people, general insurance premium rates are applied, the total amount of which is 30% (Part 1.1 of Article 58.2 of Law No. 212-FZ).
Insurance premiums from NS and PP
Clause 1 of Art.
2 of the Federal Law of December 22, 2005 N 179-FZ “On insurance tariffs for compulsory social insurance against accidents at work and occupational diseases for 2006” (hereinafter referred to as Federal Law N 179-FZ) for organizations of any organizational and legal forms that pay labor of workers who are disabled people of groups I, II and III, it is established that insurance contributions for compulsory social insurance against accidents at work and occupational diseases (hereinafter referred to as contributions from NS and PP) are paid in the amount of 60% of the amount of insurance tariffs established by Art. 1 of Federal Law N 179-FZ. By virtue of Art. 1 Federal Law of December 1, 2014 N 401-FZ “On insurance tariffs for compulsory social insurance against accidents at work and occupational diseases for 2020 and for the planning period of 2020 and 2020” (hereinafter referred to as Law N 401-FZ) in 2020, the same procedure and the same insurance premium rates that were established by Federal Law N 179-FZ are applied.
In addition, in 2020, the specified procedure for applying the tariffs for contributions to NS and PZ (60% of the insurance tariff) applies not only to organizations (legal entities), but also to individual entrepreneurs making payments and rewards to disabled people of groups I, II or III (Article 2 of Law No. 401-FZ).
With regard to the possibility of applying reduced tariffs to payments in favor of disabled people by payers of insurance premiums calculated on the basis of Law N 212-FZ, the authorized bodies explained that the right to apply reduced tariffs arises from the 1st day of the month in which the employee received disability and is lost from the 1st day of the month in which the employee, as a result of examination (re-examination), loses the right to receive disability. See paragraph 4 of the Information message of the FSS of the Russian Federation dated 02/03/2011, letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated 06/22/2010 N 1977-19, letter of the FSS of the Russian Federation dated 11/17/2011 N 14-03-11/08-13985, dated 12/01/2010 N 02- 03-10/08-12891. We believe that this logic also applies to contributions from NS and PP.
In our opinion, the basis for applying a reduced rate of contributions from NS and PP in relation to payments and remunerations paid to disabled people of groups I, II and III can be a certificate issued based on the results of a medical and social examination.
The certificate indicates the disability group and the degree of limitation of the ability to work, or indicates the group of disability without limitation of the ability to work, as well as an individual rehabilitation program (clause 36 of the Rules for recognizing a person as disabled, approved by Government Decree No. 95 dated 20.02.2006).
The form of the certificate confirming the fact of disability was approved by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated November 24, 2010 N 1031n.
It should be noted that neither the Labor Code of the Russian Federation nor the Federal Law of November 24, 1995 N 181-FZ “On the social protection of disabled people in the Russian Federation” obliges the employee to inform the employer about the fact of his disability and provide documents confirming this fact.
Form 4-FSS
Information about disabled employees is subject to reflection in FSS Form-4 (the form and procedure for filling it out (hereinafter referred to as the Procedure for filling out Form 4-FSS) were approved by order of the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation dated March 19, 2013 N 107n).
Namely: Information on the average number of working disabled people must be reflected on the title page of form 4-FSS;
Information on the amount of payments and other remuneration to individuals who are disabled people of groups I, II, III is indicated in line 5 of table 3 “Calculation of the base for calculating insurance contributions” of form 4-FSS;
Information on the amount of payments and other remuneration to individuals who are disabled people of groups I, II, III is also subject to reflection in column 4 of table 6 of form 4-FSS.
In addition, Form-4 of the FSS contains Table 3.1 “Information necessary for the application of the reduced tariff of insurance premiums by the payers of insurance premiums specified in paragraph 3 of part 1 of Article 58 of the Federal Law of July 24, 2009 N 212-FZ.” This table is filled out by payers who apply a reduced rate of insurance premiums in relation to payments and other remunerations accrued in favor of individuals who are disabled people of groups I, II or III, if the specified rate is lower than the basic rate established for these payers (clause 11 Procedure for filling out form 4-FSS).
Since from January 1, 2020, general insurance premium rates are applied to payments and benefits accrued in favor of disabled people, this table, starting with reporting for the first quarter of 2015, should not be filled out by policyholders who make payments to disabled people.