What is return on equity
Definition of return on equity
This is the most important financial accounting indicator, indicating the ratio of the shareholder’s net profit to the investments made in the activities of the LLC. It is of significant importance for investors who sacrifice a certain part of their personal savings to form the company’s statutory investments. In return, they have the right to count on the company’s profit in a share corresponding in size to the previously made investment.
By studying the return on capital, you can find out what percentage of return each ruble invested in the business will bring. By studying the financial statements, the owner/founder of the company will be able to determine the level of profitability and its value for investment.
Important: unlike return on assets, this capital indicator makes it possible to assess the degree of profitability and efficiency of invested personal money.
The coefficient makes it possible to study the level of profitability from sales. It does not provide an objective assessment of the level of business efficiency, since borrowed funds may be involved.
It follows that the indicator indicates the profit of the enterprise received for the co-founders.
Return on working capital
When determining the economic efficiency of a company's activities, they also use the return on working capital (or current assets).
Working capital is funds allocated to current activities to ensure the production cycle.
Working capital can be divided into constant or variable:
- Constant working capital is the funds that provide the minimum acceptable economic results of activity.
- Variable capital is the attraction of additional funds to expand production tasks.
How to correctly register entries for profit and tax on it? How are fixed assets written off in accounting, how are postings made? Read the rules for writing a single settlement document for the Pension Fund here:
Return on working capital is calculated as the ratio of profit to the average annual (or average for the period under review) value of current assets.
You can calculate profitability using accounting data as follows:
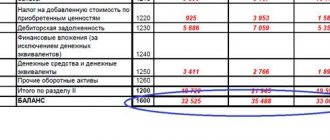
Line 2400 of the income statement: Line 1200 of the balance sheet.
How to calculate return on equity ratio
Return on investment is the ratio of income to the investment object, in this case to personal funds. To obtain the data of interest, you need to apply a formula in which the size of the investment will be taken into account.
The indicator is abbreviated as ROE according to international sources. Taking into account this abbreviation, the formula for calculations is used:
ROE = Pr / SK × 100
In it:
- Pr – net receipts, only it is used for calculation;
- SC – personal amount of injections into the transaction. For subtractions, the average is taken, obtained by adding the data at the beginning and end of the period and dividing it by 2.
Important: the resulting return on personal capital is relative, expressed as a percentage.
Dupont formula
Additionally, return on earned capital is determined using the DuPont formula. Its components are:
ROE = (Pr / Vyr) * (Vyr / Act) * (Act / SK)
In the above algorithm, in addition to the indicators considered above, the following were added: revenue - Exp and assets - Act.
GLAVBUKH-INFO
Return on Equity - DefinitionReturn on equity is a coefficient equal to the ratio of net profit from sales to the average annual cost of equity. The data for its calculation is the balance sheet.
Return on equity - what it shows
Return on equity shows the amount of profit that an enterprise (organization) will receive per unit of equity value.
Return on Equity - Formula
General formula for calculating the coefficient:
Krsk =
| Net profit | *100% |
| Average equity capital |
Calculation formula based on balance sheet data:
| Krsk = | p.190 | *100% |
| 0.5 * (page 490 ng + page 490 kg) |
where line 190 , line 490 ng - at the beginning of the year, line 490 kg - at the end of the year of the profit and loss report (form No. 2).
Return on Equity - Meaning
Return on equity (ROE) is essentially the main indicator for strategic investors (in the Russian sense, those investing for a period of more than a year). It allows you to determine the efficiency of use of capital invested by the owners of the enterprise. Owners receive profitability from their investments in the form of contributions to the authorized capital. They donate those funds that form the organization’s own capital and in return receive rights to a corresponding share of profits. From an owner's perspective, profitability is best expressed as return on equity and is most important to a company's shareholders. Since it characterizes the profit that the owner will receive from the ruble of funds invested in the enterprise.
The use of this coefficient has certain limitations. Real income comes not from assets, but from sales. Based on Krsk, it is impossible to assess the efficiency of a company’s business. In addition, in most cases, companies have a significant share of debt capital. For example, in the banking sector, borrowed capital is generally the basis of the entire business. In fact, all the bank’s operating activities are based on attracted deposits, and equity capital acts only as a reserve, a guarantor of the bank’s solvency and financial stability. Either way, as an accounting metric, Return on Equity provides insight into the income a company earns for its shareholders.
As a rule, the Return on Equity indicator is usually compared with possible alternative investments in shares of other enterprises, bonds, bank deposits, etc. those. where there is an opportunity to make a profit.
The minimum (normative) level of profitability of an entrepreneurial business can be considered the level of bank deposit interest.
The minimum standard value of the Krsk indicator is determined by the following formula:
Krnk = Sd*(1-Snp)
where Krnk is the standard value of return on equity capital, relative units; SD – average rate on bank deposits for the reporting period; STP – income tax rate.
If the Krk indicator for the analyzed period turned out to be lower than the minimum Krk or even negative, then it turns out that it is not profitable for the owner to invest in the company. It is worth analyzing investments in other companies.
In order to finally make a decision on exiting the company’s capital, you need to analyze the Krsk in recent years and compare it with the minimum level of profitability for this period.
| < Previous | Next > |
Formula for calculating return on equity on balance sheet
The balance sheet total is calculated mathematically according to accounting information, but it can also be viewed in the accountant’s documents. To do this, it is enough to be able to read them.
To obtain the data, it is necessary to emit information in the balance sheet records of table 1 and in the financial statements based on the results compiled in table 2.
The return on equity ratio is subtracted using the following formula on the balance sheet
ROE = line 2400 form 2 / line 1300 form 1 * 100.
How to analyze eigenvalues
Compiling such calculations allows investors to evaluate how effectively the selected company uses cash loans and financial borrowings. An increase in the share of raised funds in the authorized capital leads to an increase in the company's costs. Even in cases where the use of the coefficient in question allows one to obtain positive results, it is necessary to pay attention to additional factors. One of these factors is the efficiency of using credit funds. Such decisions are advisable only when the amount of funds received is many times greater than the amount of interest payments.
Many experts say that the investor’s income depends on the value of the indicator under consideration. That is why investors prefer to choose projects that demonstrate a high level of return on equity. However, in some cases, exceeding the standards may be explained by the use of borrowed capital as part of the authorized capital. This means that the investor's investment is at high risk.
Return on equity is essentially the main indicator for strategic investors
Standard value of return on equity
In order to soberly assess the level of profitability of personal investments in a particular area of activity, you need to compare the resulting indicator with identical ones for investments in other areas.
After the calculation, the ROE percentage is taken into account, which in developed countries should be no lower than 10 - 12%. With significant inflation in the country, the indicator exceeds the indicated result. Therefore, in Russia its value of 20% is considered the norm.
If the value is negative, you should increase your personal investment capacity. If the average indicator is significantly exceeded, increased investment risks arise.
Normal value of efficiency of use of equity capital
Return On Equity shows owners how their invested funds work: how much net profit each unit of the insurance company brought. In this situation, the following statements can be made regarding the ROE indicator:
- The higher the coefficient, the higher the return on investment in business.
- If the calculation result turns out to be close to zero, then the feasibility of investing in enterprises is very doubtful.
Important point! Some domestic experts believe that in the Russian economy the standard ROE value is 20% (0.2). However, for analysis it is still better to compare the calculation results with industry averages.
The resulting profitability value is usually compared with the average profitability in the industry, the average interest rate in the economy, and then with the return on investments in stocks, bonds, bank deposits, etc.
Important point! An excessively high value of KRSK may indicate a decrease in the financial stability of the enterprise: the higher the return on investment, the greater the level of risk.
Using the return on equity ratio
After obtaining data by applying one of the formulas or several, they are analyzed. It is necessary to determine the effectiveness of work in the chosen direction and adjust further actions. The level of the coefficient affects the amount of dividends of participants and the value of the company as a whole.
The analysis determines:
- the level of competent use of financial instruments by the company, including funds raised from outside, after comparing the results on the return on personal investments and assets;
- In the process of studying the data, you should not neglect the profitability ratio of borrowed funds. The profit from the use of the loan must exceed the amount of interest paid for its use;
- a large ROE ratio, significantly exceeding the established average result, is a consequence of large financial leverage. This means that the share of borrowed funds significantly exceeds the share of own investments.
Important: the right to determine the justification of such financial risks belongs to the owners of the company.
To really assess the situation at an enterprise, it is necessary to systematically calculate coefficients to compare them over several periods.
Based on the calculations carried out, conclusions can be drawn regarding:
- Increasing the volume of personal funds
- Growth in the total amount of debt obligations
- Reducing the level of asset turnover
- Company profit growth
- Increased financial risks.
After receiving data and an objective assessment of the situation, further actions can be taken to improve the financial microclimate.
What is return on assets (ROA)?
In its broadest sense, ROA is the ultra-version of ROI. Return on assets tells you what percentage of each dollar invested in the business was returned to you as profit.
You take everything you use in your business to make a profit - any assets such as cash, fixtures, machinery, equipment, vehicles, inventory, etc. - and compare it all to what you were doing during that period in terms of profit.
ROA simply shows how effectively your company uses its assets to generate profits.
This ratio is more useful in some industries than others, in part because how much money your business invests in assets will depend on your industry:
- A manufacturing company may have a lot of capital tied up in plant and equipment.
- A service business may have expensive computer and information systems.
- Retailers need a lot of inventory.
But no matter your industry, ROA gives you insight into your overall profitability.
How to calculate return on assets?
It's a simple calculation that goes like this.
net profit / assets = return on assets
For simplicity, let's assume that your net income for the year is $248 and that your business assets are $5,193. Therefore you should calculate ROA as follows:
$248 / $5,193 = 4.8%
Naturally, you are wondering, is 4.8% good? This again depends on your industry.
For ROA, as for most financial indicators, there is no single correct value to strive for. There are ranges and expectations for different types of companies.
Banks tend to reduce ROA to around 1%. Technology companies have very few assets, so they often have high ROA. You need to compare your ratio with other companies in the same field to understand where you stand and how you could make better use of your assets.
Most profitability ratios, such as gross profit and net profit, are rarely too high, although you generally want them to be as high as possible. Return on assets, on the other hand, may be too high.
In fact, an ROA that is higher than the industry norm may indicate that the company is not updating its assets with an eye toward the future. The company may not be investing in new plant and equipment, which could be detrimental to its long-term prospects, no matter how good the ROA looks at the moment.
Another reason you might see a very high ROA is because of its balance sheet.
Take the infamous Enron. This energy company had a very high ROA. This was due to the fact that she created her own assets separately. Since its assets were thus taken off the balance sheet, the company appeared to have a higher return on assets and equity. This technique is called “denominator control.”
But "denominator management" is not always a scam. In fact, it's a smart way to think about how to run a business.
How can we reduce assets so that we can increase our ROA?
You're essentially figuring out how to do the same job at a lower cost. You may be able to restore it instead of throwing away money on new equipment. It may be a little slower or less efficient, but you will have lower assets.
Now let's look at return on equity.
Is it possible to influence the value of the coefficient?
The profitability ratio is easy to adjust. To do this, you need to know what can reduce the significance of return on equity and what can increase it. A drop in the parameter is typical in a situation where investment funds are increased at the expense of third-party organizations or when the authorized capital is increased due to additional contributions from the founders. A decrease in the ratio will certainly follow with a sharp decrease in the amount of borrowed capital due to the full repayment of the company's obligations. A drop in asset turnover will negatively affect the company's efficiency with depositors' funds.
You can count on an increase in the profitability of your own assets when profitability increases due to competent management of activities. Registration of loans and credits helps to increase the indicator, but in such a situation, using it in analyzing business performance will be unrealistic.
https://youtu.be/1QvuRBh7JNo