Hello, Vasily Zhdanov is here, in this article we will look at the profitability of production assets. Profitability ratios are used in a company to measure the effectiveness of various processes and elements. This indicator is determined for almost any component, for example, for production assets.
The return on assets formula can be used by an investor or a company internally to evaluate whether a company is making a profit relative to its assets. It is important for an investor to consider that the profitability of a company's operating assets may vary depending on the industry in which the company does business. A particular company may produce a product that requires additional assets to produce the product compared to another industry.
What are production assets?
Production assets should be understood as the totality of all assets that an enterprise requires to carry out production processes. These include:
- equipment;
- building;
- structures;
- means and objects of labor;
- other elements necessary for carrying out production activities.
Important! To determine them, from the entire mass of funds, firms subtract those assets that are used by the company for social and other non-productive purposes.
Calculation formula:
PF = VA+OA-NA,
Where PF – production assets, t.r.;
VA – non-current assets, etc.;
OA – current assets, t.r.;
NA – non-productive assets, etc.
Profitability and its main types
Note 1
As you know, any organization carries out activities using a variety of objects of labor, within which we can conclude that the financial condition of any enterprise is influenced by such an indicator as the profitability of fixed assets. This means that fixed production assets must be used optimally and rationally.
Profitability can be called economic efficiency, which is expressed in an indicator reflecting the degree of efficiency in the use of resources, such as material, monetary, production, labor, etc. Thus, profitability is a general indicator of how effectively the organization under study functions. Profitability can be used to compare the profits and costs of producing a product or service.
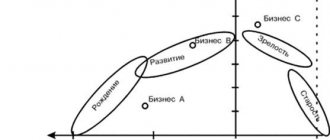
There are different types and types of profitability. The types that can be distinguished within the framework of the concept of “profitability” are represented by return on assets, return on fixed assets and return on sales. How these types of profitability are calculated can be seen in the figure below.
Finished works on a similar topic
- Course work Profitability of fixed production assets 440 rub.
- Abstract Profitability of fixed production assets 250 rub.
- Test work Profitability of fixed production assets 230 rub.
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
Figure 1. Methods for calculating some types of profitability. Author24 - online exchange of student work
The profitability of fixed assets is often called the profitability of fixed assets. This indicator can be calculated as the quotient of net profit divided by the cost of fixed assets, and multiply all this by 100 percent. The profitability indicator of production assets is the resulting integrated indicator of production efficiency. Within the framework of this indicator, the manifestation of other partial performance indicators is carried out, and only after that, the actual causes and factors of these indicators.
The indicator of profitability of fixed production assets is especially important, since the effective use of fixed production assets of an enterprise plays an important role in the development of the economy of the entire state as part of the constant influence on the factors and conditions that determine the level and dynamics of the functioning of the means of production. The goal of managing the efficiency of using fixed production assets can be called the need to ensure organizational and economic conditions for the effective use of specific types of means and objects of labor.
Too lazy to read?
Ask a question to the experts and get an answer within 15 minutes!
Ask a Question
Let us consider in more detail the features of calculating this indicator.
The concept of an indicator of the efficiency of production assets
The capital asset return ratio is a profitability ratio that measures the net profit produced by productive assets over a period.
In other words, the return on assets ratio measures how effectively a company can manage its assets to generate profits during a period.
Since the sole purpose of such company funds is to generate revenue and generate profits, this ratio helps both management and investors see how well a company can convert its productive investments into profits.
You can think of this indicator as the return on investment for a company, since capital expenditure is often the largest investment for many companies.
This ratio shows how profitable a company's productive assets are.
Return on production assets is an indicator of production efficiency
Any labor activity is characterized by the fact that with the help of labor tools one or another effect is produced on the object of labor. In relation to the production activities of an enterprise, the totality of means and objects of labor represents the value of production assets. This is precisely the part of the property that is directly involved in production. This reason makes it particularly important to determine the degree of efficiency of using this part of the assets.
It will be easiest to use the most popular method of assessing efficiency, so we will look at how to calculate the profitability of production assets. In general, profitability indicators are determined through the ratio of profit to the indicator whose profitability needs to be known. As for our situation, the profitability of production assets is determined by dividing the profit from sales by the average cost of production assets.
It is necessary to explain the choice of these particular indicators. Let's start with the numerator, where we used sales profit. Of course, we could take the simple route and use net profit, as in most profitability indicators, but this would not be very correct. The fact is that net profit also takes into account the financial result from other activities in which production assets do not participate. But the sales profit indicator actually characterizes the beneficial effect from the sale of pre-produced products.
As for the denominator, it is important to explain the use of the average value. This choice is due to the fact that profit is an indicator accumulated over a period, and during this period the value of the property could change. To somewhat smooth out the impact of these changes, the average cost is used in the calculations. Such a calculation will be the most accurate and correct, but it requires additional information and additional labor costs. If these resources are not available, then the cost of production assets at the end of the period can be used, but this may reduce accuracy.
As already noted, the profitability of production assets shows the effectiveness of their use. As for the meaning of specific numerical values, it consists of the amount of profit that falls on each ruble of the value of this part of the assets. Obviously, the larger this value, the more efficiently the company's resources are used.
The production assets of an organization are usually divided into two fundamentally different groups: fixed assets and working capital. Each of these parts represents means and objects of labor, respectively. For these parts, it is also possible to calculate profitability indicators using an identical methodology. Please note that it is also better to use the average cost over the period to make the calculations more accurate.
The profitability of production assets must not only be determined, but also analyzed. The analysis techniques in this case are similar to other profitability indicators. It will be enough to analyze the dynamics of the indicator over several periods (conduct a horizontal analysis) and compare the values with the industry average or with the levels of analogous enterprises. In addition, you can resort to factor analysis, which will allow you to determine the reasons for certain changes. For this type of analysis, the methodology of DuPont specialists and the corresponding formulas are often used, but nothing prevents you from applying other mathematical models that, in your opinion, will more accurately reflect the current situation.
The need for calculation and application
Below are some of the main most common reasons why companies conduct profitability analysis of productive assets:
- Using the indicator to determine profitability and efficiency. Return on production assets shows the amount of money earned per ruble of assets in production. Therefore, a higher profitability value indicates that the business is more profitable and efficient.
- Using a ratio to compare performance between companies. It is important to note that such profitability should not be compared across industries. Companies in different industries vary significantly in their use of productive assets. For example, in some industries, generating income may require expensive fixed assets that are not in demand in other industries. Consequently, these companies naturally show lower returns on capital assets. Thus, the indicator under study should only be used for comparison across companies within the same industry.
- Using the indicator to identify companies that intensively use production assets.
Important! Profitability can be used to assess how active a company is:
the lower the indicator under study, the more active the company. An example of such an organization would be an airline
the higher the indicator under study, the less active the company. An example of such an organization would be a software development company.
As a rule, when the return on productive assets is below 5%, the business is considered active.
Indicator value
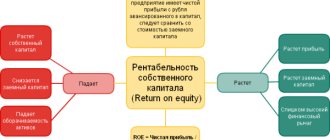
Return on productive assets tells what income was received from productive capital. When using an indicator as a benchmark, it is best to compare it with the company's previous performance or with similar competitors.
The indicator gives investors an idea of how effectively a company converts invested capital into net income.
The higher the ratio, the better, because the company makes more money on less investment.
Ratio Analysis
The return on assets ratio shows how efficiently a company can generate income from its investment in assets. In other words, it reflects how effectively a company can convert money used to purchase productive assets into net income.
Since all productive assets are financed through equity or debt, some investors try to ignore the cost of acquiring such assets when calculating returns by adding interest expense to the formula.
It only makes sense that a higher ratio is beneficial to investors because it shows that the company is managing its productive assets more efficiently to generate a larger amount of net profit.
A positive indicator value usually also indicates an upward trend in profits.
The ratio is most useful for comparing companies in the same industry, since different industries use productive assets differently. For example, construction companies use large, expensive equipment, while development companies use computers and servers.
Overall profitability
This indicator is the most common in determining the profitability of an enterprise and is calculated as the ratio of profit before tax to revenue from the sale of goods, works and services produced by the enterprise.
The indicator shows what part of the sales revenue is profit before tax, is analyzed over time and compared with the industry average values of this indicator.
,Where
Pdn -
profit before tax, Vreal - sales revenue
What is the importance of the indicator?
The indicator formula is an important indicator when analyzing the profitability of a company. This ratio is commonly used when comparing company performance across periods or when comparing two different companies of the same size in an industry.
Important! The size of the business and operations performed should be taken into account when comparing two different firms using the return on assets ratio.
Typically, different industries have different indicators. Industries that are highly capital intensive and require a high cost of fixed assets for operating activities tend to have a lower ratio because their large productive asset base increases the denominator of the formula.
Dynamics of the indicator
The coefficient changes depending on the values in the numerator and denominator of the formula:
- as the amount of net profit increases, the value of profitability increases;
- when the amount of net profit decreases, the value of profitability decreases;
- as production assets grow, their profitability decreases;
- when production assets are reduced, their profitability increases.
Therefore, the profitability of production assets depends directly on net profit and inversely depends on the size of the assets themselves.
Increased profitability means:
- cost reduction;
- increase in product quality;
- increase in profit.
A decrease in fund profitability means:
- fixed and working capital are used ineffectively;
- reduction in product quality;
- increase in cost.
Calculation component: net profit
Net profit is the amount a firm receives after deducting all costs of doing business for a given period, including taxes and interest. The calculation includes all interest paid on debt, income taxes, and all operating and non-operating expenses.
Operating expenses may include cost of goods sold, manufacturing overhead, administrative and marketing costs, and depreciation of equipment and property.
Additional income arising from investments or those transactions that are not directly related to the main activities is also added to net income. Example: proceeds from the sale of equipment or fixed assets.
Net income/loss is found at the bottom of the income statement
How to calculate the percentage of profitability
To assess this indicator, you need to know the digital expression of net profit for a selected time period (most often a year is chosen for analysis), as well as the value of property assets (fixed assets) for the same period.
To calculate what return corresponds to each invested ruble, it is enough to find the ratio of these indicators. Formula for calculating profitability:
R = (PRh / STos) x 100%
Where:
- R – profitability indicator;
- PRch – net profit of the organization for the accounting period (year);
- STos is the cost of fixed assets of the enterprise for the same period.
Both profit and asset value for the formula are taken in monetary terms (in rubles).
Sometimes, instead of net profit, book profit is used. These figures should be taken from the reporting accounting documents, namely:
- balance sheet (form 1);
- report on the financial results of the organization (form 2).
Calculation example
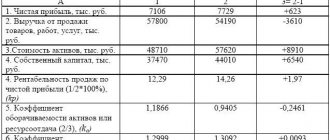
Example No. 1. We use the information from the table below as basic data.
| Index | 2017, t.r. | 2018, t.r. | ||
| beginning of the year | the end of the year | beginning of the year | the end of the year | |
| Fixed assets | 24150 | 28496 | 28496 | 33100 |
| Productive reserves | 12748 | 15466 | 15466 | 17899 |
Net profit data at the end of the year:
- 2017: 56,777 tr;
- 2018: 43544 tr.
We carry out the calculation.
- Let's determine the average annual cost of the company's production assets.
By fixed assets:
2017: (24150+28496) /2 = 26323 tr;
2018: (28496+33100)/2 = 30798 tr.
By reserves:
2017: (12748+15466)/2 = 14107 tr;
2018: (15466+17899)/2 = 16683 tr.
- The table below summarizes the data obtained.
| Index | 2017, t.r. | 2018, t.r. |
| Average annual cost of fixed assets | 26323 | 30798 |
| Average annual inventory value | 14107 | 16683 |
| Net profit | 56777 | 43544 |
- We calculate the profitability ratio of production assets:
2017: 56777/(26323+14107) * 100% = 140.4%
2018: 43544/ (30798+16683)*100% = 91.7%
The presented calculations indicate a downward trend in the profitability of production assets by 48.7%, which is a negative trend and indicates a decrease in the efficiency of assets in the company’s production.
The decrease in the coefficient was due to the following factors:
- a decrease in net profit by 13,233 rubles;
- an increase in the average annual cost of fixed assets by 4475 tr;
- an increase in the average annual value of inventories by 2576 tr.
The following coefficients are used as the main indicators of profitability in modern market conditions at domestic and foreign enterprises, which quite fully characterize the efficiency of the enterprise:
♦ product profitability;
♦ profitability of production;
♦ profitability of sales (sales);
♦ return on equity (capital);
♦ profitability of fixed production assets;
♦ return on assets.
Let us consider the content and methods of calculating these profitability indicators.
Product profitability (or product profitability ) is determined as a percentage as the ratio of the profit received from the sale of the corresponding product to the total costs of its production and sale (i.e., to the total cost of this product).
Depending on the purposes of the calculation, you can calculate the level of profitability of both one product and the entire volume of products sold by the enterprise.
Profitability per unit of production is calculated using the formula:
Ri = (Qi - Si) / Si * 100% (2)
where Ri is the profitability of the product, %;
Qi – product sales price, rub.;
Si – total cost of the product, rub.
The profitability of production volume is determined by the formula:
Rp = (Qp – Sp) / Sp * 100% (3)
where Рп – profitability of production volume, %;
Qп – cost of volume of commercial products (revenue), rub.;
Sp – total cost of commercial products, rub.
Product profitability indicators characterize the profitability of various types of products and the entire volume of production, and thereby not only determine the efficiency of using enterprise resources, but also serve as a starting point in the pricing process.
Production profitability is a relative indicator of the efficiency of using fixed assets and working capital of an enterprise. It shows the degree of overall profitability per 1 ruble of production resource costs.
The overall profitability of production (Ррр) is determined by the following formula:
Rpr =( P / F av + N rev ) * 100% (4)
where P is the total profit of the enterprise, rub.;
F average - average annual cost of fixed production assets (FPF) of the enterprise, rub.;
Nob – average annual working capital standard of the enterprise, rub.
The production profitability indicator more objectively reflects the overall level of efficiency of the production and economic activities of an enterprise than the profitability of individual types of products, goods and services. Production profitability is divided into two types: total profitability, which is calculated as the ratio of total profit to the average annual cost of fixed production assets and working capital, and estimated (or net), determined by the ratio of the enterprise’s net profit to costs.
Profitability of sales or sales is defined as the ratio of profit to the cost of sales volume and shows the percentage of profit from each ruble of sales. This indicator is calculated using the formula:
RPP = PP / V *100% (5)
where PP is profit from sales,
B – sales revenue
Return on equity or capital is calculated as the ratio of the enterprise's net profit to share capital with reserves. This indicator is one of the main criteria for the efficiency of the enterprise for all shareholders and senior management. Return on equity characterizes the upper limit of the potential internal development of an enterprise. A high net profitability ratio is an important incentive to attract new shareholders and increase production volumes.
Return on equity is calculated using the following formula:
RSK = PE / SK * 100% (6)
where PE is the net profit (loss) of the reporting period,
SK - average annual value of equity capital
Note that the reciprocal value, i.e. the ratio of the average amount of equity capital and net profit represents the payback period of equity capital.
An important indicator is also the profitability of fixed production assets, calculated as the ratio of the enterprise's profit to the average annual cost of fixed capital. This indicator serves to compare the efficiency of using fixed capital or production assets in different enterprises of the same industry and (or) the level of profitability of different industries.
In general, the profitability of OPF can be expressed by the formula:
Rf = P/F avg * 100% (7)
where Рф – profitability of OPF, %;
P – total profit of the enterprise, rub.;
F avg – average annual cost of OPF, rub.
The most general assessment of efficiency and profit generation is return on assets (economic profitability). It characterizes the overall level of profit received from the use of all assets of the enterprise, i.e. shows the ratio of total profit to the value of the company's economic resources. This ratio characterizes the ability of an enterprise to make a profit from all the total resources at its disposal.
This indicator is calculated using the formula:
RA = P/A * 100% (8)
where RA is return on assets, %;
P – total or accounting profit (profit before tax), rub.;
A – average cost of all assets used, rub.
Similarly, the profitability of individual groups of enterprise assets can be determined, for example, non-current and current assets, as well as their individual elements (fixed assets, inventories, etc.). When calculating return on assets indicators, along with total profit, the net profit of the enterprise can be used.
Thus, profitability indicators express the ratio of income and expenses of an enterprise in the process of production and sales of products, which ultimately determines the actual effectiveness of the total production and financial activities of the enterprise per unit of expenditure of all economic resources or the achieved rate of profit on all capital (fixed, working and human) . Profitability indicators allow us to judge the economic activity of the enterprise and the possibilities of expanding production using its own savings.
The analysis of the profitability of an organization's activities can be continued with factor analysis, which allows one to determine the reserves for increasing profitability. In this case, you can use the so-called Dupont model.
DuPont's two-factor model (return on assets) is as follows:
The above formula reveals the dependence of the profitability of an organization’s assets on two factors: return on sales and asset turnover. The economic meaning of the connection is that the model directly indicates ways to increase the profitability of assets: when the return on sales is low, it is necessary to strive to accelerate asset turnover, and vice versa.
DuPont's three-factor model (return on equity) is as follows:
As you can see, return on equity depends on three factors: the level of return on sales, the rate of asset turnover and the capital structure of the organization. This directly indicates areas for increasing return on equity. So, for example, from this dependence it follows that, other things being equal, return on equity increases with an increase in the share of borrowed funds in the total capital of the organization (the effect of financial leverage).
FAQ
Question No. 1. How does the profitability of production assets differ from the return on capital?
Answer. Return on equity and operating assets are an indicator of how a company uses its resources. Essentially, the second indicator only measures the company's return on equity, excluding liabilities. Return on production assets takes into account the company's debt, but capital does not. The more leverage and debt a company has, the higher the return on equity relative to the return on productive assets.
Question No. 2. What are the limitations in calculating the indicator?
Answer. The biggest problem with return on assets is that it cannot be used across industries. This is because companies in one industry, such as technology, and another industry, such as oil drillers, will have different asset bases in production.
Some analysts also believe that the basic indicator formula is limited in its applications, being most suitable for banks. Bank balance sheets better reflect the true value of their assets and liabilities because they are reported at market value (through mark-to-market accounting). Interest expenses and interest income have already been included in the financial statements.
Question No. 3. How can I increase this indicator?
Answer. Ways to increase the indicator:
- increase in net profit;
- increase in the value of fixed assets;
- increase in inventory value.
Profitability of fixed assets: formula
All fixed assets of the company are divided into categories of participation in the production process. For example, furniture, office equipment, machinery are operated by the administrative and management apparatus or auxiliary facilities, and machine tools, power machines and equipment are directly involved in the production of the product. Therefore, there is the concept of a company's fixed production assets (FPF). It is their cost that indicates what part of the OS is used by the company when releasing a product or providing a service.
The profitability of fixed production assets is an indicator of the company's profitability from the use of property in the main production process. Limiting the category of general fund and calculating the profitability of these assets allows you to analyze the effectiveness of capital investments in both production and all other categories of the enterprise's fixed assets.
You can calculate the profitability of OPF using a formula similar to calculating the profitability of fixed assets, replacing the indicator of the cost of fixed assets with OPF. It is determined as the arithmetic average of the sum of the cost at the beginning and end of the year, or taking into account the commissioned and liquidated objects according to the second formula. For ease of calculation, the accountant needs to separate the ODA category into a separate analytical group.