Net Assets (NA) is the most important financial figure that every person must know at any time: at 20 years old, at 40 and at 65. This is the only figure for which we work hard all our lives.
And our main financial task in life is to ensure that the average is greater than zero and that it constantly grows.
Why? Read here: The most important number in life that we don’t know!
So, I will tell you about the main ways to increase Net Assets.
“You can't manage what you can't measure!”
Before you start doing anything, you need to know the value of your NA. It is also important to try to set yourself a goal for NA - for a year, for 10 years, for 30 years. Download the Net Assets form here and fill it out. List all your assets, then your debts and calculate the difference. Here is an example of filling out this form:
Digital library
To assess the financial stability and solvency of an organization, modern theory and practice of economic analysis have developed numerous criteria, among which a special place is given to the net asset indicator.
The net asset indicator, widely known in world practice, began to be used to assess the financial condition of Russian organizations relatively recently. The obligatory nature of its calculation was introduced by part one of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, which came into force in 1995, and by a number of other regulations. In the Civil Code this indicator is indicated in Art. 90 and 99, devoted to the procedure for forming and changing the size of the authorized capital of a limited liability company and a joint stock company, respectively. These articles define the requirements for the value of the net asset indicator in comparison with the registered amount of the authorized capital when making various decisions.
The definition of the essence of net assets is reflected in other regulations. In particular, in the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia and the Federal Commission for the Securities Market dated January 29, 2003 No. 10n/03-6/pz “Procedure for assessing the value of net assets of joint-stock companies” under net assets
is understood as “the amount determined by subtracting from the amount of the assets of the joint-stock company accepted for calculation the amount of its liabilities accepted for calculation.” The Methodological Recommendations for conducting an examination of the presence (absence) of signs of fictitious or deliberate bankruptcy, approved by the order of the Federal Service of Russia for Insolvency and Financial Recovery of October 8, 1999 No. 33r, indicated that the value of net assets characterizes the presence of assets that are not encumbered obligations.
Thus, net assets show how much an organization's assets exceed its liabilities (both short-term and long-term), i.e. allow us to assess the level of its solvency. In fact, net assets can be identified with the amount of equity capital, since they reflect the level of security of the funds invested by the owners with the assets of the organization.
Since 1995, this indicator began to be reflected in the financial statements, in particular in Form No. 3 “Report on changes in capital.” The methodology for the formation of net assets (NA) is currently prescribed in the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia and the Federal Commission for the Securities Market and provides for the following calculation based on the Balance Sheet data:
CHA = A – P,
where A, P are, respectively, assets and liabilities taken to calculate net assets.
The value of assets (A) is determined as the sum of non-current assets (line 190 of the Balance Sheet) and current assets (line 290) minus the indicators of the articles “Debt of participants (founders) for contributions to the authorized capital” and “Own shares purchased from shareholders”.
The amount of liabilities (P) is calculated as the sum of the indicators in the articles “Long-term liabilities” (p. 590) and “Short-term liabilities” (p. 690) minus the article “Deferred income” (p. 640).
Methodology for net asset analysis
has the following main directions:
1) analysis of the dynamics of net assets. To do this, it is necessary to calculate their value at the beginning and end of the year, compare the obtained values, and identify the reasons for changes in this indicator;
2) assessment of the reality of the dynamics of net assets, since their significant increase at the end of the year may turn out to be insignificant compared to the growth of total assets. To do this, it is necessary to calculate the ratio of net and total assets at the beginning and end of the year;
1) assessment of the ratio of net assets and authorized capital. Such a study allows us to identify the degree of proximity of an organization to bankruptcy, which is evidenced by the situation when net assets in value are less than (or equal to) the authorized capital. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation establishes that if the value of the company's net assets becomes less than the minimum amount of authorized capital determined by law, then the company is subject to liquidation;
2) assessment of the efficiency of use of net assets. To do this, the following indicators are calculated and analyzed over time:
— net asset turnover (the ratio of sales revenue to the average annual value of net assets);
— return on net assets (the ratio of net profit to the average annual value of net assets).
Let's look at how these areas of net asset analysis are implemented using the reporting data of Progress OJSC as an example. An analysis of the dynamics of net assets is presented in table. 2.15.
Table data 2.15 indicate that at the end of the reporting year, the value of net assets decreased by 13,721 thousand rubles, or 19.27%, and amounted to 57,461 thousand rubles. The negative dynamics of the indicator under consideration is caused by a decrease in both assets taken into account in the calculation of net assets and an increase in liabilities. At the same time, the cost of liabilities increased to a greater extent (by 15.34%) compared to assets (their decrease was 12.51%, or by 11,067 thousand rubles). It is important to note that the decrease in the organization’s assets was caused mainly by a decrease in current assets - inventories (by 8,535 thousand rubles or 35.09%) and accounts receivable (by 285 thousand rubles or 6.5%).
Table 2.15
Dynamics of net assets of Progress OJSC.
| Indicator name | Indicator value, thousand rubles | Deviation (±) | Growth rate, % | |
| for the beginning of the year | at the end of the year | |||
| Intangible assets | 876 | 620 | -256 | 70,78 |
| Fixed assets | 40 830 | 42 834 | +2 004 | 104,91 |
| Construction in progress | 10 645 | 11 615 | +970 | 109,11 |
| Profitable investments in material assets | – | – | – | – |
| Long-term financial investments | 126 | 299 | +173 | 2.4 times |
| Deferred tax assets | – | – | – | – |
| Other noncurrent assets | – | – | – | – |
| Reserves | 24 321 | 15 786 | -8 535 | 64,91 |
| VAT on purchased values | 1 617 | 893 | -724 | 55,23 |
| Accounts receivable (minus debt of participants (founders) for contributions to the authorized capital) | 4 382 | 4 097 | -285 | 93,5 |
| Short-term financial investments | – | – | – | – |
| Cash | 5 686 | 1 272 | -4 414 | 22,37 |
| Other current assets | – | – | – | – |
| Total assets accepted for calculating net assets | 88 483 | 77 416 | -11 067 | 87,49 |
| Credits and loans | 8 521 | 5 233 | -3 288 | 61,41 |
Continuation of Table 2.15
| Deferred tax liabilities | – | – | – | – |
| Accounts payable | 8 780 | 14 722 | +5 942 | 1.68 times |
| Debt to participants (founders for payment of dividends | – | – | – | – |
| Reserves for future expenses | – | – | – | – |
| Other obligations | – | – | – | – |
| Total liabilities accepted for calculating net assets | 17 301 | 19 955 | +2 654 | 115,34 |
| Net asset | 71 182 | 57 461 | -13 721 | 80,73 |
At the same time, there was a decrease in the most liquid assets - cash - by 4,414 thousand.
r., or by 77.63%. The increase in net assets was facilitated by an increase in construction in progress by 970 thousand rubles, fixed assets - by 4.91%, or by 2,004 thousand rubles, long-term financial investments - by 2.4 times, or by 173 thousand rubles. This means that in the reporting year, the company allocated most of the funds received to replenish non-current assets, which negatively affects the organization’s capital turnover.
The management of the organization, in order to avoid freezing of funds, the occurrence of illiquid inventories, and overdue debts, must strengthen control over the status of inventories and settlements with debtors, the feasibility of unfinished construction, and the timeliness of completion of capital work.
An increase in liabilities by 15.34% was caused by a significant (by 5,942 thousand rubles, or 1.68 times) increase in accounts payable, while a simultaneous reduction in the more expensive source of financing activities - loans and borrowings by 3,288 thousand rubles, or by 38.59%.
Thus, the analysis of the factors that caused the decrease in net assets made it possible to see areas that require increased attention from managers.
At the next stages, you should compare the value of net assets with the total assets and authorized capital of the organization (Table 2.16).
Table 2.16
Analysis of the ratio of net assets to total assets and
authorized capital of OJSC "Progress"
| Indicator name | Indicator value | Deviation (±) | |
| for the beginning of the year | at the end of the year | ||
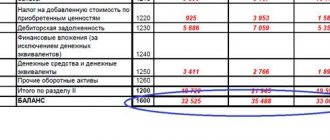
| Net asset value, thousand rubles | 71 182 | 57 461 | -13 721 |
| Value of total assets, thousand rubles | 88 483 | 77 416 | -11 067 |
| Ratio of net assets to total assets | 0,804 | 0,742 | -0,062 |
| Authorized capital, thousand rubles | 26 | 26 | — |
| Ratio of net assets to authorized capital | 2 738 | 2 210 | -28 |
From the data in table. 2.16 shows that the ratio of net assets to total assets at the end of the reporting year is decreasing. In particular, if at the beginning of the analyzed period the share of net assets in total assets was 80.4%, then at the end of the year it was already 74.2%. This is caused (see Table 2.15) by the rapid growth of liabilities compared to the organization’s assets. At the same time, the calculation of the second ratio showed that net assets significantly (221 times at the end of the year) exceed the authorized capital. This circumstance indicates that the analyzed organization has no signs of bankruptcy.
To complete the analysis, it is necessary to evaluate the efficiency of using net assets (Table 2.17). Since the value of net assets should be compared with volumetric (generated during the year) indicators of sales revenue and net profit, then in the calculation it is more correct to use not a fixed value of net assets for a specific date (for example, at the end of the year), but their average annual value, which is the most
in a simple way it can be calculated as the arithmetic mean (one-half of the sum of the values at the beginning and end of the year).
Table 2.17
Analysis of the efficiency of using net assets of Progress OJSC
| Indicator name | Meaning indicator | Deviation (±) | Growth rate, % | |
| for the beginning of the year | at the end of the year | |||
| 1 Average annual value of net assets, thousand rubles. | 71 182 | 57 461 | -13 721 | 80,72 |
| 2 Revenue from sales of goods, products, works, services, thousand rubles. | 42 936 | 41 673 | -1 263 | 97,06 |
| 3 Net profit (loss), thousand rubles. | 4 901 | 2 288 | -2 613 | 46,68 |
| 4 Net asset turnover, turnover (clause 2: i. 1) | 0,603 | 0,725 | 0,122 | 120,23 |
| 5 Duration of net asset turnover, days (360: p. 4) | 597 | 497 | -100 | 83,25 |
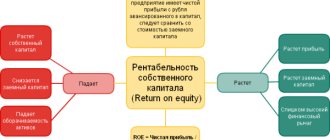
| Return on net assets, % (item 3: item 1) | 6,885 | 3,982 | -2,903 | 57,836 |
Table data 2.17 allows us to see that in the reporting year there is an acceleration of net asset turnover by 100 days, which is caused by a less significant drop in revenue from product sales (by 2.94%) compared to the drop in the average annual value of net assets (by 19.28%). At the same time, return on net assets decreased from 6.885 to 3.982%. In the future, in the course of analyzing the financial results of operations, it is necessary to identify the reasons for the fall in sales revenue and net profit. Summarizing these facts, we can talk about insufficiently efficient use of the organization’s own capital.
In general, an in-depth analysis of net assets allows us to identify ways to increase them, which include:
· improvement of the asset structure;
· selection and use of optimal methods for valuing inventories, calculating depreciation of fixed assets and intangible assets;
· sale or liquidation of property not used in the activities of the enterprise;
· increasing sales volumes by improving product quality, searching for new markets for its sales, and optimizing pricing policy;
· implementing effective control over the status of inventories, accounts receivable and payable, and other assets and liabilities of the organization.
The listed actions provide opportunities for increasing the financial stability and solvency of an economic entity, and its investment attractiveness.
Increase your income
Consider the following ideas:
- Change jobs. You can carefully “test” the market, go through interviews, and understand whether you are in the market. It will not be worse.
— Sell trash and junk that has been cluttering your home for years. Watch how my wife and I do it here.
— Find ideas for extra income. Read: Ideas for extra income or how to make money right now!
— Maybe it’s time to put some of the money that you keep “under your pillow” into a deposit account that will earn money?
— Rent out part of your apartment or a second apartment (if you have one), which you have not rented out until now.
— Rent out your apartment, and move to a rented, cheaper one.
— Look for ideas on freelancer sites and on the Internet (freelancer.ru, fl.ru, youdo.ru, etc.).
Even more ideas here: Extra income ideas or how to make money right now! The highest paying Internet and online professions of the present and future 25 real passive income ideas that you can start today to live and not work tomorrow!
Increasing and decreasing the authorized capital of a joint stock company
An increase in the nominal value of shares, with a constant number of outstanding shares, occurs due to accumulated property in the form of the joint-stock company’s own, or net, assets without attracting additional (new) capital from the market.
Reducing the authorized capital is possible by canceling part of the outstanding shares or by converting shares of a higher par value into shares of a smaller one , i.e. by reducing the par value of the outstanding shares that are in the hands of shareholders.
Reduce expenses
Another way to “earn” more money, available to absolutely everyone, is to save on expenses. “A dollar saved is a dollar earned,” said B. Franklin.
On my website, in the “expense savings” section, you will find hundreds of ideas on how you can save money at home, on the car, while traveling, in banks, in cafes and restaurants, in stores, etc. Find ideas that will work for your family . However, saving is pointless if you don't save the money you save. Remember that money set aside is an asset and it increases your NAV.
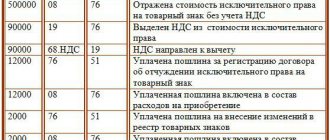
Consequences of replenishing the authorized capital
An increase in the authorized capital for a company can be carried out by making contributions by participants . If we are talking about a joint stock company, then they issue an additional block of shares.
When replenishing the authorized capital of a subsidiary by transferring property to the co-founder organization, the consequences may be as follows:
- there is no VAT on the value of property transferred to replenish the authorized capital;
- VAT, which was accepted for deduction upon the initial purchase of property, will have to be restored;
- There is no need to issue an invoice when adding property to the authorized capital, and the invoice that was received when purchasing the transferred property is recorded in the sales book;
- restored VAT is also not taken into account;
- it is impossible to reduce the tax base of the founder due to the value of the property transferred to the authorized capital.
A legal entity that receives property as a contribution to the authorized capital must also assess the impact of this operation:
- the restored VAT on the transferred asset can be deducted in full;
- the document on the basis of which input VAT is taken into account - this is the act of acceptance and transfer of property indicated in the purchase book;
- if the company is on the simplified tax system, then it does not have the right to increase the value of property by the amount of VAT, and also to take it into account as expenses for tax accounting;
- the value of the property received will not increase the tax base, as will the restored VAT.
It should also be remembered that similar consequences may arise if other methods of increasing net assets are used.
Get rid of “toxic” assets that “eat up” money
They say that in the life of a person who bought a boat, there are two happy moments: the first is when he bought this boat, and the second is when he sold it!