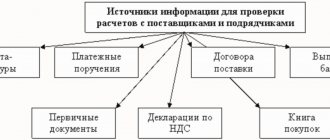
Accounting account 97 is used to reflect summarized information about the amounts of expenses actually incurred in the current reporting period, but relating to future periods. How to account for future expenses and what transactions reflect transactions on account 97 - you will find answers to these questions in our article.
What applies to deferred expenses?
Deferred expenses mean the preparatory costs that an organization incurs to generate income in the future. According to legislative norms, the debit of account 97 can reflect expenses for:
- the right to use intellectual property;
- preparatory work (seasonal, mining, start-up and other expenses);
- loan servicing;
- interest accrued on the bill amount.
The basis for reflecting amounts as deferred expenses are primary documents confirming the receipt of income in the future (contract agreement, license agreement, etc.).
Closing an account and writing off expenses in accounting
It is important to understand how account 26 is closed and what transactions are made. Writing off expenses, that is, closing account 26, is done in several ways:
- Costs are included in the cost of production using production accounts. The method can be used in the production of products.
- Costs are charged to cost of sales. For example, if an economic entity provides services or performs work.
- Expenses are written off as current expenses of the reporting period using the direct costing system.
It is not enough to simply choose a method for writing off OCR. The choice and distribution standards must be fixed in the accounting policies. And the chosen method must be justified.
Typical transactions on how to close account 26:
| Operation | Debit | Credit | Note |
| Write-off reflected at actual cost | 20 23 29 | 26 | If the production activities of an enterprise include auxiliary and service production (shops), then costs should be distributed between the corresponding accounting accounts. Provide information about the distribution method in your accounting policies. |
| Reflected write-off using the direct costing system | 90-2 | 26 | If a company uses the method of forming a reduced cost, or direct costing, then the cost and equipment are written off immediately to the account. 90-2 “Cost of sales”. Fix this decision, how and to what account account 26 is closed, in the accounting policy. |
Typical transactions for account 97
Amounts of expenses of future periods are accumulated according to Dt 97, write-off of expenses and their reduction are reflected according to Kt 97.
Expenses to be reflected in account 97 can be recognized as expenses incurred by the organization for the repair of fixed assets and intangible assets:
| Dt | CT | Description | Document |
| 97 | () | The share of general production (general business) expenses for the repair of fixed assets/intangible equipment as part of deferred expenses | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| 97 | , 69 | The amount of wages and social contributions of workers involved in the repair of fixed assets/intangible equipment as part of deferred expenses | Payroll |
| 97 | 20, | Share of main (auxiliary) production during repair of fixed assets/intangible equipment as part of deferred expenses | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| 20, | 97 | Expenses for repair of OS/intangible equipment as part of production cost | Certificate of completion |
Goods, materials, and finished products can be written off as deferred expenses:
| Dt | CT | Description | Document |
| 97 | 10 | Materials included in deferred expenses | Sales Invoice |
| 97 | 41 | Goods included in deferred expenses | Sales Invoice |
| 97 | GP as part of deferred expenses | Sales Invoice |
Why and how to use the auxiliary account “00” correctly | About banks and finance
Creator: rechargeable. V. Lesina, accountant, for the publication “Practical Accounting”
: July 21, 2014
This article will be necessary for those who are switching to an automated form of accounting, and for those who are engaged in restoring accounting. The message will be sent about why a zero account is needed, how to use it correctly, how to correctly close balances on it, how to find and correct inaccuracies that appear when using the reserve account 00.
First, we note that the auxiliary account 00 is a service account. It is seen only in accounting programs and is recommended for entering opening balances into the program.
At what time do you need to enter opening balances into the program? There are only three such cases:
- the organization is new and you need to enter the first accounting entries;
- the organization is already working, but accounting is done manually (or in a second automated program);
- the organization is already working, but accounting records were not kept and the balances on receipts are little known (the records must be returned).
In the first case, it is not necessary to use account 00. To enter all balances, simple correspondence with accounting receipts is used. But in other cases you will need to use correspondence with a reserve account.
Balance sheet account 00 “Auxiliary account” is energetically passive. The basis for the use of this account, as for other balance sheet receipts, is the principle of double entry. In other words, when entering balances on balance sheet receipts into an automated program, a posting must be made for two receipts.
Let us formulate the main rules for using account 00:
- if the account for which the initial balances are entered is active, then the balance on it is reflected as a debit, and the auxiliary account 00 is entered as a credit and vice versa;
- if the account for which the balances are entered is active-passive, then it is possible to record the balance on it by debit or credit in correspondence with the reserve account 00;
- Balances must be entered as of the last date preceding the start date of accounting. For example, if you need to start work on January 1, 2014, then
All balances should be entered as of December 31, 2013;
- balances on receipts in correspondence with account 00 must be entered in the context of analytical accounts and subaccounts;
- Based on the results of entering the initial balances, you need to organize a balance sheet.
- the organization is new and it is necessary to enter the first accounting entries;
- the organization is already operating, but accounting is done manually (or in another automated program);
- the organization is already operating, but accounting has not been maintained and account balances are unknown (accounting needs to be restored).
You can check the correctness of filling out the balance sheet if you check the amount of balances on all receipts (from 01 to 99) and on the reserve account 00. They must be equal.
We determine the price of liabilities and assets
In order to correctly organize balances according to accounting receipts, you need to make an inventory of liabilities and property as of the date of formation of the initial balances.
We evaluate the authorized capital on the basis of the constituent documents and reflect the amount in account 80 “Authorized capital”. We restore the contributions of the co-founders (financial funds, fixed assets, materials, etc.) on the basis of the relevant documents and reflect them on receipts 01 “Fixed assets”, 50 “Cash”, 10 “Materials” and without that later.
Account 00 is used only in automated accounting programs and is recommended for entering initial balances into the program.
Based on bank details
records and cash book data, it is possible to find out the balance of funds in banks (the opening balance on receipts 51 “Settlement and” Currency 52 “accounts”) and the organization’s cash desk (the opening balance on account 50 “Cashier”). If an organization has a couple of payment receipts, then the balances on bank statements need to be added up.
Indicators on receipts of loans and borrowings 66 “loans and Short-term loans”, 67 “loans and Long-term loans” can be confirmed if you reconcile settlements with creditors and debtors. Along with this, it is necessary to find out these, both by the amount of the principal debt and by the amount of interest accrued at the end of 2013.
The balance values at the end of the day on December 31, 2013 and at the beginning of the day on January 1, 2014 are the same.
Through reconciliation reports, information about the status of settlements with agents is restored. For each agent, receivables and loan debt are generated (receipt balances 60 “Settlements with contractors and suppliers”, 62 “Settlements with customers and buyers”, 76 “Settlements with creditors and various debtors”).
Here is a list of documents with which it will be possible to find out the amount of receivables and loan debt:
Particular attention should be paid to unfinished capital investments. To create balances on account 08 “Investments in non-current assets”, go to raise all documents that are related to unfinished capital investments, summarize all costs and evaluate any unfinished object. Their price can be determined from primary documents.
If, for example, the construction of an object was entrusted to a contractor, a contract agreement, certificates of completed work, and payment orders for payment of their cost are needed. If the construction was carried out independently, then estimates, cash receipts, pay slips, invoices for vacation and purchase of materials will be required.
The inventory is needed to estimate the price of inventories (account 10 “Materials”), work in progress (account 20 “Main production”), finished products (account 43 “Finished products”) and other assets that have not only a cost, but also a quantitative assessment by condition as of January 1, 2014.
Balances of inventories have their own characteristics. Since it is necessary to first calculate the amount of raw materials, goods and materials, and after that the resulting result must be assessed in monetary terms. In a situation where a company stores a pair of homogeneous groups of goods, it is possible to use an average cost estimate. What if the organization has a huge
a nomenclature of various treasures, we suggest using the FIFO method to evaluate them. Note that with this method, raw materials transferred into production and goods shipped are valued at the price of the first ones at the time of acquisition. Accordingly, inventory balances should be valued at the price of the last purchased lots.
Please note: the method you use must be enshrined in the organization's accounting policies.
To apply the FIFO method, you must: count the quantity of goods or materials of a certain type, pick up the latest invoice by date for which this type was purchased.
If the quantity of inventory items is less than the quantity purchased on the invoice or corresponds to it, then the balances can be assessed at the cost mentioned in it.
What if the last time you bought less than what was available, then you also need to pick up the data from the previous invoice.
If the average cost method is used, then you will need to add up the balances on invoices in cost and quantitative terms, find the average unit price and calculate the price of inventory items.
After all balances are posted on receipts, it is necessary to calculate the debit and credit turnover on the reserve account 00, the difference between them should be attributed to account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss).” This procedure is necessary.
If the amount on the credit of account 00 is greater than the amount on the debit, we make a posting:
DEBIT 00 CREDIT 84
– the organization’s retained earnings are reflected as of December 31, 2013;
If the amount on the credit of account 00 is less than the amount on the debit, we make a posting:
DEBIT 84 CREDIT 00
– the uncovered loss of the organization is reflected as of December 31, 2013.
We form initial balances based on receipts
Let's look at an example using the reserve account 00, and provide the documents on the basis of which records are made on receipts.
The date of formation of the initial balances is December 31, 2013.
Stalker LLC is switching to an automated form of accounting from January 1, 2014. At the end of 2013, the inventory working group completed an inventory, which resulted in the assessment of liabilities and assets.
DEBIT 00 CREDIT 80
– 800,000 rub. – the amount of the authorized capital is reflected on the basis of the charter;
– 982,374 rub. – the balance of funds in the current account is reflected based on the bank statement;
– 32,000 rub. – the balance of finished products in the warehouse is reflected on the basis of the inventory inventory;
DEBIT 41 CREDIT 00
– 100,000 rub. – the balance of goods in the warehouse is reflected on the basis of the inventory inventory;
DEBIT 62 CREDIT 00
– 5100 rub. – accounts receivable for goods sold to customers are reflected on the basis of an inventory of settlements with customers;
DEBIT 00 CREDIT 60
– 41,800 rub. – the loan debt for goods taken from the supplier is reflected on the basis of the act of inventory of settlements with suppliers;
DEBIT 00 CREDIT 70
– 83,000 rub. – the loan debt to employees for payment of wages is reflected on the basis of the payroll;
DEBIT 00 CREDIT 69
– 27,000 rub. – the loan debt to extra-budgetary funds is reflected on the basis of calculation in form No. RSV-1 and calculation in form No. 4-FSS;
DEBIT 00 CREDIT 68
– 3800 rub. – the debt to the budget for fees and taxes is reflected on the basis of the reconciliation report.
Now it is necessary to find out the monetary result of Stalker LLC - retained earnings or uncovered losses.
The credit turnover on account 00 is equal to 1,461,654 rubles (287,580 + 4600 + 982,374 + 50,000 + 32,000 + 100,000 + 5100).
The debit turnover for account 00 is equal to 1,051,625 rubles (800,000 + 40,000 + 56,025 + 41,800 + 83,000 + 27,000 + 3800).
In this case, the cash result is retained earnings, which will amount to 410,029 rubles (1,461,654 – 1,051,625) and will be reflected by posting:
DEBIT 00 CREDIT 84
– 410,029 rub. – the organization’s retained earnings are reflected.
What specific inaccuracies appear when entering opening balances?
Inaccuracy when entering balances for fixed assets
For example, the initial price of a fixed asset is 900,000 rubles, and its depreciation is 200,000 rubles.
The accountant needs to make two entries:
DEBIT 01 CREDIT 00
– 900,000 rub. – reflects the initial price of fixed assets;
DEBIT 00 CREDIT 02
– 200,000 rub. – the accrued depreciation of fixed assets is reflected.
Inaccuracy when entering balances on expense receipts
For example, an accountant needed to enter the balance of account 20 “Fixed Assets” in the amount of 78,005 rubles. When entering the initial balances, the following entry was made:
DEBIT 84 CREDIT 20
– 78,005 rub. – reflects the amount of work in progress costs.
How true? Any account for entering initial balances must correspond only with account 00. The accountant needs to make the following entry:
DEBIT 20 CREDIT 00
– 78,005 rub. – reflects the amount of work in progress costs.
Inaccuracy: entry of initial balances is completed, but the balance sheet does not “converge”
First, recall that auxiliary account 00 is a service account. It is found only in accounting programs and is intended to enter opening balances into the program.
When should you enter opening balances into the program? There are only three such cases:
In the first case, you do not need to use account 00. To enter all balances, simple correspondence on accounting accounts is used. But in other cases you will need to use correspondence with a subsidiary account.
Balance sheet account 00 “Auxiliary account” is active-passive. The basis for using this account, as for other balance sheet accounts, is the principle of double entry. That is, when entering balances on balance accounts into an automated program, a posting must be made for two accounts.
Let us formulate the basic rules for using account 00:
- if the account for which the initial balances are entered is active, then the balance on it is reflected as a debit, and the auxiliary account 00 is entered as a credit and vice versa;
- if the account for which the balances are entered is active-passive, then the balance on it can be recorded by debit or credit in correspondence with the auxiliary account 00;
- Balances must be entered as of the last date preceding the start date of accounting. For example, if you need to start work on January 1, 2014, then the opening balances should be entered as of December 31, 2013;
- account balances in correspondence with account 00 must be entered in the context of subaccounts and analytical accounts;
- Based on the results of entering initial balances, it is necessary to create a balance sheet.
The correctness of filling out the balance sheet can be checked by checking the sum of the balances for all accounts (from 01 to 99) and for the auxiliary account 00. They must be equal.
Deferred expenses when obtaining a software license
One of the most common transactions on account 97 is the reflection of deferred expenses associated with the conclusion of license agreements for the use of software.
Let's consider an example: in August 2020, Molniya LLC concluded a license agreement with Computer Service JSC. Under the agreement, Molniya LLC receives the rights to use the software for a period of 3 years. The cost of the contract is a one-time payment in the amount of RUB 342,500.
The following entries were made in the accounting of Molniya LLC:
| Dt | CT | Description | Sum | Document |
| Funds were transferred in favor of Computer Service LLC as payment under the license agreement | RUB 342,500 | Payment order | ||
| 97 | The cost of the contract is included in deferred expenses | RUB 342,500 | License agreement | |
| 012 | The software is accounted for on an off-balance sheet account | RUB 342,500 | License agreement | |
| 20 (, 44…) | 97 | Monthly write-off of expenses for using the software (RUB 342,500 / 36 months) | RUB 9,514 | License agreement |