Hello, Vasily Zhdanov is here, in this article we will look at the retained earnings of an enterprise. It is generally accepted that profit is the financial result achieved by an organization in the corresponding reporting period. It is calculated as the difference between all recognized income and expenses. If the difference turns out to be positive, this will mean the presence of profit (DT90 KT99). A negative difference indicates losses (DT 99 CT 90). At the end of the current year, profit (loss) must be written off to the account. 84 (“NP”), and actually count. 99 is reset to zero and remains “untouched” until the next new year.
Retained earnings (hereinafter abbreviated as NP) is one of the absolute indicators of the effective operation of an organization. In practice, this term is understood as an accounting account. accounting for retained earnings received by an organization for a specific period of its activity.
This account stores the organization’s funds, its total profit accumulated since its formation, which until now has not been distributed in the form of dividends among shareholders. It can increase or decrease. If the account goes negative, then this situation is called a deficit of retained earnings. It indicates that the organization has lost more money than it has received over the entire period of its existence. NP is included in the liability account. balance sheet of the organization, thereby increasing its equity capital.
A clear, simple example of the accumulation of NP. Let’s assume that the organization’s NP is RUR 10 million. rub. During the current period, another 5 million rubles were deposited into the account. rub. Consequently, the amount of NP increased to RUR 15 million. rub. In the subsequent period, if this account is replenished, the value of the NP will increase again and will be different, greater than the previous one.
It follows that for an organization to be successful and grow, it is necessary that it invest NP in its development. In this way, the efficiency of its activities will increase. Money should not just be kept in the organization. They must “work”, be used effectively in order to bring even greater profits. Then they talk about reinvestment, which ultimately leads to an increase in the profitability of the organization.
Calculation of retained earnings based on data from accounting records. balance
All changes that occurred in a specific period with retained earnings are usually recorded in the financial statements. It is formed according to the following conditional scheme.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| First, the IR is displayed at the beginning of the required period | Then the amounts from the funds are added to it | Dividends that need to be paid, as well as amounts transferred to funds, are subtracted from the amount received. | The resulting result is the NP at the end of the period under review |
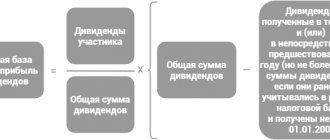
If you have data on NP recorded in the reporting, it is much easier to make any calculations related to it. So, having information about dividends and net profit, you can calculate NP for the current reporting period using the following formula:
Total (cumulative) retained earnings can be calculated by summing two amounts: for the current period and the accumulated amount that is already in the account. Thus, the calculation of NP is quite simple - you only need to collect the required data from the financial statements of the organization.
Account 84 - accounting entries and examples
Accounting account 84 is used to reflect and analyze generalized information about retained earnings (uncovered loss), the amount of which is determined based on the results of the reporting financial year.
Using standard postings and illustrative examples, we will help you understand the specifics of using account 84 and the features of recording transactions with retained earnings. The amount of net profit (loss) is determined based on the results of the reporting year when reforming the balance sheet. When determining profit, its amount is recorded according to Kt 84 in correspondence with Dt 99. If a loss is identified in the reporting year, then its indicator is reflected according to Dt 84.
The amount of net profit on account 84 can be distributed:
The loss, the amount of which is formed on accounting account 84, can be covered from the shareholders’ own funds, as well as from reserve capital:
| Dt | CT | Description |
| 82 | 84 | The loss is covered by the reserve fund |
| 84 | 83 | Profit is used to form additional capital |
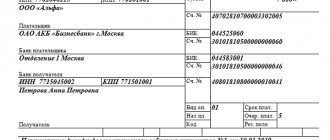
At the end of 2020, JSC Fantasia received a profit of 184,200 rubles. By decision of the board of JSC Fantasia it was established that profits will be distributed as follows:
The accountant of Fantasia JSC made the following entries:
| Dt | CT | Description | Sum | Document |
| 99 | 84.01 Retained earnings | The amount of net profit received by JSC Fantasia is reflected | 184,200 rub. | Profit and Loss Statement |
| 84.01 Retained earnings | 82 | Part of the funds from the amount of retained earnings was used to replenish the reserve fund (RUB 184,200 * 12%) | RUR 22,104 | Minutes of the board's decision |
| 84.01 Retained earnings | 75 | Part of the funds from the amount of retained earnings was used to pay dividends to the shareholders of JSC Fantasia (RUB 184,200 * 65%) | 119.730 rub. | Minutes of the board's decision |
| 84.01 Retained earnings | 84.02 Profits subject to distribution | The balance of funds in the form of retained earnings is reflected in the accounts (184,200 rubles - 22,104 rubles - 119,730 rubles) | RUB 42,366 | Minutes of the board's decision |
According to the accounting policy of Megapolis JSC, one of the sources of capital investment is retained earnings. In January 2016, Megapolis JSC purchased a conveyor machine worth 175,300 rubles, VAT 26,741 rubles.
The following entries were made in the accounting of Megapolis JSC:
| Dt | CT | Description | Sum | Document |
| 08 | 60 | Purchased a conveyor machine (RUB 175,300 - RUB 26,741) | RUR 148,559 | Packing list |
| 19.1 | 60 | The amount of input VAT on the purchased machine is taken into account | RUR 26,741 | Invoice |
| 01 | 08 | The purchased conveyor machine was accepted for accounting | RUR 148,559 | OS commissioning certificate |
| 68 VAT | 19.1 | The amount of input VAT accepted for deduction | RUR 26,741 | Invoice |
| 84.02 | 84.03 | Targeted financing of the cost of the purchased machine has been taken into account (through the use of net profit) | RUR 148,559 | Consignment note, Asset entry certificate, Profit and loss report |
At the end of 2020, JSC Fiesta received losses in the amount of 841,800 rubles. The founders of JSC “Fiesta” are Savelyev R.N. (58% share in the authorized capital) and Markov K.L. (42% share in the authorized capital). By decision of the board it was established that the coverage of losses in 2020 will be carried out at the expense of the founders:
- at the expense of Savelyev - 488,244 rubles. (RUB 841,800 * 58%);
- at Markov’s expense - 353,556 rubles. (RUB 841,800 * 42%).
The protocol of the board’s decision was signed in February 2020. In the same month, funds were received from Savelyev and Markov into the current account of JSC Fiesta.
To reflect operations to cover losses at the expense of the founders’ own funds, the following sub-accounts were opened in the balance sheet of JSC Fiesta:
- 75.1 - Savelyev’s funds aimed at repaying the loss;
- 75.2 — Markov’s funds used to repay the loss.
The following entries were made in the accounting of JSC Fiesta:
| Dt | CT | Description | Sum | Document |
| 75.1 | 84 | Savelyev's debt to repay the loss with his own funds is reflected | RUR 488,244 | Minutes of the board's decision |
| 75.2 | 84 | Markov's debt to repay the loss with his own funds is reflected | RUR 353,556 | Minutes of the board's decision |
| 51 | 75.1 | Funds from Savelyev were credited to repay the 2015 loss | RUR 488,244 | Bank statement |
| 51 | 75.2 | Funds from Savelyev were credited to repay the 2015 loss | RUR 353,556 | Bank statement |
| 99 PNO | 68 Income tax | The amount of permanent tax liability is taken into account (RUB 488,244 * 20%) | RUR 97,649 | Minutes of the board's decision |
Example 1. Calculation of NP for Prospekt LLC (total amount and for the period 2020)
It is necessary to calculate two amounts of NP. First: the size of the NP only for 2020. Second: its total size for the entire existence of Prospect LLC. According to the financial statements of Prospekt LLC:
- At the beginning In 2020, the NP indicator was RUR 120 million. rub.
- During 2020, this account of Prospekt LLC increased by another 10 million. rub.
- In addition, in the same year 2020, the company paid dividends in the amount of RUR 3 million. rub.
First, you need to calculate the value of the NP for 2020: 10 million RUR. rub. – RUR 3 million rub. = 7 million RUR rub. After this, you can calculate its total size as of the end of 2020: RUR 120 million. rub. + 7 million RUR rub. = RUR 127 million rub.
Dividend accounting entries
Accounting support for operations related to the distribution of part of the organization’s net profit between the founders is carried out in the following sequence:
- generation of information on the amount of retained net profit;
- adoption of a decision by the general meeting of owners (shareholders) on the amounts and timing of payments;
- accrual of dividends separately for each participant;
- taxation of amounts;
- dividend payment;
- transfer of taxes;
- writing off unclaimed amounts.
Dividends mean part of the net profit of a legal entity (joint stock companies or LLC), which is the income of the founders (shareholders). They are distributed among the participants in proportion to the shares they own in the company.
The frequency of payments and the amount of retained earnings to be paid to the owners are determined at the general meeting of shareholders (founders of the LLC) and are specified in the organization’s charter.
The payment procedure can be changed: adjustments are registered in the company's Charter and registered with the Federal Tax Service. Based on the results of the meeting, a protocol is drawn up, on the basis of which the distribution of income begins.
Payments can be made quarterly, at the end of six months or at the end of the year.
Note from the author! The maximum period for the distribution of net profit between owners is established by law - no more than 60 days from the date of the decision at the general meeting (the date of the minutes); no more than 10 days for payments to nominee shareholders and trustees and no more than 25 days to the remaining shareholders in the JSC.
Accounting for undistributed net profit is carried out on an accrual basis on the account. 84. It is active-passive: debit balance is the presence of an uncovered loss based on the results of the company’s activities, credit balance is part of the net profit subject to subsequent distribution (after payment of all necessary taxes and contributions).
Basic entries for the accrual and payment of dividends
Accounting for dividend payments depends on the status of the founder:
- The founders of the company are individuals who are employees of the company: mutual settlements on accrued amounts are displayed in the company’s accounting records in correspondence with the account. 70, to which additional accounting can be opened for the distribution of employee payments.
Dt84 Kt70 – calculation of dividends from the company’s net profit.Dt70 Kt50.51 – cash payment or non-cash transfer of funds to the founders.
Note! Monitoring of amounts collected on the account. 70 is carried out separately for each employee of the organization for an in-depth assessment of mutual settlements with personnel.
- The founders of the company are individuals who are not employees of the organization and legal entities: accounting of mutual settlements with owners is carried out on the account. 75, to which a separate active-passive sub-account is opened.
Author's addition! Accounting for mutual settlements on the account. 75 is carried out similarly to the 70 account: data is recorded separately for each participant.Dt84 Kt75.02 – accrual of dividends on the basis of the general meeting of shareholders or founders of the LLC.
Dt75.02 Kt50.51 – payment of accrued amounts.
Taxation of payments
Since dividends represent the income of the founders (individuals and legal entities), these payments are subject to income tax in accordance with current legislation:
- Founders - individuals: personal income tax 13% for citizens of the Russian Federation and 15% on amounts due to foreign citizens.
- Founders are legal entities: amounts are subject to income tax of 13% for companies created in Russia and 15% for dividends of foreign companies.
Note! If an organization is the recipient of a portion of its own dividends, the tax base may be reduced when calculating income tax when the total amount allocated for distribution among the company's participants is reduced. The tax base in this case will be calculated as follows: the amount to be issued minus the amount of dividends received.
Based on the protocol for the distribution of net profit between the participants of a legal entity, it is necessary to immediately calculate taxes, since they are transferred no later than the working day following the payment.
Tax accounting is carried out on the account. 68 for the corresponding subaccounts:
- Dt70 Kt68 – accrual of personal income tax on payments to the founders - employees of the company.
- Dt75 Kt68 – calculation of taxes for the remaining founders.
- Dt68 Kt51 – transfer of taxes to the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
Unclaimed amounts
There are situations when a company participant has not received the amount of dividends due to him on time. He has the right to demand payment within 3 subsequent years (the period can be extended to 5 years, if determined by the Charter of the company) from the date of signing the protocol in joint-stock companies or the completion of the 60-day period after the decision is made in limited liability companies.
If the participant has not claimed these amounts within 3-5 years, then they are transferred to the company’s net profit:
Dt70.75 Kt84.
Case Study
Based on the results of 2020, Compass LLC determined the amount of retained net profit: 100 thousand rubles. At the annual meeting of the founders of the company, the following decision was made: to distribute 60 thousand rubles between 3 founders, 20 thousand rubles each, since they have equal shares in the company. Transfer the remaining amount of funds to the reserve fund.
Note! One of the founders is the general director of the company, and an employment contract has been concluded with him.
Accounting entries for transactions:
- Dt99 Kt84.
100 thousand rubles - the undistributed part of net profit is displayed. - Dt84 Kt75.02.
20 thousand rubles - dividends were accrued for payment to 1 founder.20 thousand rubles - dividends were accrued for payment to the 2nd founder.
- Dt75.02 Kt68.
5,200 rubles – personal income tax is charged, which will be withheld. - Dt84 Kt70.
20 thousand rubles. – payment was accrued to the founder - general director of the company. - Dt70 Kt68.
2,600 rubles – personal income tax is charged, which will be withheld. - Dt84 Kt82.
40 thousand rubles – replenishment of the reserve fund from the company’s net profit. - Dt75.02 Kt51.
34,800 rubles - funds were transferred to the founders. - Dt70 Kt51.
17,400 rubles - the CEO's dividends were transferred to his current bank account. - Dt68 Kt51.
7,800 rubles – tax paid to the Federal Tax Service.
Accounting for dividends by the recipient - a legal entity
Dt76 Kt91 – accrual of payments due (posting date – date of decision on distribution of net profit).
Something to keep in mind! The amounts of dividends due must be reflected minus income tax, which will be withheld by the tax agent organization.
Dt51 Kt76 – actual receipt of funds.
How is profit distributed in an LLC (OJSC) using the simplified tax system and what remains for the NP
Most often, LLCs act as payers of the simplified tax system. The profit for its founders is dividends. According to Art. 28 Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 14 “On LLC” dated 02/08/1998 (as amended on 04/23/2018), available profits can be distributed quarterly or once a year. The procedure for its distribution, as is customary, is fixed in the Charter, and the basis for this is the decision of the founders, which must be recorded at the meeting.
Meanwhile, there are a number of restrictions under which society has no right to make such decisions and share profits. Art. speaks about this. 29 Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 14. Such restrictions, for example, are:
- presence of signs of financial insolvency of the company at the time of making a decision or payment;
- a situation in which the value of a private equity capital is less than its capital and reserve fund or may become less after a decision is made (or due to payment).
LLC participants have the right to make such decisions only after the management capital and the real price of the participant’s share (part thereof) have been paid in full in accordance with Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 14.
If we are talking about the distribution of profit in a joint-stock company using the simplified tax system, then the procedure established by the Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 208 “On Joint-Stock Companies” dated December 26, 1995 (as amended on April 15, 2019) is applied. Payment of dividends to shareholders can be carried out quarterly, half-yearly or at the end of the year. All decisions on payments are made and formalized by shareholders.
There are also restrictions on payments, which are established by Art. 40 Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 208. They are in many ways similar to the prohibitions that are defined for LLCs. Thus, shareholders do not have the right to make decisions (or declare) payments until the management company has paid in full and all available shares have been repurchased (in relation to Article 76 of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 208).
Important! The founders have the right to decide not to distribute all available profits, but only half or part of it. The remaining part remains in retained earnings.
It should be noted that it can be used not only for dividends, but also for other purposes. For example, to pay off past losses, mat. assistance, increase in capital, etc. From among the NPs, the company can form a certain reserve to pay for vacations and a repair fund. But spending NP for purposes not specified in the Charter or other documentation is prohibited.
For those who are simplified when maintaining accounts. and tax accounting, a standard procedure for each situation is established and applied. In the bay. accounting uses the accrual method, and in tax accounting the single tax is determined by the cash method. Moreover, in the latter case, when calculating the tax, only those expenses that are specified in Art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Thus, in the first and second cases, the display of operations will be different. That is why the accounting and tax accounting data will vary based on the results, which, in principle, is accepted as the norm.
Distribution of enterprise profits - what needs to be taken into account?
In the process of profit distribution, not only internal but also external factors are taken into account. For example, the state of the competitive environment may contribute to the need to expand production or create a new product.
For this reason, when generating and distributing profits, the feasibility of transferring money to the following areas is analyzed:
- production development and modernization;
- investment in capital construction and purchase of innovative equipment;
- purchasing raw materials to improve productivity;
- scientific and research activities within the framework of production organization;
- improving the organization of the labor system.
These points are generally interconnected. So, with an increase in production volumes, it will be necessary to improve the organization of labor and introduce work in three shifts, which requires an increase in wages.
Features of displaying retained earnings in accounting. balance using standard situations as an example
NP is displayed in accounting. balance sheet, taking into account all changes that occurred based on the results of each reporting period. This is a cumulative total for the entire existence of the organization. Since today the updated form of accounts is used. balance sheet No. 1 (according to OKUD - 0710001), then the amount of NP is shown on line 1370 (in liabilities). The updated balance sheet was approved and introduced by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 66n dated July 2, 2010. As an illustrative example, let's consider two typical situations related to the calculation and display of accounting income. balance.
Situation 1. Suppose that an LLC using the simplified tax system (6%) received a profit in the total amount of RUR 500,000 during the year of its activities. rub. Consequently, the company must pay tax in the amount of: RUR 500,000. rub. x 6% = 30,000 RUR. rub. Due to the tax paid, the size of the NP for the same year is reduced: RUR 500,000. rub. – RUR 30,000 rub. = RUR 470,000 rub. Thus, in the bay. In the balance sheet on line 1370 (liabilities), at the end of the year under review, retained earnings in the amount of RUR 470,000 should be displayed. rub.
Situation 2. Let’s assume that an LLC on the simplified tax system (15%) was charged 200,000 rubles for the provision of certain services. rub. In addition, he received non-operating income in the amount of RUR 100,000. rub. The total profit of the company by the end of the reporting year amounted to RUR 300,000. rub. During the year under review, there were production expenses (250,000 Russian rubles), as well as expenses that are not taken into account for tax purposes (35,0000 Russian rubles).
The amount of tax payable, taking into account all expenses and profits received for the year, was: (300,000 – 250,000) x 15% = 7,500 RUR. rub. It follows that the NP at the end of the reporting year is 7,500 (300,000 – 250,000 – 35,000 – 7,500). According to page 1370 in the book. the balance sheet will need to show exactly this amount (7,500).
It should be noted that many economists separate NP indicators for the current year and for previous ones. For this purpose, two separate lines are allocated in the ledger. balance. What is noteworthy: NP for previous years can be distributed and divided at any time, and not only at the end of the year. But the distribution of NP for the just past year is possible only taking into account the summed up results of the organization’s activities.
Cumulative and residual profit (loss), procedure for determining residual profit (loss)
The residual profit (loss) of an enterprise is the difference for the analyzed transaction between the total profit and the amount of estimated profit (loss) from sales regarding all parties to the analyzed transaction.
Tax norms establish the current procedure for determining residual profit (loss):
- For each person participating in this analyzed transaction, the estimated profit (loss) is determined based on the existing market price range. In this case, the estimated profit must be calculated under certain conditions, taking into account the following indicators: functions performed by the person, assets used, risks taken - economic and commercial;
- The final stage is to determine the existing difference between the total and estimated sales profit. This profit must concern each of the existing parties to the analyzed transaction.
In cases where organizations or enterprises, the total profit of which is subject to mandatory distribution, maintain appropriate accounting records on existing modern conditions, then the use of the profit distribution method will be possible and legal only after all data has been brought to uniform accounting requirements.
When distributing residual profit between the parties to the analyzed transaction, the final amount of this profit (loss) must be determined by adding the relevant data - estimated profit (loss) and residual profit (loss).
Key differences between retained and net earnings
NP is often confused or completely identified with net profit (NP). Very often you can hear the following phrase: NP is an emergency that was not divided between the founders. What is noteworthy is that both profits are indeed very similar, and, at times, can coincide, and often differ only in the amount of deferred tax liabilities. For comparison, let's look at some of the distinctive features of reproducing them in booze. reporting.
NP is displayed in the account. balance sheet (on p. 1370) and has a value different from net profit. An account with an NP is called active-passive. The amount of NP for a specific period is the profit received throughout the entire period of the company’s existence. Defined as the amount of profit minus taxes. In the bay. the balance sheet displays IR not only for each reporting period, but also in general, for the entire period of existence of the LLC (JSC) on the simplified tax system.
The state of emergency is that part of the profit that remains after paying all obligatory budget payments (fees, taxes, etc.). It is recorded in the financial report (on line 2400) at the end of the year, and is displayed on the CT account. 84 (“NP”). The form of this report is the same as the accounting. balance, approved The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, in particular, by Order No. 66n dated July 2, 2010. The company organizes analytical accounting for it autonomously. The payment of dividends for the year or quarter to the founder-employee can be shown with the following entry: DT 84 CT 70. When directing an emergency to increase the capital, they show: DT 84 CT 80, etc.
Procedure for spending in JSC
Article 67.1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and Article 48 of Federal Law No. 208-FZ establishes that the distribution of profits and losses in a joint-stock company is the prerogative of the general meeting. Additionally, Order No. 12-6/pz-n of the Federal Financial Markets Service of the Russian Federation establishes the obligation to obtain recommendations on the issue of expenditure from the board of directors.
The process of distributing profits and losses of a joint stock company is a right, but not an obligation. This legal position is contained in the Resolution of the FAS VSO dated September 1, 2009, case No. A33-9804/08, the determination of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated December 27, 2007, case No. A40-52516/06-83-327. The company independently formulates the purposes for which the net profit will be used:
- dividend payment;
- replenishment of various company funds;
- increasing the size of the authorized capital;
- technical modernization of production.
When deciding on spending the profit received for the reporting year, it should be taken into account that it can only be used to pay tax deductions and calculate dividends. Any other spending of money is considered unlawful (letter of the Bank of Russia No. 9-E of 2003).
Example 2. Difference between PE and NP
In order to clearly understand the difference between PE and NP, it is proposed based on data from the accounts. reporting of Prospekt LLC to determine the total size of the company’s NP as of the end of 2020.
| Accumulated amount of NP for the entire existence of Prospekt LLC (at the beginning of 2020) | The size of the state of emergency based on the results for the current year 2020. | Total amount of NP at the end of 2020 |
| RUR 400,000 rub. | RUR 200,000 rub. | RUR 400,000 rub. + 200,000 RUR rub. = RUR 600,000 rub. |
What dividends can there be?
For convenience, we have collected all the information in a table:
| By payment method | By payment amount | By payment frequency | By type of shares | |||
| Cash bonuses | Enterprise property | Full | Partial | Quarterly, semi-annual, annual | Regular | Privileged |
| Payments are made in cash equivalent | The organization puts into circulation additional shares through transfer to shareholders | One-time payments | Paid in installments throughout the year | Dividends are distributed by the board of directors | Shares are enshrined in the charter of the enterprise, their profitability is higher and there are advantages in the order in which they are received | |
In what cases can a company not pay dividends?
According to the Law “On Joint Stock Companies”, declared dividends on shares cannot be paid in the following cases:
- the company has signs of bankruptcy;
- the company will go bankrupt when paying these dividends;
- the value of the company's net assets is less than the sum of its authorized capital and reserve fund;
- the value of the company's net assets will become less than the above amount as a result of the payment of dividends.
In fact, all this can be boiled down to one thing - dividends are not paid in the case where the payment will lead to serious consequences for the organization or an increase in the risks of such consequences.
Answers to frequently asked questions
Question No. 1: It is well known that NP may change from one period to another depending on the income received. What else can influence its size?
In fact, there are quite a lot of influencing factors. First of all, these include changes in the size of dividends, net profit, taxes, cost of products sold, as well as administrative expenses.
In practice, a detailed financial analysis is carried out, which shows which factors in a given situation “helped” to make a profit.
Question No. 2 : Are dividends subject to mandatory insurance contributions?
No, they are not taxed, since they are not considered as an employee’s salary. Only income tax is withheld from them.
Are dividends due to the founder of an LLC: posting, payment, accrual, taxes
When registering an LLC, the founders of this company must be approved, who contribute their own funds or materials, equipment, etc. in shares to the authorized capital.
They are prescribed in the Charter of the enterprise and their percentage is determined. According to this contribution, the share of each founder is determined and the profit received as a result of the activities of the LLC is subsequently distributed.
Are dividends due to the founder of an LLC?
The part of the enterprise's profit that must be paid to the founders is called dividends. In 2020, the owners of the enterprise are required to pay dividends. In order for the founders to be able to receive the profit due to them, they must first determine the amount of this profit.
In this case, it is advisable to pay it once a year, after paying all taxes and fees. Since each enterprise has its own nuances in its work, the profit may be uneven quarterly. That is, in the case when the organization’s profit is seasonal, it is possible to receive both profits and losses in different quarters.
The video below will tell you whether the founder of an LLC is entitled to dividends:
How to pay them
In order to pay the money due to two or more founders of the enterprise, it is necessary to draw up a protocol, which will indicate the amount of net profit that is allocated for payment.
This procedure is established by paragraph 6 of Article 37 No. 14-FZ and Article No. 208-FZ.
The law does not establish a special sample protocol, so each organization has the right to develop it independently.
But despite this, the protocol must reflect the following information:
- The period for which the farm's profit will be distributed;
- The amount of profit to be distributed among the founders;
- How the profit will be distributed according to the invested funds;
- Dividend payment terms;
- Methods of issuing profits.
In the case where the organization has only one founder, dividends can be paid without a protocol. Here, Article 39 No. 14-FZ, paragraph 3 of Article No. 208-FZ is included in the work, which allows for independent signing of a decision on the issuance of financial profit.
Step by step procedure
Since the issuance of dividends is not mandatory for the organization, it has the right to independently decide on their payment.
The law does not prohibit making additions and changes to the Charter on the ratio of payments in proportion to the invested funds.
Therefore, most often, company management convenes a general meeting of founders at which a decision on payments is made. At the meeting, a report from the accounting department on the financial situation of the organization is heard.
In addition, accounting documentation and reports must be submitted.
- The general meeting determines the timing of dividend payments and the procedure for distributing profits among the founders.
- After the meeting, the management of the LLC issues an order setting out the essence of the meeting.
By law, dividends must be paid within two months from the date of the decision on payment by the general meeting. If other deadlines were approved, this must be enshrined in the charter.
The payment of dividends to the sole founder of the LLC is described in this video:
Taxation
After the due dividends have been accrued to their legal owners, it will be necessary to withhold personal income tax in favor of the budget. The tax should be:
- accrued at a rate of 13% for taxpayers permanently residing in Russia,
- and at a rate of 15% for all non-residents.
The deadlines for paying personal income tax to the budget are established by law and oblige them to be deducted no later than the next day after the payment of dividends. After taxes have been entered into the budget, the data should be recorded in the quarterly and annual reports (6-NDFL and 2-NDFL).
Accounting entries
Let's consider the situation when dividends are accrued to the founders, what the payers' postings look like:
- D 84 – K 75 – for individuals and legal entities not connected by labor relations with the organization paying them money;
- D 84 – K 70 – for individuals working in an enterprise that pays them dividends;
Calculation of tax subject to withholding on dividends:
- D 75 – K 68 – for legal entities and individuals not working in the organization;
- D 70 – K 68 – for individuals working in an organization.
Dividend payment:
- D 75 – K 51(50) – legal entities and individuals who are not connected by labor relations with the organization paying dividends;
- D 70 – K 51(50) – to individuals who officially take part in the labor activities of the dividend payer’s organization.
Payment of taxes:
- D 68 – K 51 – you need to make a detailed posting for taxes.
After this, you need to write off unpaid and unreceived dividends for previous years to profit:
- D 75 – K 84 – those that were previously taken into account in account 75;
- D 70 – K 84 – respectively, listed on account 70.
And now, accordingly, you should look at what entries are used when calculating dividends from their recipients.
- When a decision is made to pay dividends in accounting, this is reflected by entries D 76 - K 91
- When dividends have already been received by the founders, this is recorded as D 51 - K 76.
Important! For tax accounting, the payment of dividends is recorded based on the actual date of their payment.
Alimony from dividends
- If the founder of an LLC is one person, then he can independently decide whether to receive dividends or not. In the event that a decision is made to receive funds, he is obliged to pay alimony from the money received.
- But if he does not decide to pay dividends to himself, then, accordingly, he will not receive any profit, and, therefore, there is nothing to pay alimony from.
- If a citizen is registered as an individual entrepreneur, then all profits are considered personal income of the individual entrepreneur. Accordingly, alimony is calculated for this amount.
- If the founder is a person who simply invested free funds in the company as shares, this is also considered a source of income. It doesn’t matter whether a citizen is an employee of this organization or not, alimony must be collected from all income received.
How to calculate accruals
You can consider the issue of calculating dividends using a specific example. Let's take the organization StroyServis LLC. Over the past reporting year, the organization earned a profit of 216,400 rubles, which can be distributed among participants according to their share in the authorized capital.
- A.I. Soloviev has a 40% stake in the management company. RUB 86,400 was credited.
- A.L. Olezhko has a 27% stake in the management company. RUB 58,428 accrued.
- D.V. The final share in the management company is 20%. RUR 43,299.8 accrued.
- WELL. Beregovaya – share in the management company 13%. RUB 28,132 accrued.
We calculate personal income tax using the formula: personal income tax = PR start. x%, where PR start. this is the amount of dividends accrued to the shareholder. After calculating and deducting taxes, you can see the final picture of the funds received in your hands:
- A.I. Soloviev - 86,400 rubles accrued. Personal income tax deducted 13% - 11,232 rubles. Total to be issued – RUB 75,168;
- A.L. Olezhko - 58,428 rubles accrued. Personal income tax deducted - 13% in the amount of 7595.6 rubles. Total for issue – 50,832.4 rubles;
- D.V. Nakonechnaya - 43,299.8 rubles accrued. 13% tax has been deducted in the amount of RUB 5,629. To be issued 37,670.8 rubles;
- WELL. Beregovaya - 28,132 rubles accrued. Taxes deducted 13% in the amount of 3657.2 rubles. Total for issue – 24,474.8 rubles.
Important! If you were given dividends in full along with taxes, you must immediately pay them yourself to the state budget. This must be done no later than the next day after the citizen received the funds. This obligation is fixed in Articles 226 and 287 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Otherwise, you can part with a larger amount.
The calculation of dividends to founders in 1C is described in the video below:
Reflection of the indicator of previous years
Retained earnings from previous years are reflected in account 84 in accordance with the above formula. In order to reflect on the balance sheet entries with account 84 for previous years, the accounting entries shown in the table below are used.
As a result of making all the necessary entries at the end of the reporting period, the enterprise’s balance sheet on account 84 displays the total result regarding retained earnings (uncovered loss) for the reporting and all previous periods using the cumulative (accumulative) method. Thus, it is always possible to analyze the activities of the enterprise, the results of which take into account the payment of all mandatory payments and dividends, based on the numerical value of this account.