Personal income tax is a tax established by the legislation of the Russian Federation for individuals. Citizens who receive income as a result of performing labor duties, carrying out business activities, etc., must pay a mandatory state payment to the budget. This type of deduction stands for personal income tax. Let's look at what personal income tax is, at what interest rate it is calculated, and who should make the contributions.
What is personal income tax
Income tax is a mandatory government payment that must be withheld from the individual receiving the profit. Sources of receipt of remuneration from which income tax is levied may be the following:
- earnings received for the performance of duties under a TD or a contract;
- income from business activities (IP on OSNO);
- rental of property;
- sale of property;
- receiving a gift (in cases provided for by law);
- winnings, etc.
That is, in simple words, personal income tax is a tax levied on the income of an individual. In Russia, the income tax rate for the bulk of citizens is 13%. But for a certain category of individuals and for certain types of remuneration, other interest rates are provided. For example, for non-residents deductions are made at a rate of 30%.
Depending on the source of income, the obligation to withhold personal income tax to the budget is determined. If this is remuneration under a TD, then the employer acts as a tax agent, and if the profit is received from the sale of real estate, then the citizen is obliged to report to the Federal Tax Service of Russia by submitting a declaration of income in Form 3 of the personal income tax.
Thus, we can conclude that personal income tax is a type of direct tax, calculated as a percentage of the total income of an individual minus the expenses provided for by law, for a certain period.
https://youtu.be/4xgYdleD03k
An example when personal income tax is not included in expenses
M.V.
Proshkin works at Zvezda LLC. The organization applies a simplified system with the object of taxation being income minus expenses. The employer pays the employee monthly compensation for renting an apartment in the amount of 25,000 rubles. So, on July 27, 2020, the organization transferred 21,750 rubles to his account, and the personal income tax withheld from income in the amount of 3,250 rubles. - to the budget. Payment of compensation for rental housing is not provided for by either the labor or collective agreement. Does Zvezda LLC have the right to reflect these expenses in the tax base? No. As part of labor costs, you can take into account payments provided for by law or labor (collective) agreement (clause 2 of article 346.16 and article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Since compensation for rental housing is not specified in the employment or collective agreement and is not provided for by law, then 21,750 rubles paid to M.V. Proshkin, and 3250 rubles. Personal income taxes transferred to the budget will not affect the tax base of the organization.
“Simplified” must keep separate records of accrued and paid personal income tax amounts. This approach will allow you to avoid writing off unnecessary expenses. After all, employees are often paid income that is subject to personal income tax, but is not taken into account in expenses for the single tax. And since personal income tax is often paid by general payment, you need to track which personal income tax is due on payments included in expenses and which is not.
Where does personal income tax go?
The question arises where the personal income tax withheld from an individual goes, how it is distributed and according to what rules it is spent. There is such a concept - a consolidated budget, which is defined as a set of budgets of three levels:
- federal;
- regional;
- local.
Most of the budget revenues are various types of tax deductions necessary in connection with the expenditures of authorities on the maintenance and improvement of the territory. As for income tax, it is distributed at 2 levels - regional and local. About 85% goes to the treasury of the subject, and the rest to local budgets. The procedure for spending the funds received is determined by the relevant authorities.
What income is subject to personal income tax?
Let's take a closer look at the types of income subject to personal income tax:
- The total profit received under an employment contract. Personal income tax on wages includes such types of remuneration as bonuses, vacation pay, temporary disability benefits, etc. But the legislation defines types of earnings paid by the employer, from which personal income tax is not withheld, for example, a one-time benefit for the birth of a child, financial assistance, within the established limits limit legislation.
- Profit under a contract for the sale of property owned for less than 3 years. But here it is important to consider the method of acquiring ownership of this property. For example, inherited real estate is not subject to income tax when sold.
- Income received by an individual from sources outside the Russian Federation - from foreign companies, through the Central Bank of foreign issuers, etc. This rule applies only to residents of the Russian Federation.
- Earnings from renting out property, including real estate, vehicles, etc. Individuals and individual entrepreneurs are required to declare this type of income independently.
- Winnings of various kinds, prizes for participation in competitions, competitions, etc. But for this type of income, different rates are provided - 13% for winnings received for participation in events that are not advertising and 35% for promotions carried out to advertise goods and services.
- Income from entrepreneurial activities of individual entrepreneurs on OSNO. This does not mean income tax, which is withheld from the earnings of employees, but personal income tax, which is levied on profits from business. That is, an individual entrepreneur without hired personnel is required to deduct this type of tax on income received as a result of his business activities.
We recommend additional reading: Methods and options for reducing personal income tax
When calculating the amount of personal income tax to be withheld, tax deductions may be applied. An individual who is officially employed has the right to apply for personal income tax compensation on each basis through the employer. In this case, income tax from wages will not be withheld until the full amount of the deduction provided has been collected.
List of expenses according to the simplified tax system for 2020 - 2019
Taking into account the requirements of the norms of Ch. 26.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the object for calculating tax under the special regime in question must be determined in one of 2 ways:
- income;
- income minus expenses.
For the first method, the issue of expenses for tax purposes does not matter, but for the second it plays a very important role.
For information on how to change the object of taxation under the simplified system, read the article “The procedure for changing the object of taxation under the simplified taxation system “income””.
Clause 1 Art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation identifies the following expenses under the simplified tax system - income minus expenses:
- costs for the purchase, production and installation of fixed assets;
Read about the procedure for writing off fixed assets for expenses under the simplified tax system.
- costs of purchasing intangible assets;
- costs for the purchase of exclusive rights, know-how, intellectual property;
- costs incurred in obtaining patents;
- costs associated with R&D;
- costs of repairing and improving fixed assets - both own and leased;
- expenses incurred under lease agreements;
- material costs;
- labor costs;
- costs for all types of compulsory insurance (pension, social, medical, life insurance);
- expenses related to payment for services provided by credit institutions;
What services provided by credit institutions can be taken into account in expenses under the simplified tax system, read the article “Accounting (nuances)”.
- costs in the form of input VAT amounts;
Read about the reflection of VAT under the simplified tax system in the material “How to take into account input VAT under the simplified tax system?”.
- costs aimed at paying customs duties;
- expenses associated with business trips (payment for travel to the place of performance of an official assignment and back, payment for accommodation, daily allowance);
- costs of accounting, auditing, legal and other similar services, including accounting services;
Is it possible to take into account consulting costs under the simplified tax system, find out from the material “Consulting costs under the simplified tax system, income minus expenses”
- costs of training and retraining of personnel;
Can participation in a conference be considered expenses for training and retraining of personnel? Find out from the publication “Participation of employees in conferences - an expense under the simplified tax system?”
- stationery costs;
- costs for postal, telephone and other office services.
A detailed list of expenses under the simplified tax system is given in Art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It is closed, that is, other expenses that are not indicated in this list cannot reduce the tax base under the simplified tax system.
To learn about the requirements for expenses taken into account under the simplified tax system, read the article “Accounting for expenses under the simplified tax system with the object “income minus expenses.”
What are the income tax rates?
According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the following personal income tax rates are provided, depending on the type of profit and taxpayer status:
| TAX RATE | TAXPAYER STATUS | TAX RATE | TYPE OF INCOME |
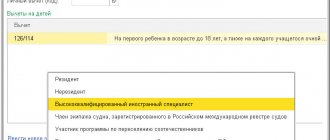
| 13% | Resident of the Russian Federation | 13% | · all types of income of residents, except those to which other rates apply; · remuneration of citizens who are not residents of the Russian Federation, in respect of whom this tax rate is established by law (highly qualified specialists, participants in state programs, refugees, etc.) |
| 30% | Non-resident of the Russian Federation | 30% | all remuneration of non-residents, except those to which different tax rates apply |
| 9% | income on bonds issued before 01/01/2007 | ||
| 15% | for non-residents when receiving dividends from Russian companies | ||
| 35% | · winnings and prizes for participation in promotions; · interest on bank investments, in part of the excess profit limit; · material benefit in the form of savings on interest on loan obligations if the amount established by law is exceeded; · from the use of capital of members of the consumer cooperative |
For tax residents
According to the general rules for calculation, the tax rate is 13%, including for individual entrepreneurs. With the exception of the types of remuneration provided for in Article 224 of the HK RF clause 2 - 35% and clause 5 -9%.
For non-residents
For citizens living in the country for less than six months, income tax in Russia is calculated at a rate of 30%, except for the situations provided for in Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 3. Taxation at a rate of 13% applies to individuals engaged in types of labor activity established by Article 227 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 1).
When personal income tax is considered an expense under the simplified tax system
It is not enough to know whether personal income tax is included in expenses under the simplified tax system. You also need to understand at what point simplifiers can recognize costs. According to paragraph 2 of Art. 346.17, companies using the simplified tax system have the right to recognize expenses only after they have actually been paid. In relation to expenses for personnel wages, the moment of repayment of obligations is considered to be the day the accrued amounts are issued from the cash register or written off from the employer’s current account.
Note! When filling out the KUDiR, taxpayers should separately reflect the amounts for wages minus personal income tax and the amount of transferred personal income tax. If these transactions occurred on the same day, the summation of indicators is allowed.
- How to keep a book of income and expenses under the simplified tax system (sample)?
What tax breaks are there for personal income tax?
Tax legislation provides for the use of several types of tax breaks for citizens:
- exemption from personal income tax for certain categories of remuneration of individuals (in whole or in part);
- application of tax deductions on various grounds;
- reducing the size of the tax base.
Let's take a closer look at the options for reducing income tax:
| Not subject to tax (in whole or in part) | Tax deductions | Reducing the tax base |
| fully: · state capacity; · pension payments; lump-sum benefits from the employer (upon the death of the employee or his close relatives; · scholarships; · material benefits from the sale of the results of the labor of the subsidiary farm; · income of farm members; · profit from the sale of real estate owned for more than 3 years; · inheritance (except for profit from the sale of copyright); · gifts, including property transferred into ownership from close relatives; · prizes for professional athletes; · financial assistance to disabled people paid by public organizations | standard – for children; · property – when purchasing residential real estate using your own funds or borrowed funds; · social – includes personal income tax compensation for training, treatment, voluntary health insurance, payment of contributions for voluntary life insurance or pension insurance, including to non-state pension funds; · professional; · investment | standard deduction for children: 1400 rub. - for the 1st and 2nd child 3000 rub. - 3rd and subsequent 6000 rub. – for a disabled child for guardians and trustees 12000 rub. – parents and adoptive parents for a disabled child; · standard deduction for persons established in Article 218 of the HK RF clause 1 - 3000 rubles (clause 1) and 500 rubles. (item 2); property deduction: when selling residential real estate – 1 million rubles. when selling a vehicle – 250 thousand rubles. |
| partially: · financial assistance, gifts and prizes (over 4 thousand rubles); · one-time benefits for the birth of a child (adoption, registration of guardianship), more than 50,000 rubles; · the amount of contributions to the funded part of the pension, no more than 12 thousand per year |
Fact No. 3 - interest on investment instruments
To ensure a comfortable old age, entrepreneurs invest their free capital in various investment instruments. Profits from them are subject to personal income tax. The tax payment process depends on the type of instrument and the place of registration of the broker:
| Tool type | Russian broker | Foreign broker | |
| Stocks, futures, options | The broker writes off 13% of the profit automatically | Individual entrepreneur pays 13% of profit after filling declaration 3-NDFL | |
| Bonds | Corporate | The broker writes off 13% of the profit automatically | Individual entrepreneur pays 13% of profit after filling declaration 3-NDFL |
| Federal loan | No tax charged | — | |
| Currency | Individual entrepreneurs pay 13% on profits from operations only if the remuneration exceeds 250,000 rubles | ||
As for income received from a bank deposit, it is almost never taxed. There is a special tax of 35% on profits received for residents of the Russian Federation, but in fact it is archaic, since in order to pay it it is necessary to receive a profit equal to the key rate of the Central Bank + 5 percentage points. Over the past 5 years, no bank has offered such high interest rates on deposits.
Who pays the tax
The obligation to withhold personal income tax depends on the source of income. In case of official employment, the employer acts as a tax agent. But in case of failure to fulfill obligations, the employee must independently declare his income.
When selling property, leasing real estate and other cases of acquiring profit, the taxpayer is obliged to deduct personal income tax independently.
How to pay personal income tax
The payment procedure is determined depending on who is responsible for paying income tax. Options for paying personal income tax for a landlord and an individual are different.
If the employer pays income tax
The employer pays personal income tax on a monthly basis when calculating the employee’s wages, except for receiving remuneration in kind. In this case, income tax is withheld upon the first receipt of profit in monetary terms.
When calculating personal income tax, all tax deductions provided to the employee are applied, including the standard one for children. Income tax is deducted at the time of salary payment. By law, the day of accrual of earnings is considered the last day of the month.
The transactions carried out must be reflected in tax reporting forms - 2 personal income tax and 6 personal income tax. Certificates are issued individually for each employee, and the declaration is generated based on generalized information on personnel. The format of personal income tax certificate 2 for the Federal Tax Service and individuals is different.
If an individual pays income tax independently
If an individual or individual entrepreneur needs to pay personal income tax, he or she will need to contact the territorial office of the Federal Tax Service at the place of registration with a certain package of documents.
To pay income tax and receive a deduction, a citizen will need to fill out an income declaration, where it is possible to indicate the required deductions and options for reducing the tax base.
The declaration must be submitted no later than April 30 of the following year, after the tax period in which the profit was made.
For individual applications, there are several options for submitting a declaration:
- through your personal account on the Federal Tax Service website;
- valuable letter with notification;
- by contacting the tax office in person.
How to calculate and pay taxes correctly?
Moscow Accounting offers to try an extremely convenient service - comprehensive outsourcing services for individual entrepreneurs. We will assign you a professional accountant who works in our office. The specialist will calculate taxes and fees, control the document flow, calculate the salaries of your employees, prepare and submit reports to the tax authorities - and all this in remote work mode, without rush jobs and deadlines.
You will save up to 80% on a full-time accountant and protect yourself from financial risks associated with accounting errors. Leave a request and a consultant will call you back within 5 minutes.
Personal income tax payment deadline
The landlord withholds funds from the budget at the time the salary is transferred to the employee. But there are reasons provided for by law when it is impossible to perform the operation. For example, if the income is received in kind. By law, the employer is obliged to notify the Federal Tax Service of the impossibility of transferring income tax to the budget. Company management may encounter a similar situation when gifts were given, the amount of which exceeds 4 thousand rubles, to former employees.
The deadline for individual individuals to submit reports is April 30, and the period for payment of accrued tax is set until July 15.
A citizen has the right to choose the most convenient way for him to repay his debt:
- through the bank's mobile application;
- at a branch of a financial institution;
- online, through the portal gosuslugi.ru.
The law provides for the right to pay tax to another person for his close relative - brother or sister, children, spouse.
What happens if you don't pay income tax?
Evasion of the obligation to deduct income tax may result in liability for both tax agents and individuals who must declare their profits on their own.
Fines
Penalties are:
- from 20% - 40% of the unpaid amount;
- up to 30% - for failure to submit tax reports.
Penalty
One of the recovery options, if income tax has not been deducted, is the additional charge of personal income tax and late fees in the amount of 1/300 of the key annual rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
Criminal liability
This preventive measure threatens malicious defaulters if 10% of the debt exceeds the amount of 900 thousand rubles. for 3 years or unpaid income tax will be over 2.7 million rubles. An individual is subject to a preventive measure by decision of the authorities:
- fine - 300,000 rubles;
- imprisonment for 1 year.