Main points of the document
A responsible person from the technical department of the enterprise is appointed to fill out the form. Information is entered into the document only after reasonable conclusions from experts. They consist of employees approved by order of the head.
The form is issued for each unit of automobile part in a single copy. The card controls the receipt of tires on the balance sheet of the enterprise, operation, and write-off of the resource as unusable. In this regard, the document displays the following information:
- technical characteristics of the part: name of the wheels for which it is intended, number, date of manufacture, manufacturing company;
- data of the vehicle, including the trailer and semi-trailer to which it is attached;
- FULL NAME. and passport details of the driver driving this car;
- monthly mark on the mileage of vehicles and, accordingly, tires. The total mileage is also indicated;
- degree of wear of the part. Here the remaining height of the projector pattern and any defects that have appeared are indicated;
- technical condition of the part. If you install already used tires, their mileage is recorded. A note is also made about existing defects and damage. If the tire needs repair, this information is also entered into the form, indicating the conclusions of the expert commission.
Important! After repair work has been carried out and malfunctions have been eliminated, control of the tire operation continues using the same card.
In case of replacement, the driver is obliged to transfer to the person responsible for filling out the form the data of the decommissioned and installed part. The reason and date of replacement are also indicated here.
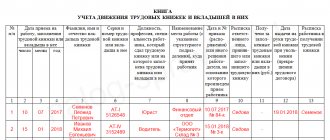
A sample of filling out the form is shown in the photo. The template can be downloaded from the link below.
In what cases is a tire subject to write-off?
Monitoring tire performance helps determine when a tire can be written off. This is done only if it is completely unsuitable for further use.
The reasons and circumstances under which a part must be replaced can be found in the video:
Tire control forms are stored by vehicle number and are closed after the tire is written off.
In this situation, the following information is entered on the accounting form:
- date of removal of the tire from the vehicle;
- full mileage at the time of dismantling;
- description of the reason for withdrawal;
- tread wear and residual height;
- further movement of the part. Here it is necessary to indicate whether it is subject to repair or restoration, whether the tread pattern will be deepened, or whether the tire is subject to disposal.
- conclusions of the commission.
After entering information into the forms, the form is signed by all members of the expert group. This is considered an act of decommissioning the tire from further use.
If the part was sent for impersonal cutting, after repair work a new form is created.
If the tire tread has been deepened, further mileage is recorded on the old card.
Important! High mileage of a tire is not considered a reason to write it off if other technical characteristics are within normal limits.
A tire record card allows you to monitor their technical condition. Thanks to this, it is possible to identify emerging defects in a timely manner and restore or replace a part if it is unsuitable.
Blanker.ru
When a tire is removed from service, its full mileage, technical condition, and where the tire is sent (for repair, for refurbishment, or for scrap) are recorded in the “Reasons for removing the tire from service” column of the registration card. When a tire is sent for restoration or scrap, the accounting card is signed by the chairman of the commission (chief engineer or head of the enterprise) and members of the commission.
In this case, the accounting card is an act of writing off the tire and the basis for resolving the issue of paying the driver a reward for returning the tire for restoration and mileage in excess of the norm or taking measures for undermileage in accordance with the regulations in force in the organization.
Our vehicles received after restoration are given new cards to record their work. To determine the mileage of tires on personal vehicles, car owners are recommended to record the speedometer readings when removing from service and installing new and retreaded tires.
For tires supplied to a motor transport enterprise together with overhauled (restored) cars, as well as with cars that have been in operation or received free of charge, tire operation cards are opened on the basis of data from acceptance certificates of fixed assets, which list with the percentage of suitability (wear) all tires installed on the car (in 2004.
Forms of acts OS-1 and OS-2, approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the USSR dated December 28, 1989 No. 241, and from January 1, 2005, forms OS-1 and OS-3, approved by Decree of the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Belarus dated December 8, 2003 No. 168, can be used). 03/29/2005 Vladimir Suzansky, auditor, “Chief Accountant” magazine.
Transport" No. 2, 2005
Tires are replaced or the cost of their under-mileage is paid during the warranty period of storage and operation. 3. The warranty period for storage and operation of tires retreaded in the first and second classes is 1.5 years; tires retreaded according to class “D” – 1 year.
Free repairs or payment for under-mileage of retreaded tires are made within 1.5 years from the date of retreading or within 1 year for tires retreaded according to class “D”. 4. The warranty operating time of tires that have undergone repair of local damage must correspond to the values indicated in the table. 2.
We suggest you read: How to hire an employee and avoid mistakes
Table 2 Type and purpose of tires Warranty operating time of tires, thousand km I type of repair II type of repair 1. Bias tires 1.1. For passenger cars 4.5 1.2. For trucks with a carrying capacity of up to 2 tons and minibuses 4.5 1.3.
PBU 10/99 “Expenses of the Organization” expenses are recognized in accounting if the following conditions are met: • the expense is made in accordance with a specific agreement, the requirements of laws and regulations, and business customs;
• the amount of expenditure can be determined; • there is confidence that as a result of a particular transaction there will be a decrease in the economic benefits of the organization. This certainty exists when the entity has transferred the asset or there is no uncertainty about the transfer of the asset.
In addition, the replacement of tires purchased instead of unsuitable tires supplied as part of the car can be considered a repair of the car, therefore, based on clause 27 of PBU 6/01, expenses are recognized in the reporting period in which the repair is completed. Based on the above, the use of this tire accounting option can be considered justified.
How to fill out a car tire registration card
Before installation, the battery is assigned a number corresponding to the garage number of the vehicle.
When installing a battery on a car, the following information is recorded in the card:
- name of company;
- battery type and garage number;
- manufacturer and date of manufacture of the battery;
- date of installation of the battery on the car;
- car make, garage number and state number;
- speedometer readings, or vehicle mileage.
The battery operation accounting card is kept by the employee responsible for accounting for the battery operation and serves as the main document for determining the operating time of the battery, its suitability, filing a complaint, write-off, etc.
The operating time in the battery operation record card is entered from the waybills as necessary (subclause 11.4 clause 11 of TKP 298-2011 (02190)).
The battery is written off by a commission appointed by order of the organization.
“card n __ tire operation accounting” (form n 424-apk)
When replacing the tire on the road wheels with a spare or, if necessary, a purchased tire, the driver is required to provide the date of replacement, the serial or garage number of the replaced tire, and the speedometer readings at the time of installation and removal of the spare tire. This data is recorded in the work record card. It is prohibited to determine the mileage of each tire by dividing the total mileage of the road wheel tires by the number of all tires on the vehicle (including the spare), as this leads to the accrual of mileage for the inoperative spare tire and incorrect determination of the actual mileage of each tire. To correctly record the mileage of tires, the employee responsible for recording tires must quarterly and selectively check, using serial numbers, the compliance of the tires actually used on the vehicle with the tires assigned to the vehicle according to the registration cards.
How to fill out a car tire registration card
With regard to their operational mileage, the regulations of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation, set out in Letter No. 03-01/10-2830sh dated 08/24/2012, apply.
Thus, according to the letter, the norms are determined (form n 424-apk)
Seasonal tires that have been removed from a vehicle and put into storage are neither unused material nor returnable waste. On the one hand, they were already in operation (were used), and on the other hand, they did not lose their consumer properties.
Accounting for wear and replacement of car tires
It is allowed to consider the replacement of unusable (worn out) specified spare parts as part of the repair. Then you should write off production costs and expenses for repairing the fixed asset. Costs associated with repairs are displayed by the accounting department using DT accounts for recording expenses for production (sales), CT accounts for accounting for expenses incurred. Thus, DT 20, 26, 44, KT 10, subaccount “Tire in the sub-account” reflects the inclusion of the price of seasonal vehicle spare parts in expenses for normal activities after their wear.
Worn-out automobile parts that are subject to modernization, repair, or reconstruction are included in the warehouse. Their accounting is kept in the subaccount “Tires subject to restoration”, “Materials sent for recycling”. The price is displayed as follows: DT 10, subaccount “Tire for restoration”, KT 91-1.
Changing seasonal vehicle tires is an integral part of the maintenance of a fixed asset, aimed at maintaining the characteristics of the vehicle in proper condition. The costs associated with this are recognized as expenses in the ordinary course of business. Their accounting department displays DT accounts for production (sales) expenses and CT accounts for production expenses (related to service costs).
But when replacing seasonal spare parts and sending them to the warehouse, their price is related to the reduction of expenses for current activities: DT 20 (26, 44), CT 10, subaccount “Tires in subaccount”. To display the replacement of summer and winter vehicle tires, account assignments are used for account 10. For example, when assembling winter tires, the price of vehicle tires put into use is displayed as follows: DT 10, subaccount “Tire in subaccount”, CT 10, subaccount “Spare tire”.
At the end of the season, winter parts are removed and summer parts are assembled. To display the price of the removed winter version, account assignment is used: DT 10, subaccount “Spare tire”, KT 10 “Tire in subaccount”. The price of the assembled summer version instead of the winter one will be displayed by account assignment: DT 10, subaccount “Tire in subaccount”, KT 10, subaccount “Spare tire”.
Filling out a car tire registration card
When developing these rules, institutions can use the basic provisions for recording car tires set out in Rules N AE 001-04, or develop them independently. Therefore, the organization of accounting for car tires will depend on the methodology approved by the institution.
If an institution does not bother itself with developing independent rules for recording car tires, but uses the provisions of Rules N AE 001-04, it would be useful to recall their main points.
These Rules indicate that institutions must create a card for recording its operation for each tire installed on a vehicle (new, reconditioned or with an in-depth tread pattern) when it is equipped or during operation.
“card n __ tire operation accounting” (form n 424-apk)
When a tire is removed from service, the card indicates: the date of dismantling, the total mileage, the name of the reason for removal, determined by the commission, the remaining tread height (according to the greatest wear), where the tire is sent - for repair, for restoration, for deepening the tread pattern by cutting, for scrap or complaint. When a tire is sent for restoration, deepening of the tread pattern or scrap, the registration card is signed by the members of the commission. In this case, it is an act of writing off a tire. Tires received after retreading are issued with new performance cards. The mileage of a tire with an in-depth tread pattern begins from scratch in the previously created accounting card, and with impersonal cutting, a new card is created. Card N for recording the operation of tires in the form 424-APK is used to register the movement of automobile tires in operation (located on the running wheels of the car and on the spare wheel) in order to make the most complete use of their resource. It is started in one copy by the technical service of the organization's motor transport division for each tire installed on the car (new, reconditioned or with an in-depth tread pattern) when it is equipped or during operation. Continues until the tire fails. Each car tire in use is assigned to a car, trailer, semi-trailer and the drivers working on them. This information is recorded on the card. Tires are recorded by the names of the car wheels (records are made in abbreviated form), serial numbers, date of manufacture and tire manufacturer.
Sample of filling out a car tire operation registration card
The tire number must be unique for its further accurate identification during accounting.
If the tire does not have a number, then it is necessary to number it, for example, by painting a number on the inside of the tire.
The most common question that arises when accepting a tire for registration is where to get information about the tire mileage rate? Tire mileage standards are specified in the document “Temporary standards for the operational mileage of vehicle tires” (RD 3112199-1085-02), but this document has become invalid since 01/01/2007.
Therefore, it is currently proposed to use the following scheme for determining the standard tire mileage: calculate the average mileage of the tire over the last 2 years of operation and take this value as the standard.
An example of filling out a car tire registration card
The guaranteed operating time of tires with adjustable pressure (GOST 13298) within the warranty storage period must correspond to the values indicated in Table 1 (except for the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation).
Table 1 WARRANTY OPERATION TIME OF TRUCK TIRES WITH ADJUSTABLE AIR PRESSURE Tire designation Ply standard Warranty operating time of tires, km 12.00-18 13.00-18 12.00-20 14.00-20 16.00-20 1200×50 0-508 1220×400-533 1300×530-535 1500×600-635 1500×600-635 1600×600-685 Notes. a) Tires that fail due to manufacturing defects with a mileage of up to 6 thousand km, and tires 12.00-20 - up to 10 thousand km, are exchanged by the manufacturer free of charge. b) With a mileage of more than 6 thousand.
Debit account 1 (2) 105 06 340 “Increase in the cost of other inventories”
Account credit 1 (2) 106 04 440 “Reducing the cost of manufacturing materials, finished products (work, services).”
Payment of expenses is reflected as follows:
Debit account 1 (2) 302 00 000 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”
Credit accounts 1 304 05 000 “Settlements for payments from the budget with bodies organizing budget execution”, 2 201 01 610 “Disposal of institution funds from bank accounts”.
Why can’t car tires be considered as fixed assets in this case, since their service life exceeds 12 months? Since they are purchased to repair vehicles that already had tires in the first place, this allows them to qualify as inventory regardless of their useful life. Yes and p.
- destruction of a production or operational nature, excluding the possibility of restoration repairs.
The application of these standards is mandatory for organizations regardless of their legal form.
Operating mileage standards for vehicle tires are established on the basis of the average mileage of tires taken out of service for each size and model of tire, as well as each modification of vehicles in use and correspond to certain operating conditions of motor vehicles.
For automobile tires used on trailers and semi-trailers, operating mileage standards are established as for tractor-trailers.
In addition, correction factors are applied to the average tire mileage, taking into account road traffic and other operational factors.
Abstract for one topic: Car tire accounting - 2020
When determining the accounting procedure for car tires, it is necessary to select sub-accounts opened for account 10 “Materials”. These may be subaccounts “Spare parts” or “Other materials”. In some cases, the cost of tires is included in the initial cost of the vehicle. In addition, the accountant must take into account the specifics of tire operation: replacement of worn tires, seasonal replacement, etc.
Our experts have prepared a special selection that will help an accountant work with these issues correctly.
Tire accounting / “Chief Accountant” No. 31-2018
The organization carries out transportation with its own transport only for its own needs on the territory of the Republic of Belarus.
Is the organization obliged to keep car tire registration cards?
Three rules for accounting for car tires / News 07/13/2018
When determining the accounting procedure for car tires, it is necessary to select sub-accounts opened for account 10 “Materials”. These may be subaccounts “Spare parts” or “Other materials”. In some cases, the cost of tires is included in the initial cost of the vehicle. In addition, the accountant must take into account the specifics of tire operation: replacement of worn tires, seasonal replacement, etc.
Options for accounting for costs of repairing car tires / “Chief Accountant” No. 30-2018
It is assumed that the tire will be used until its service life expires - the actual total mileage in kilometers from the start of its operation until the wear limit. In practice, this does not always happen: defects form prematurely, due to which the tires are subject to local repair, retreading, or scrapping. Let's consider how to take into account the costs that arise.
Maintenance and repair of tires: documentation, write-off of tires / “Chief Accountant” No. 25-2018
The result of tire operation is natural wear of the tread and rubber aging defects as their operating time and operating time increase.
Tires taken out of service due to technical condition can be divided into 3 groups:
- 1) requiring local repairs;
- 2) requiring restoration repairs;
- 3) subject to write-off and disposal.
Taking this into account, we will consider the features of documenting the operational stages of tires and their write-off.
Why is it necessary to set operational standards for tire mileage? Rules for filling out tire mileage cards / “Chief Accountant” No. 23-2018
Tire accounting has its own characteristics. This is due to the seasonality of tire use, the need to monitor their mileage and other individual characteristics. Information on tire operation is recorded on special cards. What are the requirements for filling them out and why the established rules must be followed, the author of the article explains.
Comment (Compensation rates for 2020 have been established in relation to waste of goods and packaging waste, and from April 1, 2020, the fees for manufacturers and suppliers of batteries will change) / “Chief Accountant” No. 1-2018
By Decree of the Council of Ministers of the Republic of Belarus dated December 12, 2017 No. 954 (hereinafter referred to as Resolution No. 954):
- the general amounts of funds spent on measures to ensure the collection, disposal and (or) use of waste in 2020 have been established;
- the amount of compensation for waste collection costs for 2018 has been established;
- The fees paid by manufacturers and suppliers to the account of the State Institution “Operator of Secondary Material Resources” (hereinafter referred to as the operator) for the production and import of certain goods have been changed.
Let's look at the changes made in more detail.
Check the correctness of filling out the report on fulfillment of the duties provided for by Decree No. 313* / “Chief Accountant” No. 28-2018
July 22, 2020 is the last day when organizations should have provided information on fulfilling the obligation to collect, neutralize and (or) use waste goods and packaging waste under Decree No. 313 for the second quarter of 2020 (hereinafter referred to as the report).
In the previous issue of the magazine (see “GB”, 2020, No. 27, p. 73) |*| we talked about how the Operator** monitors the fulfillment of the obligation to collect waste goods and packaging. Let us recall that the main method of control is a comparison of the information presented in the report with the information that is provided to the Operator by the State Customs Committee and other organizations.
In this publication, we will look at what information in the report is subject to control by the Operator and what the completed report for the second quarter of 2020 should look like.
There is an opportunity to quickly correct mistakes without any significant financial losses.
Sample car tire performance record card
Important: All fields on the card must be filled in, and further entries must be made before the tire fails. It provides information such as the technical condition of the tire on the vehicle (for example, defects, nature and extent of damage). For used tires, when installed on another vehicle, their previous mileage is recorded. In case of work to repair local damage, the tire operation continues to be recorded in the same card. In addition, the person responsible for recording car tires must enter data on the actual mileage into the tire operation card on a monthly basis.
When replacing a tire on the road wheels with a spare one or, if necessary, a purchased tire, the driver informs the person in charge of the date of replacement, the serial number of the replaced tire, and the speedometer readings at the time of installation.
Tire mileage card sample
The main purpose of the registration card is to document the movement of tires in use from the time they are assembled until they completely fail. The card contains the following information:
- date of manufacture, manufacturer, price, as well as the name of the wheels and serial number;
- technical condition (existing defects, damage);
- mileage (the previous one is for used tires, and the actual mileage for each month is for all types of tires);
- date of tire replacement, numbers of removed and reassembled tires;
- dismantling time, total mileage, tread pattern data, for what purpose and for what reason it was taken out of service (in case of deregistration of the tire).
The specified standard accounting forms are filled out completely and stored according to vehicle numbers, and are closed when the spare part is sent for disposal.
Attention
Testing of temporary tire mileage standards is carried out by the Federal State Unitary Enterprise NIIAT with the involvement of motor transport enterprises.
Accounting for expenses for the purchase of car tires Accounting for expenses for the purchase of car tires has its own characteristics.
https://youtu.be/5HE07D4sNEI
The order in which they are reflected in the accounting registers depends on how they are received by the institution. If car tires come with a new car, then their cost is taken into account in the cost of this car as an item of fixed assets. This conclusion can be drawn from the provisions of paragraph.
Sample car tire performance record card sample filling
If the tire needs repair, this information is also entered into the form, indicating the conclusions of the expert commission. Important! After repair work has been carried out and malfunctions have been eliminated, control of the tire operation continues using the same card.
In case of replacement, the driver is obliged to transfer to the person responsible for filling out the form the data of the decommissioned and installed part. The reason and date of replacement are also indicated here.
A sample of filling out the form is shown in the photo. The template can be downloaded from the link below.
Monitoring tire performance helps determine when a tire can be written off.
Car tire operation registration card sample filling
InfoThe norm must be updated every 2 years.
When calculating the average mileage of a tire, factors such as: • road category should be taken into account; • type of road surface on which the vehicle is operated; • type of vehicle, etc. A more complete list of correction factors is set out in paragraphs 7-8 of the document “Temporary standards for the operational mileage of vehicle tires” (RD 3112199-1085-02).
When registering a tire for the first time, you can be guided by the vehicle’s operating instructions, which indicate the recommended mileage standards for tires intended for this vehicle. When maintaining a tire registration card, you should enter data on the mileage traveled by the tire.
Mileage is determined from the waybills issued for the vehicle.
Standards for using car tires
Based on the norms provided for by Federal Law No. 196-FZ of December 10, 1995 (Article 19), it is prohibited to operate vehicles with technical defects, as this may lead to a threat to road safety.
This list of faults is determined by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 23, 1993 No. 1090. This list includes the following damages specified for car tires, in the presence of which the tires cannot be used:
- The tire tread is worn off, i.e. The tread pattern has a height below the norm: for passenger cars the norm is 1.6 mm, for trucks the tread height should not be lower than 1 mm, for buses – 2 mm.
- The tire has significant damage in the form of holes, cuts, breaks that expose the cord. Such faults include a delaminated tire carcass and a peeled tread or sidewall of the tire.
- Lack of fasteners (bolts, nuts), broken shape of mounting holes or change in size.
- The presence of various cracks on the disk and wheel rims.
- The tire mileage has exceeded the standard number of kilometers or the tire service life established by law has expired.
The presence of the above damage is grounds for writing off car tires, since they cannot be used with such damage. Therefore, new tires must be installed on vehicles.
The write-off of tires unsuitable for use must be reflected in the accounting documents. There is currently no legislation that would regulate the decommissioning of tires. As a result, organizations have to either follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the use of tires, or determine the service life of the tires themselves based on their condition and suitability for use.
Important! Using tires that have become unusable due to damage is dangerous! This may result in a traffic accident. A worn-out tread surface leads to deterioration in vehicle control, and an exposed cord can cause the rubber to rupture, which leads to a complete loss of vehicle control and an accident.
Tires subject to write-off must be recycled. To do this, a certain form of agreement is concluded with the organization that accepts tires for recycling and then transports the written-off rubber to a tire repair plant for processing.
Card for recording the operation of a car tire; sample filling in the budget
The institution has the right to develop the form of this document independently or use the one given in Appendix 12 to Rules No. AE 001-04.
For a sample of the recommended form of a car tire performance record card (new, retreaded, resurfaced, used), see the end of the article.
These cards serve as the basis for the formation of primary accounting documents on the movement of car tires in the institution and the corresponding entries in the accounting accounts.
Accounting for seasonal car tires (Korshunova N.)
Instructions No. 25n Receipt, operation and disposal are recorded by drawing up a card for recording the operation of a car tire. This control method allows you to determine the entire range of application and use of the resource. Example of drawing up a card The document reflects data on each unit of car tire, and also indicates which vehicle it is assigned to. For monthly control of operation, notes on the vehicle's mileage are made in the accounting card. In this way, the technical condition of the resource is monitored and it is determined whether further use of the tires is possible.
Card for recording the operation of a car tire in the Republic of Belarus sample filling
Under the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, such expenses are recognized in the reporting (tax) period in which they were incurred in the amount of actual expenses.
When purchasing seasonal tires (for example, winter) to complete a car purchased with seasonal tires (for example, with summer), an institution can consider expenses as costs for the maintenance and operation of fixed assets and account for them as material expenses in accordance with paragraphs. 2 p. 1 art. 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: for the purchase of materials used for other production and economic needs (testing, control, maintenance, operation of fixed assets and other similar purposes). The date of material expenses in terms of materials is the date of their transfer to production (clause 2 of Art.
RD 3112199-1082-02.
The tire mileage rate (Hi) is calculated by multiplying the average tire mileage by correction factors:
Hi = H x K1 x K2,
where H is the average tire mileage, thousand km;
K1 – correction factor taking into account the category of operating conditions of the vehicle;
K2 is a correction factor that takes into account the operating conditions of the vehicle.
In this case, the standard tire mileage should not be lower than 25% of the average tire mileage.
For new models of tires and new brands of cars for which tire mileage standards have not been established, the head of the institution has the right to introduce, by order of the enterprise, a temporary standard based on the average mileage of scrapped tires, agreed with the Federal State Unitary Enterprise NIIAT.
BC RF).
As for budgetary and autonomous institutions, they have the right to engage in other types of activities only insofar as this serves to achieve the goals for which they were created, and these types of activities correspond to these goals, provided that such activities are indicated in their constituent documents (charters) (Clause 4, Article 9.2 of the Federal Law of January 12, 1996 No. 7-FZ, Clause 7 of Article 4 of the Federal Law of November 3, 2006 No. 174-FZ).
State institutions are required to send funds received from such activities to the appropriate budget of the budget system of the Russian Federation (Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But budgetary and autonomous institutions have the right to dispose of them independently (clause 3 of article 298 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, clause 8 of article 2 of Federal Law No. 174-FZ).
The budgetary cultural institution wrote off 4 car tires that had become unusable from off-balance sheet accounting. in the amount of 6,000 rubles.
In the winter of this year, Avtodor LLC purchased a passenger car with a winter set of tires. The car is used for administrative purposes. In October of the same year, a set of summer tires (4 pieces) was purchased for 9,440 rubles, including VAT 18% - 1,440 rubles, and installed on the car.
Who keeps the tire log?
The following accounting entries were made in the accounting records of Avtodor LLC: Debit 10 “Materials” subaccount 5 “Spare parts” Credit 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” - 8,000 rubles.
— a set of summer tires was received at the warehouse; Debit 19 “VAT on purchased assets” Credit 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” - 1440 rubles. — the amount of “input” VAT is reflected; Debit 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”, subaccount “VAT” Credit 19 “VAT on acquired values” - 1440 rubles.
— the amount of “input” VAT is presented for tax deduction; Debit 26 “General business expenses” Credit 10 “Materials” subaccount 5 “Spare parts” - 8000 rub. — tires are installed on a passenger car.
Seasonal tires that were removed from the vehicle due to the change of season must be entered into the warehouse. The procedure for recording such transactions is not provided for by accounting regulations.
23 journal of registration and write-off of tires
Enterprises that have motor vehicles on their books must keep records of all consumables necessary for the operation and maintenance of the proper technical condition of the transport. One type of accounting is monitoring the movement of car tires.
Receipt, operation and disposal are recorded by drawing up a card for recording the operation of a car tire. This control method allows you to determine the entire range of application and use of the resource. The document reflects data on each unit of car tire, and also indicates which vehicle it is assigned to.
For monthly control of operation, notes on the vehicle's mileage are made in the accounting card.
In this way, the technical condition of the resource is monitored and it is determined whether further use of the tires is possible.
Accounting for car tires in a government agency
As a result, a taxable temporary difference arises in the amount of 3,600 rubles, on the basis of which a deferred tax liability is formed: Debit 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” subaccount “Calculations for income tax” Credit 77 “Deferred tax liability” - 960 rubles. (RUB 4,800 x 20%) - a deferred tax liability has been formed.
Tire accounting
The cost of tires returned to the warehouse is calculated using the formula: Cost of tires returned to the warehouse = ( Tire mileage rate - Actual mileage ): Tire mileage rate x Tire purchase price In other words, if the cost of a new set of car tires (4 pieces) is 40,000 rubles .
, the mileage rate in the organization is set at 50,000 km, then after actual operation (mileage) of 15,000 km and shift, this set of tires must be entered into the warehouse, reflected in the accounting entry: Debit 10.5 Credit 25 - 28,000 rubles.
– 4 car tires were capitalized ((50,000 km – 15,000 km): 50,000 km) x 40,000 rub.).
Accounting for seasonal car tires (Korshunova N.)
For separate accounting, auxiliary subaccounts of the third order are opened to the subaccount “Spare tires”.
Tires of motor vehicles of the working capital (in the sub-report) are accounted for separately from those that are listed in the warehouse.
Tax accounting of tires When purchasing a car, the price of installed and spare tires is combined with the initial cost of the vehicle (Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Article 257).
These spare parts do not appear on the accounting accounts as separate objects. Tires purchased separately are not included in the purchased vehicle and are not added to its cost. Here, tax accounting of spare parts is regulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- Art. 254 (payer’s expenses for production and economic needs);
- Art. 260 (restoration of fixed assets);
- Art.
Features of accounting for seasonal, summer and winter tires on vehicles in 2018
For tax purposes, tire repair costs can be taken into account as other costs associated with production and sales.
It should be noted that at present there are no regulatory documents establishing cost standards for restoring wear and tear and repairing car tires.
That is why these costs are the costs of carrying out routine repairs, which are included in the cost of products, works, and services as the costs of maintaining fixed assets in working condition.
However, rationing of these expenses is not provided. If tires have damage that cannot be repaired locally or restored by applying a new tread, then, by decision of a special commission created at the enterprise, they are written off as scrap.
Such tires are brought to the warehouse by weight at list prices, at which they are delivered to tire repair plants. The form, as stated above, can be developed independently or you can use the form given in Appendix No. 12 to Rules No. AE 001-04 (see on p. 28).
After the end of the service life of car tires, as a rule, for reasons that can be found in Appendix No. 9 to the Rules for the operation of car tires (AE 001-04), in the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated October 23.
1993 No. 1090 “On the Rules of the Road” (together with the Basic Provisions for the admission of vehicles to operation and the duties of officials to ensure road safety), data from registration cards is transferred to statements (acts) for the write-off of car tires, on the basis of which accounting reflects these facts of the economic life of organizations.
- procedure for monitoring the rational use of car tires.
As a rule, the primary accounting documents for registering the movement of car tires in an organization are:
- documents on acceptance and receipt of car tires;
- various cards or records of car tires issued for use;
- statement (act) for writing off car tires.
Purchased car, bus tires, tires for agricultural vehicles, motorcycles and scooters must have a certificate (letter of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology dated April 29.
2011 No. A3-101-32/3615 “On products subject to mandatory confirmation of conformity (in the form of mandatory certification) in the GOST R certification system, indicating regulatory documents establishing mandatory requirements”).
Thus, production costs (or sales costs) of the current reporting period are reduced by the amount of tires returned to the warehouse.
An organization can independently determine the cost of tires removed from wheels by setting operational mileage standards, focusing on the technical characteristics of the corresponding tires.
You can also focus on the Temporary standards for the operational mileage of vehicle tires RD 3112199-1085-02.
On the one hand, the norms were abolished back in 2004. On the other hand, by decision of the commission of the Ministry of Transport of Russia dated April 18, 2006, their validity was again extended until the relevant technical regulations came into force (information letter of the Ministry of Transport of Russia dated December 7, 2006 No. 0132-05/394).
Source: https://yuridicheskaya-praktika.ru/kto-vedet-zhurnal-ucheta-raboty-avtoshin/
Tire registration card: form, examples
Topic: Tire accounting (Tire appearance).
See two examples of filling out the card: Example 1 >>>, Example 2 >>>.
BONUS: Directory “Car at the enterprise”
See also Battery Accounting Card.
The principles for drawing up a card for recording the mileage (hours) of a pneumatic tire are as follows.
01. The date of manufacture of the tire is written down in the same way as it is marked on the side of the tire - with four digits: the first two are the designation of the serial number of the week of the year of manufacture; last two - designation of the last two digits of the year the tire was manufactured.
02. Columns 1 - 4, 7, 8 and 10 of the tire mileage (hours) accounting table are filled in in all cases when the tire is used as part of individual vehicles, when the vehicle drivers responsible for operating the tires change. The remaining tread height is determined according to the tire operating rules.
03. Columns 4 and 9 are filled in according to the relevant conclusions of the commission, in the event of a tire repair, due to which its use on the vehicle is shortened or interrupted.
04. Records can be kept on paper or machine media.
05. If the mileage (hours) is recorded on computer media, the card is printed and signed in the event of a change in the responsible driver (operator), in the event of drawing up the conclusions of the commission.
06. The tire registration card is stored for at least three years after the tire is written off.
07. The mileage (hours) of a retreaded tire is recorded on a separate card. Accordingly, if the tire has used its standard mileage and is naturally worn to a state in which it can be economically feasible to restore it using acceptable methods, then the issued card is an act of writing off the tire (and after restoration, a new card is issued).
Car tire performance record card
Approved by order of the Ministry of Natural Resources dated October 4, 2011 N 413-OD
CARD RECORDING the operation of a car tire (new, reconditioned, used - underline what is necessary) Tire designation ___________________ Tire model _____________________ GOST or specifications for the tire _________________ Serial number ___________________ (write down all numbers and letters) Ply rating or load capacity index __________________________ Warranty / operational mileage rate _________________________ The cost of a set of tires is ________________________________________ rub. Enterprise - manufacturer of a new tire or tire repair company of a retreaded tire _________________________________________________________ Name of the motor transport enterprise ___________________________ ——————————————————————————————— ¦ Model ¦ Date ¦Mileage of the tire, thousand ¦Technical¦ Reasons ¦Signature ¦ ¦ of the car +———————+ km ¦condition ¦removal of the ¦driver tire¦ ¦ (trailer), its ¦installation ¦ removal +—————— + tires at ¦ from ¦ ¦ ¦state¦ tires on ¦ tires from ¦ for ¦ from the beginning ¦ installation ¦operation¦ ¦ ¦ number ¦ running ¦vehicle¦month¦operation¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ or ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ spare ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ wheel ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ car¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ —————-+———-+———-+——+ ————+————+————+——— Responsible for recording the operation of the tire (Signature) Conclusion of the commission to determine the suitability of the tire for use Chairman of the commission Members of the commission
* * *
In conclusion, let us formulate the main conclusions:
- Features of organizing the accounting of tires must be specified in the internal local act of the institution.
- Tires purchased together with a car are accounted for as part of an item of fixed assets, and separately - as inventory.
- When installing new tires on a car, their cost is written off as expenses of the institution and at the same time, to ensure control over their use, is reflected in off-balance sheet account 09.
- Tires that have become unusable (cannot be repaired) must be credited to the institution's balance sheet for further write-off as scrap. Before disposal, their accounting should be organized on off-balance sheet account 02.
____________________________________________________________ full name of the institution CARD for recording the operation of car tire No. __________ (new, retreaded, re-deepened, used) (underline as necessary)
Tire designation (size) _________________________________
Tire model ________________________________________________
Serial (factory) number ______________________________
Date of manufacture (week, year) ______________________________
Operating mileage ____________________________
Manufacturer of a new tire or tire repair shop
company ________________________________________________
Responsible for keeping track of tire operation __________________________
| date | Vehicle inventory number | Make and model of the car, its registration number | Speedometer readings during installation, thousand km | Speedometer readings when removed, thousand km | date | Technical condition of the tire during installation | Reasons for removing a tire from service | Driver's signature | Conclusion of the commission to determine the suitability of the tire for use (for retreading, deepening of the tread pattern, complaint or scrap) | |
| tire installation | tire removal | |||||||||
Chairman of the commission __________ _________ ________
(position) (signature) (full name)
Committee members: __________ _________ ________
Instructions for the application of the Unified Chart of Accounts for public authorities (state bodies), local government bodies, management bodies of state extra-budgetary funds, state academies of sciences, state (municipal) institutions, approved. By Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n.
Instructions on the procedure for applying the budget classification of the Russian Federation, approved. By Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 1, 2013 No. 65n.
Cultural and art institutions: accounting and taxation, No. 6, 2020