Overpayment may occur due to the following circumstances:
— During the year, individual entrepreneurs under the simplified tax system “income” paid advance payments on income.
All contributions for the year were paid in December and their amount is greater than the tax due for the year.
— Insurance premiums were paid throughout the year, but the amount of all advance payments based on the results of the 1st quarter, half a year and 9 months turned out to be greater than the amount of tax for the entire year (for example, on the simplified tax system “income-expenses”, if there was little income in the 4th quarter , and there are a lot of expenses).
— Error in payment or calculations.
Possible options
The return and offset procedure is regulated by Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For convenience, we present it in the form of a diagram.
The whole procedure can be represented step by step as follows:
- We establish the fact of excessive payment to the budget.
- We check whether there is arrears on any of the taxes, penalties or fines, against which the inspectorate can offset the overpaid amounts.
- We check whether the declaration needs to be clarified at the same time.
- We determine our preferences, two options are available: refund or credit.
- We reconcile payments to the budget.
- We are preparing the necessary applications.
- We send the necessary package of documents to the inspection.
What to do under the simplified tax system
If the option of leaving everything as is is not to the benefit of the payer , he can make an alternative decision, in fact, as with any other tax payment:
- refund of the amount to a personal bank account;
- crediting as payment of another tax, the transfer of which is made to a budget of a similar level.
To carry out each of these actions, you will need to complete an application in the prescribed format. Another logical question arises: is it possible to take into account the overpayment made in upcoming payments under the simplified tax system?
to use the simplified regime in the future , then the simplest way to apply the overpayment is an accounting operation within the framework of upcoming payments under the simplified tax system.
For example, if a businessman refrained from paying 6% for the simple reason that the total amount of the fee turned out to be less than the amount of advance payments made during the tax period.
The overpayment will be accounted for in advances of the next calendar period for the same type of contribution. With all this, there is no need to submit an application to the tax office in order for the overpayment amounts to be offset.
Accounting for overpayments occurs within the same OKTMO and KBK for which tax is paid.
This means that if the taxpayer does not take any action regarding the overpayment, in the new calendar period these amounts will be taken into account as advances under the simplified tax system. However, conducting a reconciliation for errors together with representatives of regulatory authorities will not be superfluous.
Particularly noteworthy is the issue associated with the return and offset of overpayments under the simplified tax system for payments to compensate for other forms of tax deductions.
For example, if the payer, due to any circumstances, refuses to leave the overpayment as an advance for upcoming payments, he can count on a refund to his own current account or on their offset as payment of tax. The transfer of such tax is carried out to a budget of a similar level.
The example is simple: transport tax in Russia is strictly regional in nature . Accordingly, it will not be possible to transfer his overpayment paid to the federal budget and then distribute it to other treasuries. For both refund and offset measures, it is necessary to contact the Federal Tax Service at the place where the taxpayer is registered.
How to identify
Before you begin filling out an application for a refund or tax credit, you need to determine whether this treasured amount exists or is it just an accounting error in the records. So, how to identify the overpaid amount in taxes.
Step No. 1. Check your accounting.
Of course, first of all it is necessary to check the correctness of registration of transactions in the organization’s accounting records. It is quite possible that the error crept not in the payment order, but in the way the accountant compiled the posting. Particular attention should be paid to the procedure for registering transactions in specialized accounting programs.
Check what? Accounting accounts and analytics on them (KBK, subaccount, KOSGU, type of payment, etc.). Re-grading by BCC or type of transaction (fine, tax, fine) are the most common errors in accounting programs.
After checking, be sure to create a balance sheet and an account card for the period you are interested in. This is necessary to check whether the errors are fixed or not.
Step No. 2. Check with the bank.
If no accounting errors are found, check your bank statements. Are the transactions posted correctly in accounting, and did the bank execute payment orders correctly?
In the bank statement, you can verify the tax recipient, KBK and other payment details; it is against these indicators that you can verify the accounting data. Correct any errors found in your accounting. If the bank makes a mistake, contact your local branch to resolve the problem. It is worth noting that banking errors are isolated cases.
Step No. 3. Reconciliation with the Federal Tax Service on taxes and contributions.
So, if internal control and reconciliation with the banking organization did not produce results, then you should contact the Federal Tax Service. To do this, just contact the nearest territorial inspection office. If the institution exchanges documentation with the Federal Tax Service via secure Internet channels, then you can request an extract in electronic format. You can also obtain information in your personal account on the official website of the Federal Tax Service. For more details, see the material “Instructions: how to check tax arrears.”
Based on the results of reconciliation with the Federal Tax Service, we determine the overpaid amount for taxes. Now we decide what to choose: offset or issue a tax refund.
Consequences for the entrepreneur
The consequences of overpaid taxes to the budget depend solely on the decision of the taxpayer. He has the right to leave everything as is (i.e., the amounts paid will go in advance for subsequent payments) or pay off other fees , as well as return the overpaid amount of money to his current account.
If we consider this issue more specifically, then Art. 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows:
- offset the surplus against future payments for the same type of tax;
- reimburse the monetary amount to a current account belonging to the organization.
In practice, resolving this issue involves several difficulties for the simple reason that tax authorities often do not take into account the nuances of arbitration practice and use departmental interests.
This may serve as a reason for organizing a desk audit , especially if the company is submitting an updated report due to a decrease in the amount of the calculated fee.
Thus, an overpayment, which, although it can act as a guarantee of repayment of arrears, is often undesirable for individual entrepreneurs and enterprises of other forms of ownership. How to deal with it is up to everyone to decide for themselves. The main thing is that all actions are carried out in accordance with the law.
How to count
As a general rule, any federal tax, including income tax, can be offset against future payments for any other federal payment or fines and penalties to the federal budget. In this case, the existing arrears are repaid by the inspection itself and do not require the participation of the organization. However, the latter retains the right to submit an application for offset of overpayments on taxes; an application for this is submitted to the inspectorate at the place of registration of the organization in paper or electronic form.
To reflect the offset operation, according to the chart of accounts approved by Order 94n, analogous accounts are used for budgetary institutions.
| The amount of profit was offset against VAT payment | 68-VAT | 68-pr | 20,000 rub. | Decision, accounting certificate |
Credit only for the tax of the corresponding budget
If the overpayment of penalties relates to federal tax, then it can only be offset against federal tax. If to the regional - at the expense of the regional, and if to the local - at the expense of the local.
Thus, “extra” VAT penalties can be offset against income tax, but not against land tax, because VAT and income tax are federal taxes, and land tax is local.
What level a particular tax belongs to can be found in Articles 13, 14 and 15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
How to fill
First of all, we note that applying for a credit is required separately for each type of tax, fee or contribution. It is not possible to combine fiscal payments in one document.
If an organization is registered with several Federal Tax Service Inspectors at once, for example, it has several branches or separate divisions, then the document should be submitted exactly to the inspection department where the overpayment of taxes occurred.
Instructions for filling:
- In the header of the document we indicate the TIN and KPP of the taxpayer-applicant.
- The application number is a serial number for the current year.
- Payer status: for an organization it is either “1” - taxpayer, or “4” - tax agent.
- Enter the article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in accordance with which we carry out the offset. Indicate the article number in the field: “176” - for VAT credit, “203” - for excise tax and “78” - for other fiscal payments (taxes, fees, contributions).
- Select the type of payment from the list provided. For example, to offset income tax, select “1”, to offset VAT penalties, select “4”.
- Then we determine the period or specific date for which the overpaid amount was generated. For example, for January 2020 - MS.01.2019, for the 1st quarter of 2020 - KV.01.2019, for the 1st half of the year - PL.01.2019, for the year - GD.00.2019. We indicate a specific date if the law establishes the exact date for filing a declaration or paying a tax. For example, 03/28/2019 to pay income tax.
- OKTMO - the code corresponds to the code of the place where the taxpayer is registered.
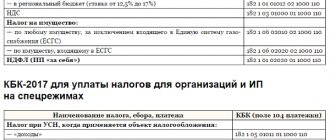
- Indicate the BCC corresponding to the tax, fee, contribution for which the overpayment was detected.
- On the second sheet of the document, indicate the overpaid amount in rubles and kopecks. Then determine what the payment should be redirected to: “1” - for arrears, “2” - for future periods. Specify the tax period to be offset against future payments.
- Enter OKTMO at the place where the payment was made.
- BCC of the tax, fee, contribution against which the offset is made.
- The last page (section “Information about an individual who is not an individual entrepreneur”) is not filled out by institutions.
When does an overpayment occur under the simplified tax system?
In order to understand the peculiarities of overpayment of single tax for a “simplified” person, let’s look at a few examples:
Option #1. Overpayment on advances.
Individual Entrepreneur Gavrilov is a payer of the simplified tax system 15% income minus expenses. During 2020, Gavrilov made prepayment tax calculations and transferred the following amounts to the budget:
- 01.18 – 23.606 rub.;
- 04.18 – 38.516 rub.;
- 10.18 – 32.714 rub.
At the end of the year, Gavrilov compiled and submitted a tax return to the Federal Tax Service, in which he reflected the amount of annual income (584,990 rubles) and the amount of tax for the year (584,990 rubles * 15% = 87,748.50 rubles).
Since the total amount of advance payments (23,606 rubles + 38,516 rubles + 32,714 rubles = 94,836 rubles) exceeded the amount of Gavrilov’s tax obligations at the end of the year (87,748.50 rubles), the entrepreneur had an overpayment according to the Tax Code in the amount of 7,087.50 RUB (94,836 RUB – 87,748.50 RUB).
Option #2. Error when transferring payment.
Based on the tax return filed by Factor-5 LLC (payer of the simplified tax system) to the Federal Tax Service, at the end of 2020, the enterprise is obliged to make a final payment for the single tax in the amount of 104,770 rubles.
When filling out the payment order, the accountant of Factor-5 LLC made a mistake, and as a result, the amount of 107,770 rubles was paid to the budget, and an overpayment of 3,000 rubles arose. (RUB 107,770 – RUB 104,770).
Option #3. Overpayment based on an updated declaration.
Mustang LLC is a payer of the simplified tax system 15% income minus expenses. During 2020, the accountant of Mustang LLC made calculations and transferred the following advance amounts to the budget:
- 01.18 – 45.002 rub.;
- 04.18 – 48.108 rub.;
- 10.18 – 49.100 rub.
In January 2020, the accountant of Mustang LLC submitted a declaration to the Federal Tax Service, according to which the tax amount for 2020 was 203,050 rubles. Thus, for the final calculation, the Mustang accountant should pay the amount of 60,840 rubles to the budget. (RUB 203,050 – RUB 45,002 – RUB 48,108 – RUB 49,100). The final payment was made on January 12, 2019 (the debt was transferred).
On January 25, 2020, the accountant of Mustang LLC submits an updated tax return to the Federal Tax Service, according to which the total amount of tax liabilities for 2020 is 181,405 rubles. Thus, Mustang LLC incurred an overpayment of tax in the amount of 21,645 rubles. (RUB 203,050 – RUB 181,405).
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |
How to return
It makes sense to return funds when you are sure that the organization has no debts to pay taxes, penalties and fines. Ideally, you need to obtain a reconciliation report from the tax office. Please keep in mind that the refund will be made only after the existing arrears have been repaid. Otherwise, the return application will be rejected.
If the head of the organization has decided that the overpaid amount needs to be returned, it is necessary to fill out an application for a refund of the overpayment of taxes; the terms of transfer to the organization's current account are calculated from the date of filing the application and amount to no more than one calendar month.
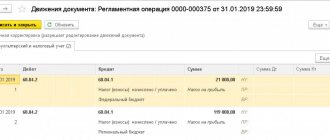
The return of the overpaid amount must be reflected in standard posting.
| Wiring | Operation |
| Dt 51 Kt 68 | Overpaid income tax refunded |
Please note that applying for a refund from the budget should take into account the current circumstances. For example, for monthly payments, such as insurance premiums or personal income tax, it makes no sense to return overpaid amounts, because next month the organization will again calculate wages and calculate payments towards insurance coverage. However, if we are talking about a company being reorganized or liquidated, then the return is justified.
You should also take into account the company's planned performance indicators. For example, if a budget institution previously provided paid services. Based on the results of the reporting provided to the Federal Tax Service, an overpaid amount of VAT was identified. However, business activity was terminated by the decision of the founder. Let us remind you that public sector employees are exempt from paying VAT on activities financed by subsidies. Consequently, the institution has no obligation to calculate and pay VAT in the current period. And it will not be possible to offset the overpayment against future VAT charges (paid services have been discontinued). It is in this case that you need to fill out an application for a refund of the overpaid tax.
But even in such a situation, the institution has the right to transfer the overpaid money to other payments. For example, to pay off debts on transport, land tax or property tax. Therefore, the decision must comply with the provisions of the law and satisfy the needs of the taxpayer.
“Shelf life” of overpayment – 3 years
You must have time to submit an application for a refund or offset of the overpayment of penalties within three years from the date of payment (Clause 5 of Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Otherwise, the surplus will be lost and it will be impossible to return it.
Attention!
Do not rely on the tax office; it is not in its interests to inform you of an overpayment. If the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate becomes aware that the company has overpaid, the tax authorities are required to report this within 10 days (clause 3 of Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But if they don’t do this, even if they knew about the overpayment, and for three years the organization never finds out about it, then this does not change anything for the taxpayer.
This does not extend the three-year period, and the overpayment “burns out.” In this case, the courts side with the tax inspectorate (rulings of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 19, 2019 No. 304-ES19-1659, dated August 30, 2018 No. 307-KG18-12491).
In order to identify overpayments in a timely manner and not lose money, independently monitor the status of settlements with the budget and regularly carry out reconciliations with the tax office.
It is better to initially avoid overpayments to the budget, because in this way you are actually lending to the state, while this money could remain in the company’s circulation and be beneficial.
To avoid such situations, outsource your accounting to 1C-WiseAdvice, and not a single extra ruble will go into your budget.
More details
How to fill out a tax refund application
The tax refund application is filled out according to similar rules. Please note that the updated KND form 1150058 itself already contains detailed instructions and tips for filling out.
The document can only be issued in relation to a specific fiscal payment. You cannot combine several types of overpayments in one refund application. Even if the taxpayer returns overpaid penalties and fines for one fee, he will have to prepare two refund applications. One is for a tax penalty, the second application is for a refund of the fine. Since for each payment the corresponding budget classification code is determined - KBK.
Submit an application for a tax refund to the exact branch of the Federal Tax Service where the taxpayer is registered. If the overpaid amount is identified in a separate division, report it to the Federal Tax Service at the place where the OP is registered.
Instructions for filling out a tax refund application, key aspects:
- The checkpoint should indicate the code assigned to the organization or separate division in the tax authority to which you are submitting an application for a tax refund.
- Correctly indicate the reason for the overpayment. There are several options available to choose from. For example, if you overpaid, indicate code “1” in your tax refund application. If the taxpayer is claiming a refund of VAT or excise taxes from the budget, then enter “3”.
- Detail the type of payment for which you are processing a refund from the budget. If you are returning the amount for the main obligation, write “1” in the return application, “4” for compensation of overpaid penalties, “5” for fines.
- In the “Account Information” section of the tax refund application, enter the necessary information about the banking organization in which the corresponding current account is opened. Then indicate the type of account, according to the decoding indicated in paragraph 6 of the filling rules (see the KND 1150058 form itself). The recipient is the applicant organization.
Please note that there are exceptional filling rules for public sector institutions. So, for example, a budgetary institution in the “Name of the bank” paragraph must indicate the name of the Federal Treasury body in which the personal account is opened. The account number is the standard 20 characters. But the recipient of the payment for public sector employees is not the name of the organization, as, for example, NPOs or commercial firms must register. In this paragraph, you must indicate code “3” and enter the name of the body that opens and maintains personal accounts. In most cases, this is a territorial branch of the Federal Treasury.
NPOs and commercial firms do not indicate the personal account number and BCC for enrollment. But public sector institutions are required to fill out the fields. The personal account number is a unique number (can contain not only numbers, but also Latin letters). But the BCC is determined for each type of institution individually:
- autonomous ones enter zeros in the budget classification code;
- budgetary - indicate KBK 000000000000000000130;
- government - fill out the KBK in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 132n.
The last section of the tax refund application does not need to be completed. It is intended for individuals.
Refund of overpaid tax
The procedure for returning an overpaid “simplified” tax is no different from the procedure for returning any other tax “overpaid” to the budget.
note
Currently there are standard samples of applications for tax credits and refunds. They were approved by order of the Federal Tax Service dated March 3, 2020 No. ММВ-7-8/ [email protected] Until this time, we would like to remind you that companies and entrepreneurs submitted applications for offset or refund of tax payments in free form.
You can return the overpayment under the simplified tax system in two cases:
- if you yourself overpaid the tax;
- if the tax authorities made additional charges to you, and you challenged them with the Federal Tax Service or in court and proved that they were illegal.
In such situations, you can only return the overpaid amounts to your current account. Overpayments are not refunded in cash.
And entrepreneurs have the right to indicate in the application for a tax refund the account of their personal bank card (determination of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated September 17, 2013 No. VAS-12390/13). In this case, three years must not pass from the date of payment of the excess amount of taxes (Clause 7, Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Calculate three years from the date of filing the declaration for the year, but no later than the deadline established for its submission (Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated June 28, 2011 No. 17750/10, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 15, 2012 No. 03-03-06 /1/309).
To return the overpayment, submit an application to the Federal Tax Service in the form approved in Appendix No. 8 to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 3, 2015 No. ММВ-7-8/ [email protected]
In the application, indicate the name of the inspection and your details: name of the company or surname, first name, patronymic of the entrepreneur.
Also fill out the basis for the return - the article of the Tax Code in accordance with which the return is made. For overpaid amounts this is Article 78 of the Tax Code, and for overcharged amounts - Article 79. And mark the type of overpayment - what amount you want to return: overpaid or overcharged.
Then indicate the tax for which the overpayment was incurred and the period to which it relates, KBK and OKTMO, as well as the amount you are asking to be returned, in full rubles, in numbers and in words.
Here is a sample application for a “simplified” tax refund:
Inspectors will return the overpayment only to the current account. Therefore, be sure to indicate in the application the details of this account to which the tax authorities must transfer money to you: name of the bank, correspondent account, BIC, INN, KPP, the account number of the company or businessman. In addition, be sure to indicate in the application who exactly is returning the overpayment - the taxpayer, the payer of the fees or the tax agent. Include the date the application is completed and the signature of the person who is returning the overpayment.
Submit the application to the Federal Tax Service on paper or electronically (clauses 4, 6 of Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Within 10 days from the date of receipt of your application for a tax refund or from the date of signing the act of joint reconciliation of taxes paid, if such a joint reconciliation was carried out, the tax office must make a decision on the return of overpaid or collected tax (clause 8 of article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) . Within five working days from the date of the decision, tax authorities are required to inform you about the decision made (clause 9 of Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The inspection will return the overpayment within a month after it receives your application (Clause 6, Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But if you have tax arrears identified during the tax reconciliation, those will be paid first. And the controllers will return the remaining funds to you. If the tax inspectors violate the one-month deadline, then you will be entitled to interest for the delayed return. They are accrued for each calendar day of delay based on the refinancing rate of the Bank of Russia (Clause 10, Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
How to return an overpayment of “simplified” tax to your current account, read in the berator “STS in practice”
Special cases
Sometimes there is an overpayment of federal taxes and an underpayment of those regulated by the subject, that is, payments are made to different levels of the budget system. This is called a violation of interbudgetary regulation, and such cases are regulated not by Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, but by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated November 12, 2013 No. 107n and the Budget Code.
First of all, in such a situation, it is necessary to clarify the tax payment that caused the problem. And then, to correct the situation, write and send a letter to the tax office to clarify the details of the payment order regarding the budget classification code. It is compiled in free form and submitted in written or electronic form.
What to do if you yourself overpaid tax
You can overpay tax by mistake: for example, you or your accountant made a mistake when calculating tax or filling out a payment order.
If an error occurred in calculating the tax, then Article 81 of the Tax Code requires submitting an updated declaration for this tax to the tax office if the error led to an understatement of the tax. When overpaying tax, submitting a “clarification” is a taxpayer’s right, not an obligation.
In accordance with Article 78 of the Tax Code, overpayment can be:
- offset against the subsequent payment of the corresponding type of tax;
- offset against debt repayment for relevant types of taxes, penalties, and fines;
- return to the company's bank account.
In order for the tax authorities to count the overpayment against further payments for the same or other taxes, the company must submit an application in the form approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 3, 2015 No. ММВ-7-8/ [ email protected] Having received this document, the tax authorities in within 10 days they will make a decision on the credit. The inspectorate is given another five days to inform the company of its decision.
Here is a sample application for a “simplified” tax credit:
If you want to pay off arrears on one tax by overpaying on another, it is not necessary to submit an application.
The inspectors will decide on such offset independently. They will do this within 10 days after they discover the overpayment, or after your company and the inspectorate sign a joint reconciliation of taxes paid.
Having made a decision, tax authorities are obliged to inform you about it within five days. However, this does not mean that, having discovered an overpayment yourself, you should wait until the tax authorities do it.
Having found the “extra” payment before the inspectors, the company can apply to offset the arrears. The tax office must refund the overpaid tax within one month from the date of receipt of the application.
However, this will happen after the overpayment is offset against your debt to other taxes of the corresponding type.
As a result (if you have such a debt), the difference between the overpayment and the repaid debt will be “returned” to your current account (if, of course, the amount of overpaid tax was sufficient).
If the tax office violates this deadline, it will have to pay you interest for each day of delay based on the refinancing rate of the Bank of Russia.
EXAMPLE On March 4 of this year, Passive LLC brought to the tax office an application for a refund of an overpayment of tax in the amount of 20,000 rubles. The monthly refund period expired on April 4, but the money was credited to the account only on April 20, that is, the delay was 16 days. The refinancing rate is all this time was equal to 10.5% per annum. The tax office must pay interest to “Liability” in the amount of: 20,000 rubles. × 10.5%: 365 days. × 16 days = 92 rub.
You can offset overpaid amounts only within the limits of taxes of one type (Clause 1, Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). For example, you can offset federal taxes only against federal taxes, regional taxes against regional taxes, and local taxes against local taxes. It will not be possible to direct an overpayment of federal taxes towards regional or local taxes, and vice versa. For example, the simplified tax system, UTII, personal income tax are federal taxes, and land taxes are local taxes (Articles 13 and 15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This means that the overpayment under the simplified tax system cannot be used to pay off the arrears of land tax (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 13, 2011 No. 03-05-06-01/86).
By the way, it is allowed to offset the overpayment of tax to one budget and the underpayment of the same tax to another budget.
If the overpayment is not credited or returned, you can appeal to the arbitration court.
Tax authorities often refuse to offset or refund an overpayment, since the amount due to the fault of the bank did not go to the budget or extra-budgetary fund.
They are wrong: the tax is considered paid from the moment the bank accepted your payment order for its transfer. Of course, provided that there was enough money in the account.
Read about what actions an organization or entrepreneur should take to offset the “simplified” tax in the “STS in practice” berator.
What to do if the tax authorities wrote off money from your account by mistake
In fact, they must return the excess amount plus interest. To do this, you submit the same return application. This must be done within a month from the moment the money left your current account. If you delay and a month has already passed, then to get your money back you will have to go to an arbitration court.
The deadlines in this case are the same: the application is given 10 days to consider, a month is given to return the money; if there is a delay, the tax office must not only return the money, but also pay the accrued interest.
Where does the overpayment of the simplified tax system for the year come from?
Tax calculation under the simplified tax system is carried out quarterly on an accrual basis. That is, each subsequent calculation additionally includes data significant for the formation of the tax base for the last quarter of the reporting period. And the last calculation is made for all 4 quarters of the year at once.
What is the deadline for paying tax under the simplified tax system for the 4th quarter, see here.
Based on the results of the first 3 quarterly calculations, tax advances are paid without submitting reports on it to the Federal Tax Service. The final amount of the simplified tax system is determined by the calculation for the year, reflected in the declaration submitted to the tax authority.
Find the declaration form under the simplified tax system for 2020 - 2020 here.
Where does the overpayment come from? It arises due to the fact that the amount of advances transferred to the budget for the year may be greater than the entire amount of tax accrued for the year. That is, the simplified tax system for payment for the year by an individual entrepreneur or legal entity will not only be absent, but will also not cover the entire amount of payments already made under it.
Why is this happening? Because in the 4th quarter the taxpayer may have quite significant additional expenses that are taken into account in calculating the tax. They allow you to significantly reduce either the volume of the tax base (for the object “income minus expenses”), or the very amount of tax calculated for payment (for the object “income”).
Find out how to correctly offset or return an overpayment under the simplified tax system and how to reflect these transactions in accounting in the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. If you don't have access to the system, get a free trial online.
To learn about what expenses reduce the amount of the already calculated tax, read the material “Which object under the simplified tax system is more profitable - “income” or “income minus expenses”?” .